Understand the Problem
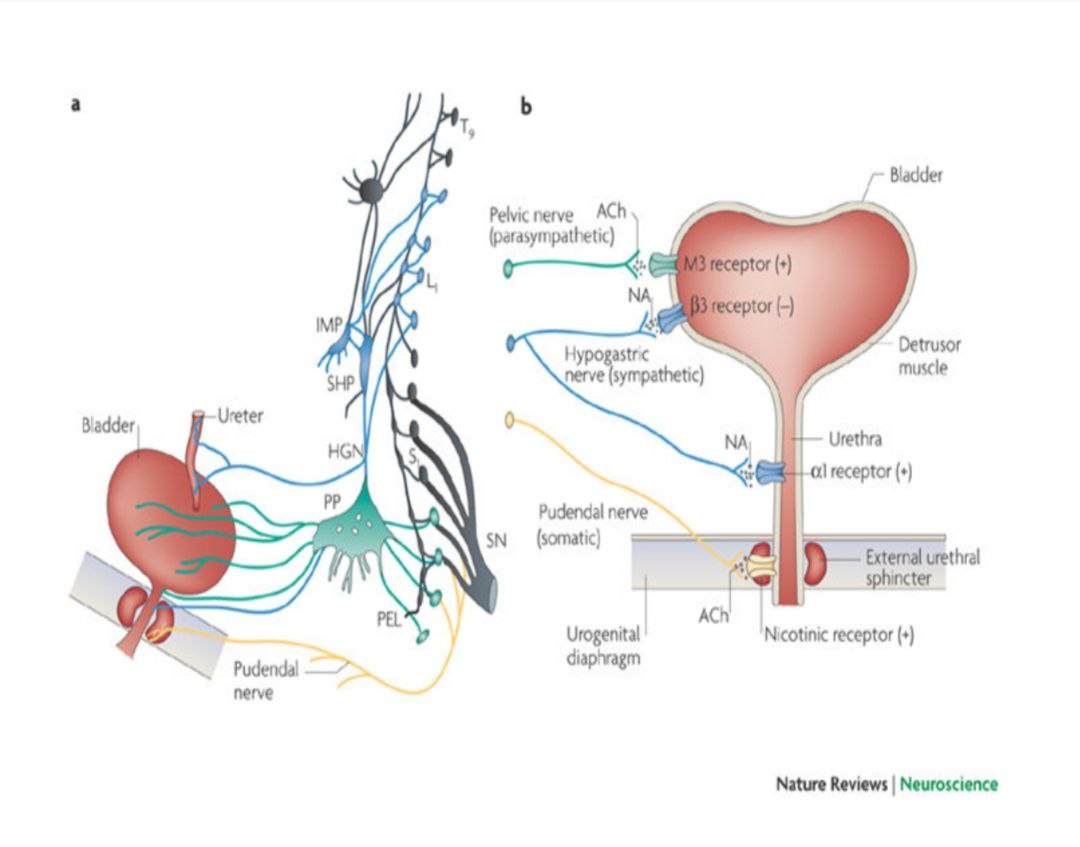
The image appears to be a diagram related to the nervous system's control over the bladder, illustrating various nerves and receptors involved in bladder function.
Answer
Neural control of micturition, involving parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nerves.
The image illustrates the neural control of micturition (urination). Diagram (a) shows the neural pathways involved, while diagram (b) details the innervation of the bladder and external urethral sphincter, highlighting the roles of parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nerves.
Answer for screen readers
The image illustrates the neural control of micturition (urination). Diagram (a) shows the neural pathways involved, while diagram (b) details the innervation of the bladder and external urethral sphincter, highlighting the roles of parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nerves.
More Information
Micturition involves a coordinated effort between the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. The parasympathetic nerves promote bladder contraction, the sympathetic nerves facilitate urine storage, and the somatic nerves control the external urethral sphincter.
Tips
Confusing the roles of parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves can lead to errors. Remember, parasympathetic usually aids in rest-and-digest activities, including urination.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information