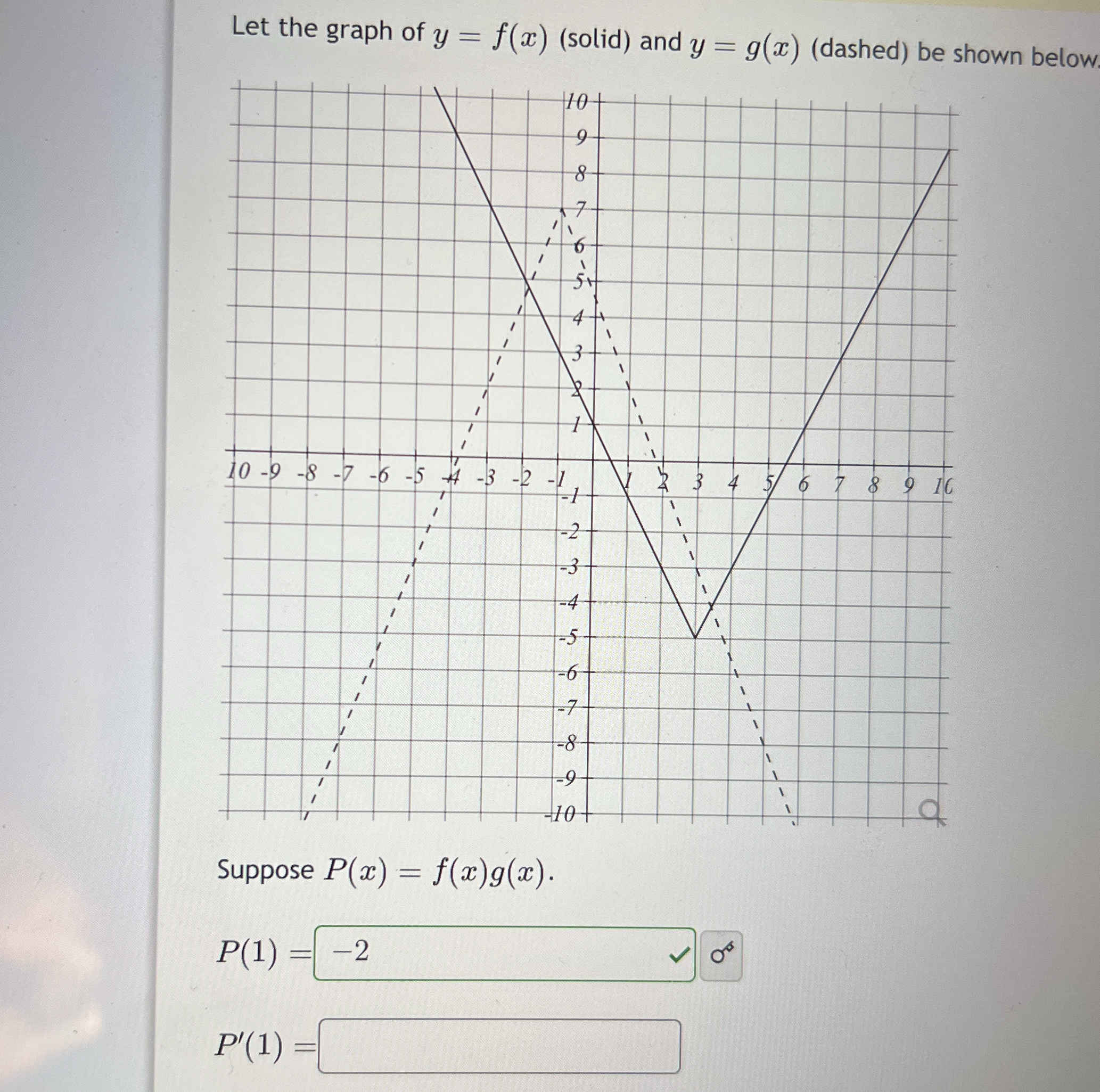
Given the graphs of \(y = f(x)\) and \(y = g(x)\), where \(P(x) = f(x)g(x)\), find \(P'(1)\).
Understand the Problem
The problem provides the graphs of two functions, (f(x)) and (g(x)). It defines a new function (P(x) = f(x)g(x)) and asks you to find (P'(1)), the derivative of (P(x)) evaluated at (x=1). This requires using the product rule to find (P'(x)) and then evaluating it at (x=1) using the information from the graphs.
Answer
$P'(1) = -2$
Answer for screen readers
$P'(1) = -2$
Steps to Solve
- Apply the product rule
Since $P(x) = f(x)g(x)$, we use the product rule to find $P'(x)$:
$P'(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)$
- Evaluate at $x=1$
Now, we need to find $P'(1)$:
$P'(1) = f'(1)g(1) + f(1)g'(1)$
- Find $f(1)$ and $g(1)$ from the graph
From the graph, we read the values of $f(1)$ and $g(1)$. $f(1) = -1$ $g(1) = 2$
- Find $f'(1)$ and $g'(1)$ from the graph
$f'(1)$ is the slope of the tangent line to $f(x)$ at $x=1$. Since $f(x)$ is linear in the neighborhood of $x=1$, we can compute the slope directly from the graph. The line passes through points $(0,1)$ and $(2, -3)$. Therefore, the slope is: $f'(1) = \frac{-3 - 1}{2 - 0} = \frac{-4}{2} = -2$
$g'(1)$ is the slope of the tangent line to $g(x)$ at $x=1$. Since $g(x)$ is linear in the neighborhood of $x=1$, we can compute the slope directly from the graph. The line passes through points $(0, 4)$ and $(2, 0)$. Therefore, the slope is: $g'(1) = \frac{0 - 4}{2 - 0} = \frac{-4}{2} = -2$
- Calculate $P'(1)$
Substitute the values we found into the expression for $P'(1)$:
$P'(1) = f'(1)g(1) + f(1)g'(1) = (-2)(2) + (-1)(-2) = -4 + 2 = -2$
$P'(1) = -2$
More Information
The product rule is very useful in calculus, it allows us to find the derivative of a function that is expressed as the product of two other functions.
Tips
A common mistake is to incorrectly read the values or slopes from the graph or to mix up which graph represents $f(x)$ and $g(x)$. Another common mistake is to apply the product rule incorrectly, such as forgetting to take the derivative of one of the functions.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information