Understand the Problem
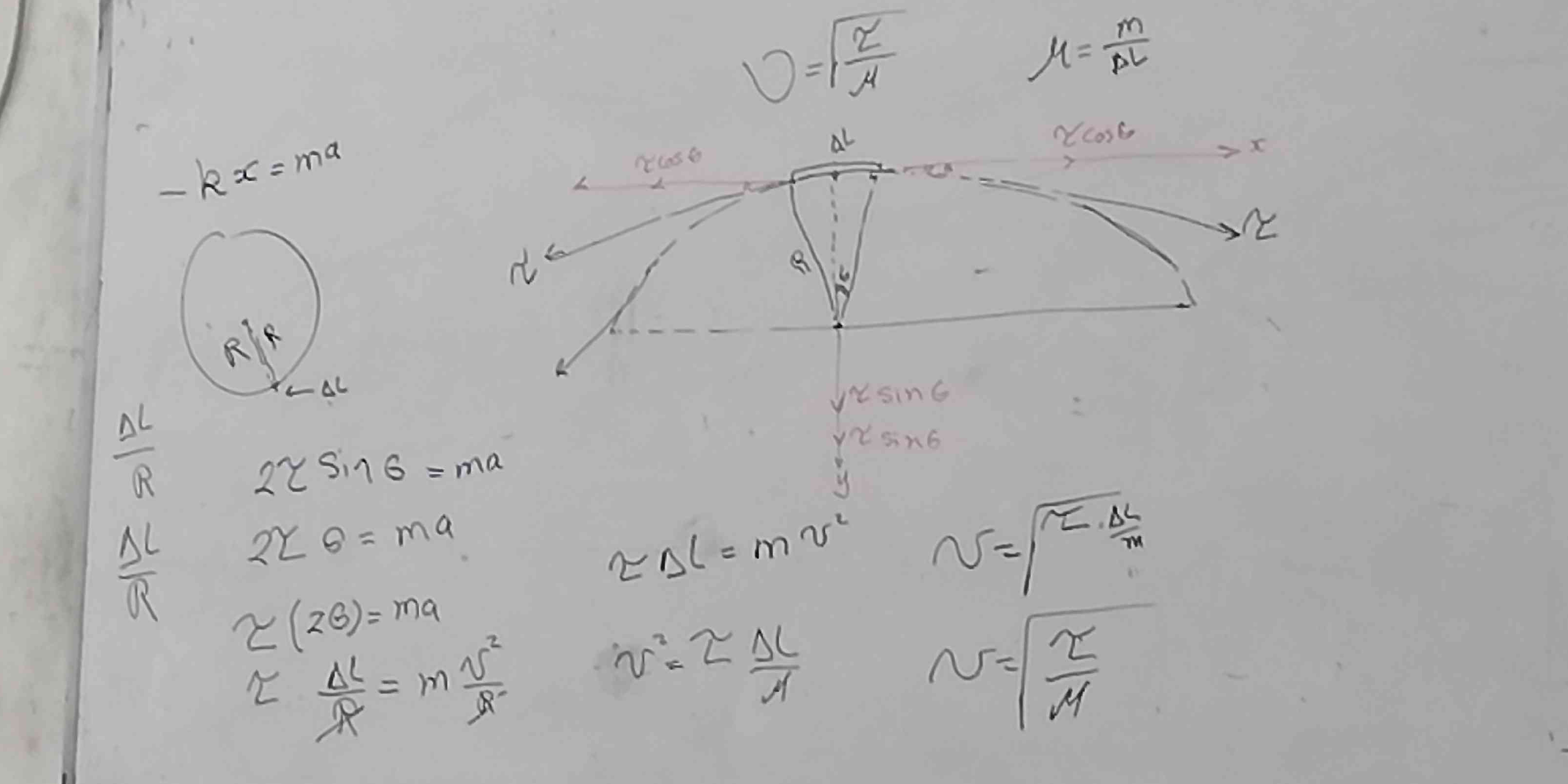
The question contains equations related to physics, specifically dealing with forces and motion. It appears to be exploring concepts around oscillations, forces acting on a mass, and the relationships between various physical quantities like mass, acceleration, and displacement.
Answer
The velocity for the mass is given by $v = \sqrt{\frac{k \Delta L}{m}}$.
Answer for screen readers
The final equation for velocity of the mass in a harmonic oscillator context is given by: $$ v = \sqrt{\frac{k \Delta L}{m}} $$
Steps to Solve
- Understanding Oscillation Dynamics
The system involves a mass attached to a spring. The force acting to restore the mass to equilibrium is given by Hooke's law: $$ -k x = m a $$ where $k$ is the spring constant, $x$ is the displacement, $m$ is the mass, and $a$ is the acceleration.
- Relating Forces to Motion
For small angle approximations, the restoring force can be expressed in terms of angular displacement ($\theta$) as: $$ F = -k \Delta L $$ This translates to: $$ \Delta L \cdot \frac{2\theta \sin(\theta)}{R} = ma $$
Here, $\Delta L$ refers to a small change in length, $R$ is the radius, and $\theta$ indicates the angle of displacement.
- Analyzing the Acceleration
Using the centripetal acceleration equation, we relate the angular motion as: $$ \Delta L = m \frac{v^2}{R} $$
- Calculating Velocity
Substituting for acceleration ($a = \frac{d^2x}{dt^2}$), where $x$ represents the position of the mass, we can express: $$ v^2 = \frac{k \Delta L}{m} $$
- Final Equation for Velocity
From the earlier substitutions, we find: $$ v = \sqrt{\frac{k \Delta L}{m}} $$
The final equation for velocity of the mass in a harmonic oscillator context is given by: $$ v = \sqrt{\frac{k \Delta L}{m}} $$
More Information
This equation shows how the velocity of a mass oscillating on a spring depends on the spring constant $k$, the mass $m$, and the displacement $\Delta L$. The system behaves like a simple harmonic oscillator, where the motion is periodic.
Tips
- Ignoring the small angle approximation: When dealing with oscillations, applying the small angle approximation correctly is crucial.
- Misinterpreting forces: Ensure all forces are accounted for in the free body diagram.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information