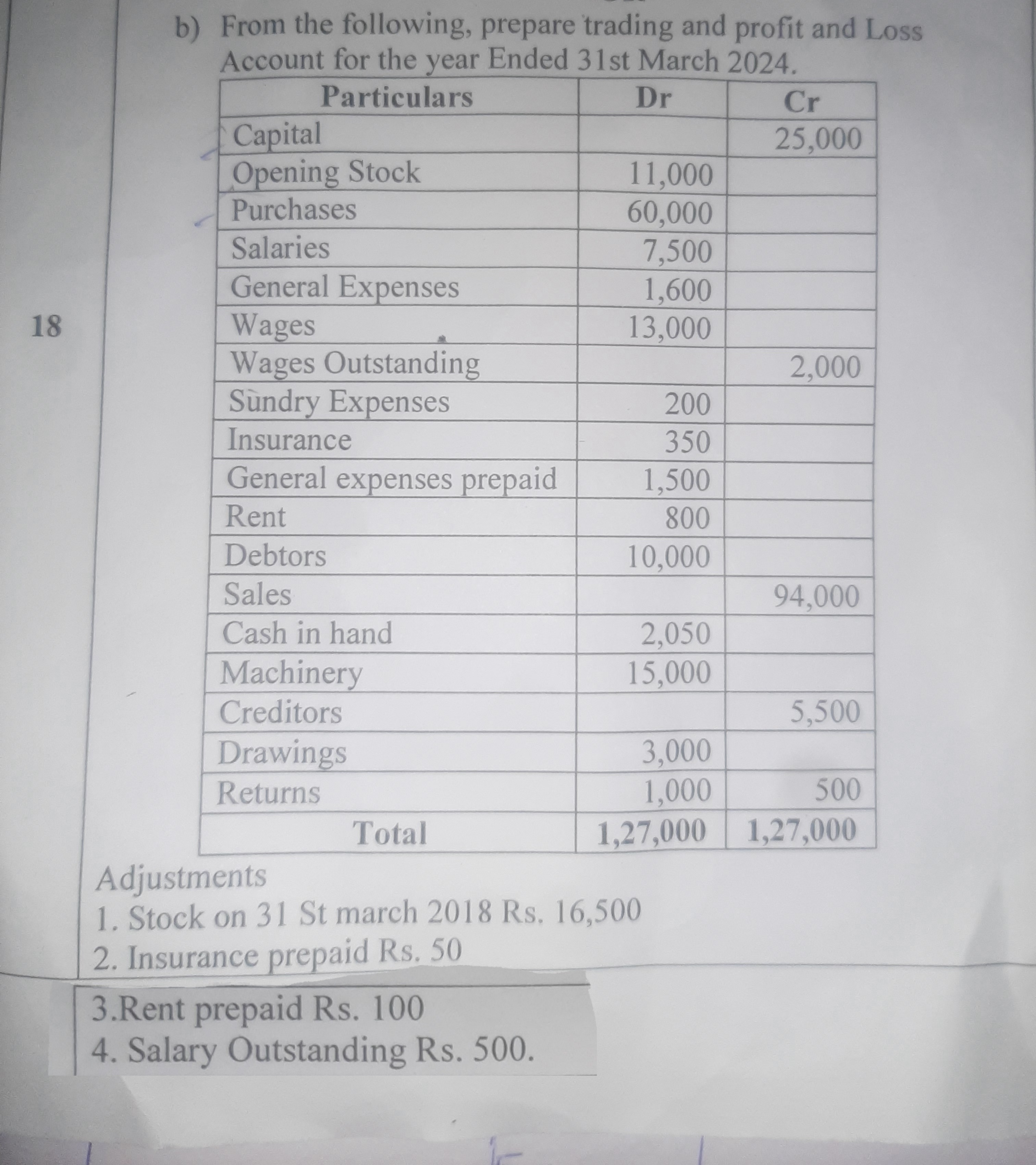
From the following, prepare trading and profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March 2024.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the preparation of a trading and profit and loss account for a specified financial year using the provided financial data. This involves summarizing the revenues and expenses to determine the net profit or loss.
Answer
The net profit is Rs. 14,200.
Answer for screen readers
The net profit for the year ended 31st March 2024 is Rs. 14,200.
Steps to Solve
-
List the Revenues First, we need to identify the total revenues from sales.
Sales = Rs. 94,000
-
List the Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) To calculate COGS, we will consider:
- Opening Stock
- Purchases
- Closing Stock (to be accounted from the adjustments)
COGS = Opening Stock + Purchases - Closing Stock
Here, Closing Stock = Rs. 16,500
Hence, $$ \text{COGS} = 11,000 + 60,000 - 16,500 = 54,500 $$
-
Calculate Gross Profit Gross Profit is determined by subtracting COGS from total revenues.
$$ \text{Gross Profit} = \text{Sales} - \text{COGS} $$ $$ \text{Gross Profit} = 94,000 - 54,500 = 39,500 $$
-
List Operating Expenses Next, sum up all the operating expenses:
- Salaries = Rs. 7,500
- General Expenses = Rs. 1,600
- Wages = Rs. 13,000
- Sundry Expenses = Rs. 200
- Insurance (adjusted) = Rs. 350 - Rs. 50 (prepaid) = Rs. 300
- General Expenses Prepaid = Rs. 1,500 (not included)
- Rent = Rs. 800 - Rs. 100 (prepaid) = Rs. 700
- Outstanding Wages = Rs. 2,000 (included)
Operating Expenses Total = 7,500 + 1,600 + 13,000 + 200 + 300 + 700 + 2,000 = Rs. 25,300
-
Calculate Net Profit or Loss Finally, subtract the total operating expenses from the gross profit to find the net profit or loss.
$$ \text{Net Profit} = \text{Gross Profit} - \text{Total Operating Expenses} $$ $$ \text{Net Profit} = 39,500 - 25,300 = 14,200 $$
The net profit for the year ended 31st March 2024 is Rs. 14,200.
More Information
A trading and profit and loss account summarizes the revenues and costs over a specific period, allowing businesses to assess their financial performance. In this case, the adjustments such as prepaid insurance and outstanding wages were key to calculating accurate expenses.
Tips
- Ignoring adjustments such as prepaid expenses or outstanding liabilities.
- Confusing closing stock with opening stock in the COGS calculation.
- Miscalculating total operating expenses by excluding certain entries.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information