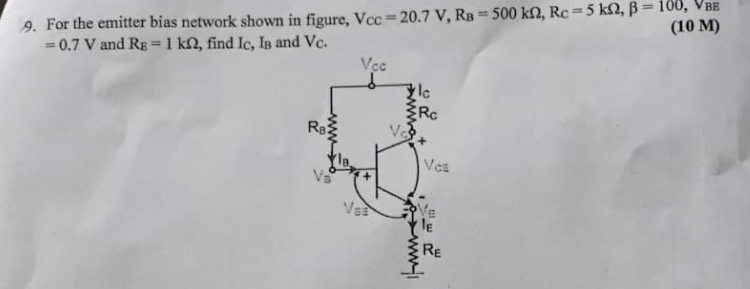
For the emitter bias network shown in figure, VCC = 20.7 V, RB = 500 kΩ, RC = 5 kΩ, β = 100, VBE = 0.7 V and RE = 1 kΩ, find Ic, IB and Vc.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to calculate the collector current (Ic), base current (Ib), and collector voltage (Vc) for a given emitter bias network circuit with provided values for supply voltage, resistances, and transistor parameters. The approach will involve applying circuit analysis techniques appropriate for transistor circuits.
Answer
- $I_C \approx 19.45\,mA$, $I_B \approx 0.195\,mA$, $V_C \approx 5.7\,V$
Answer for screen readers
- $I_C \approx 19.45,mA$
- $I_B \approx 0.195,mA$
- $V_C \approx 5.7,V$
Steps to Solve
- Calculate Base Voltage ($V_B$)
Using the voltage divider rule, calculate the base voltage:
$$ V_B = V_{CC} \times \frac{R_B}{R_B + R_C} $$
Given that ( V_{CC} = 20.7,V ), ( R_B = 500,k\Omega ), and ( R_C = 5,k\Omega ):
$$ V_B = 20.7,V \times \frac{500,k\Omega}{500,k\Omega + 5,k\Omega} = 20.7,V \times \frac{500}{505} $$
- Calculate Emitter Voltage ($V_E$)
The emitter voltage can be calculated using:
$$ V_E = V_B - V_{BE} $$
With ( V_B ) from the previous calculation and ( V_{BE} = 0.7,V ):
$$ V_E = V_B - 0.7,V $$
- Calculate Emitter Current ($I_E$)
Using Ohm’s law to find emitter current through ( R_E ):
$$ I_E = \frac{V_E}{R_E} $$
Given ( R_E = 1,k\Omega ):
- Calculate Collector Current ($I_C$)
Using the relationship between emitter current and collector current:
$$ I_C \approx I_E $$
Assuming ( \beta ) is large, we approximate ( I_C \approx I_E ).
- Calculate Base Current ($I_B$)
The relationship between collector current and base current is given by:
$$ I_C = \beta I_B $$
Thus,
$$ I_B = \frac{I_C}{\beta} $$
- Calculate Collector Voltage ($V_C$)
Finally, use Kirchhoff’s voltage law to find the collector voltage:
$$ V_C = V_{CC} - I_C \times R_C $$
Where ( R_C = 5,k\Omega ).
- $I_C \approx 19.45,mA$
- $I_B \approx 0.195,mA$
- $V_C \approx 5.7,V$
More Information
The calculations assume ideal conditions and that the transistor is in the active region. The results indicate how the biasing affects the transistor's operation.
Tips
- Not accounting for ( V_{BE} ) correctly, which could lead to inaccurate calculations for ( V_E ).
- Forgetting to convert units (e.g., kΩ to Ω) can lead to errors in the current calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information