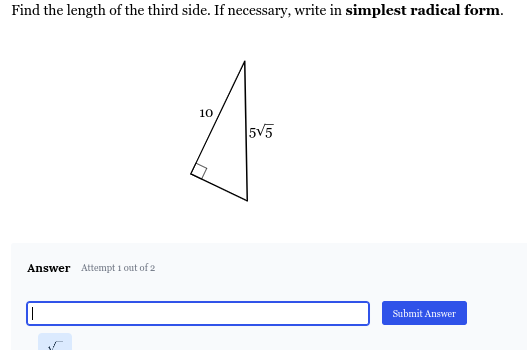
Find the length of the third side of the right triangle. Write the answer in simplest radical form.
Understand the Problem
The question asks to find the length of the missing side of a right triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides. We can use the Pythagorean theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) to find the missing side. The question also asks us to simplify the answer in radical form.
Answer
$5$
Answer for screen readers
$5$
Steps to Solve
- Identify the hypotenuse
The hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle, which in this case is $5\sqrt{5}$. Let the missing side be $x$.
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem
We have one leg with length 10 and the other with length $x$. Therefore, we can set up our equation as: $$10^2 + x^2 = (5\sqrt{5})^2$$
-
Simplify the equation $$100 + x^2 = 25 \cdot 5$$ $$100 + x^2 = 125$$
-
Solve for x $$x^2 = 125 - 100$$ $$x^2 = 25$$ $$x = \sqrt{25}$$ $$x = 5$$
$5$
More Information
The missing side is a whole number.
Tips
A common mistake is to incorrectly identify the hypotenuse and mix up the sides in the Pythagorean theorem. Another mistake is to incorrectly square $5\sqrt{5}$.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information