Find all real and imaginary solutions to the equation x^3 + 3x^2 - 14x - 42 = 0.
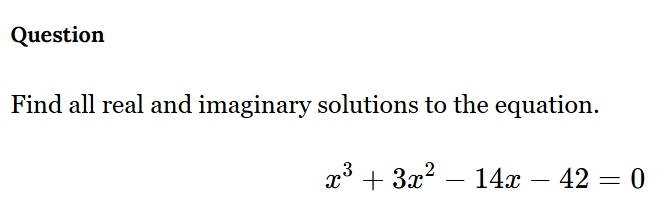
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to find the solutions, both real and imaginary, of the given cubic equation. This involves identifying the roots of the equation by applying appropriate algebraic methods.
Answer
The solutions are $x = -3, \, x = \sqrt{14}, \, x = -\sqrt{14}$.
Answer for screen readers
The solutions to the equation are:
$$ x = -3, , x = \sqrt{14}, , x = -\sqrt{14}. $$
Steps to Solve
- Identify the Cubic Equation
The given equation is
$$ x^3 + 3x^2 - 14x - 42 = 0. $$
- Use the Rational Root Theorem
Check possible rational roots using factors of the constant term (-42) and the leading coefficient (1). The factors of -42 include ±1, ±2, ±3, ±6, ±7, ±14, ±21, ±42.
- Test Possible Rational Roots
Let's test $x = 3$:
$$ 3^3 + 3(3^2) - 14(3) - 42 = 27 + 27 - 42 - 42 = -30 ,(\text{not a root}). $$
Now test $x = -6$:
$$ (-6)^3 + 3(-6)^2 - 14(-6) - 42 = -216 + 108 + 84 - 42 = -66 ,(\text{not a root}). $$
Next, test $x = -2$:
$$ (-2)^3 + 3(-2)^2 - 14(-2) - 42 = -8 + 12 + 28 - 42 = -10 ,(\text{not a root}). $$
Test $x = -3$:
$$ (-3)^3 + 3(-3)^2 - 14(-3) - 42 = -27 + 27 + 42 - 42 = 0 ,(\text{is a root}). $$
- Factor the Polynomial
Since $x = -3$ is a root, we can factor the polynomial using synthetic division by $x + 3$:
Perform the division and we get:
$$ x^3 + 3x^2 - 14x - 42 = (x + 3)(x^2 - 14). $$
- Solve the Quadratic Equation
Now solve
$$ x^2 - 14 = 0 $$
which gives:
$$ x^2 = 14 \implies x = \pm \sqrt{14}. $$
Thus, the solutions are:
- Real root: $x = -3$
- Real roots: $x = \sqrt{14}, -\sqrt{14}$.
The solutions to the equation are:
$$ x = -3, , x = \sqrt{14}, , x = -\sqrt{14}. $$
More Information
The roots of the cubic equation can include both real and imaginary solutions. In this case, all the solutions found are real. The method used involved first finding a rational root and then factoring the polynomial.
Tips
- Overlooking possible rational roots.
- Failing to properly execute synthetic division.
- Misclassifying the nature of the roots (real vs. imaginary).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information