Evaluate the limit: lim (x→0+) (1/x - (x^2 + 3x + 4)/(x^2 + 4x))
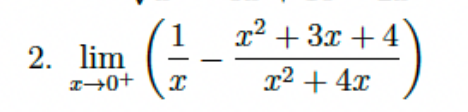
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to evaluate the limit of an expression as x approaches 0 from the positive side. The expression involves rational functions, and we need to carefully consider how to simplify and evaluate the limit to determine the final value.
Answer
$-\frac{1}{2}$
Answer for screen readers
$-\frac{1}{2}$
Steps to Solve
- Find a common denominator
To evaluate the limit, first combine the two fractions into a single fraction. The common denominator is $x(x+4) = x^2 + 4x$.
$$ \lim_{x\to 0^+} \left( \frac{1}{x} - \frac{x^2+3x+4}{x^2+4x} \right) = \lim_{x\to 0^+} \left( \frac{x+4}{x(x+4)} - \frac{x^2+3x+4}{x(x+4)} \right) $$
- Combine the fractions
Combine the numerators over the common denominator
$$ \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{(x+4) - (x^2+3x+4)}{x(x+4)} = \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{x+4 - x^2 - 3x - 4}{x(x+4)} $$
- Simplify the numerator
Simplify the numerator by combining like terms.
$$ \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{-x^2 - 2x}{x(x+4)} $$
- Factor out x and cancel
Factor out an $x$ from the numerator and cancel with the $x$ in the denominator.
$$ \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{x(-x-2)}{x(x+4)} = \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{-x-2}{x+4} $$
- Evaluate the limit
Now, evaluate the limit by substituting $x=0$ into the simplified expression
$$ \lim_{x\to 0^+} \frac{-x-2}{x+4} = \frac{-0-2}{0+4} = \frac{-2}{4} = -\frac{1}{2} $$
$-\frac{1}{2}$
More Information
The limit of the given expression as $x$ approaches 0 from the positive side is $-\frac{1}{2}$.
Tips
A common mistake is not finding a common denominator before attempting to combine the fractions. Another common mistake is not simplifying the expression completely before evaluating the limit, which can lead to indeterminate forms, even though the actual answer is a real number.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information