Evaluate $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)+1}{x}$
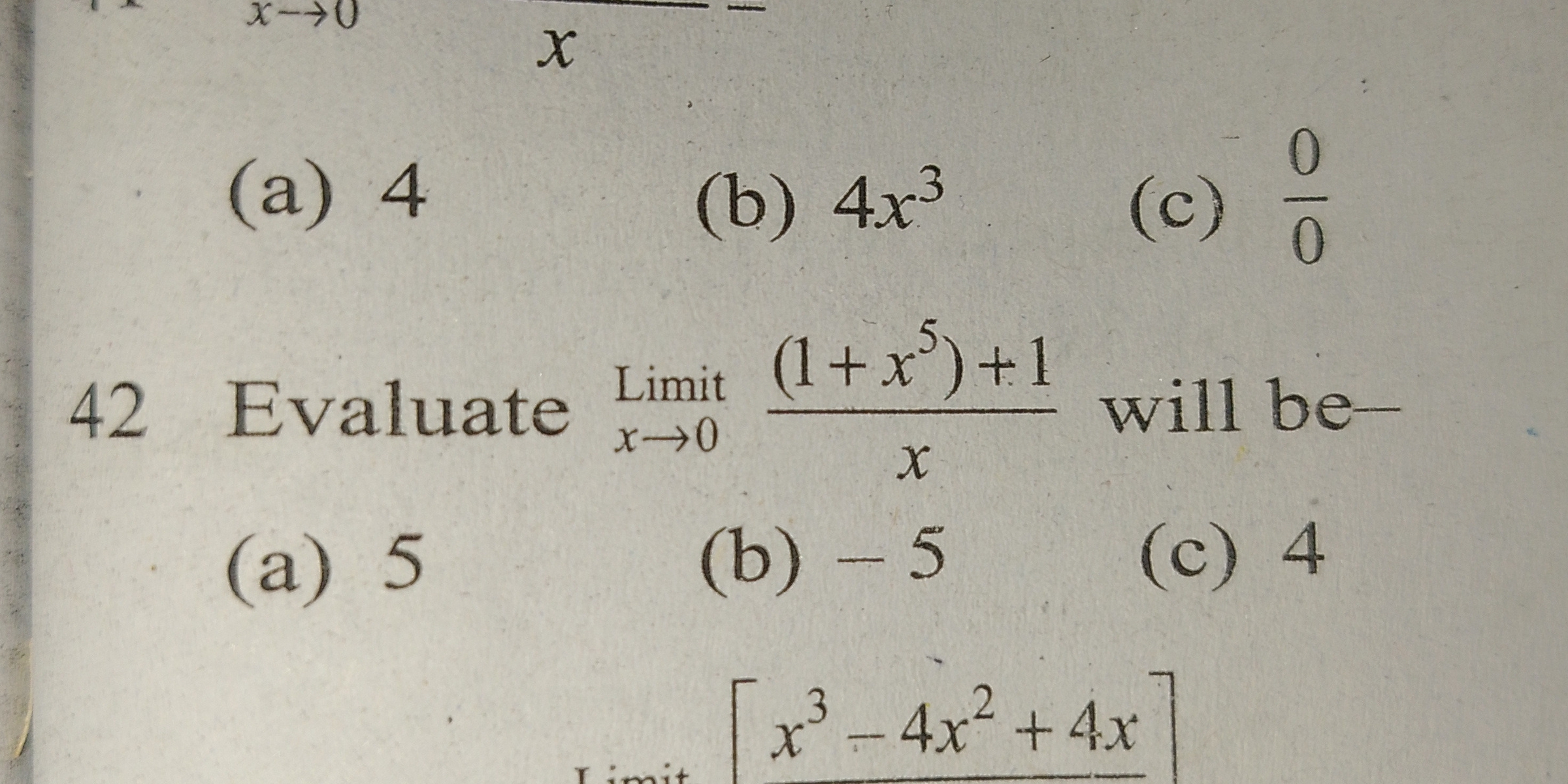
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to evaluate the limit of the given function as x approaches 0. This involves finding the value that the function approaches as x gets arbitrarily close to 0. We need to evaluate: $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)+1}{x}$
Answer
Assuming the question was $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)-1}{x}$ then the answer is 0. However, given the original equation, then the limit does not exist.
Answer for screen readers
Assuming the question was $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)-1}{x}$ then the answer is 0.
Steps to Solve
-
Simplify the expression Simplify the numerator of the fraction: $$(1 + x^5) + 1 = 2 + x^5$$ So, the limit becomes: $$\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{2 + x^5}{x}$$
-
Split the fraction into two terms We can rewrite the fraction as a sum of two fractions: $$\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{2 + x^5}{x} = \lim_{x\to 0} \left( \frac{2}{x} + \frac{x^5}{x} \right)$$
-
Simplify the second term Simplify the second fraction by canceling $x$: $$\lim_{x\to 0} \left( \frac{2}{x} + x^4 \right)$$
-
Evaluate the limit Now consider the limit as $x$ approaches 0. The term $x^4$ approaches 0 as $x$ approaches 0: $$\lim_{x\to 0} x^4 = 0$$ However, the term $\frac{2}{x}$ approaches infinity as $x$ approaches 0. Specifically, it approaches positive infinity from the right and negative infinity from the left. Therefore, the limit does not exist in the traditional sense because $\frac{2}{x}$ dominates the behavior of the function near $x = 0$. Since the function approaches infinity, none of the provided answers are correct. Assuming there was a typo and the question was $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)-1}{x}$, then the following steps can be taken
-
Simplify the expression
$$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)-1}{x}=\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x^5}{x} $$
- Evaluate the limit
$$ \lim_{x\to 0} \frac{x^5}{x} = \lim_{x\to 0} x^4 = 0 $$
Assuming the question was $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)-1}{x}$ then the answer is 0.
More Information
The original limit $\lim_{x\to 0} \frac{(1+x^5)+1}{x}$ does not exist.
Tips
A common mistake is to incorrectly simplify the expression or to not consider the behavior of each term as x approaches 0. It is important to correctly simplify the expression and then evaluate the limit of each term separately, if possible. Also, it is important to recognize when a limit does not exist, which can happen when the function approaches infinity or oscillates.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information