Distinguish between tropical and extra-tropical cyclone.
Understand the Problem
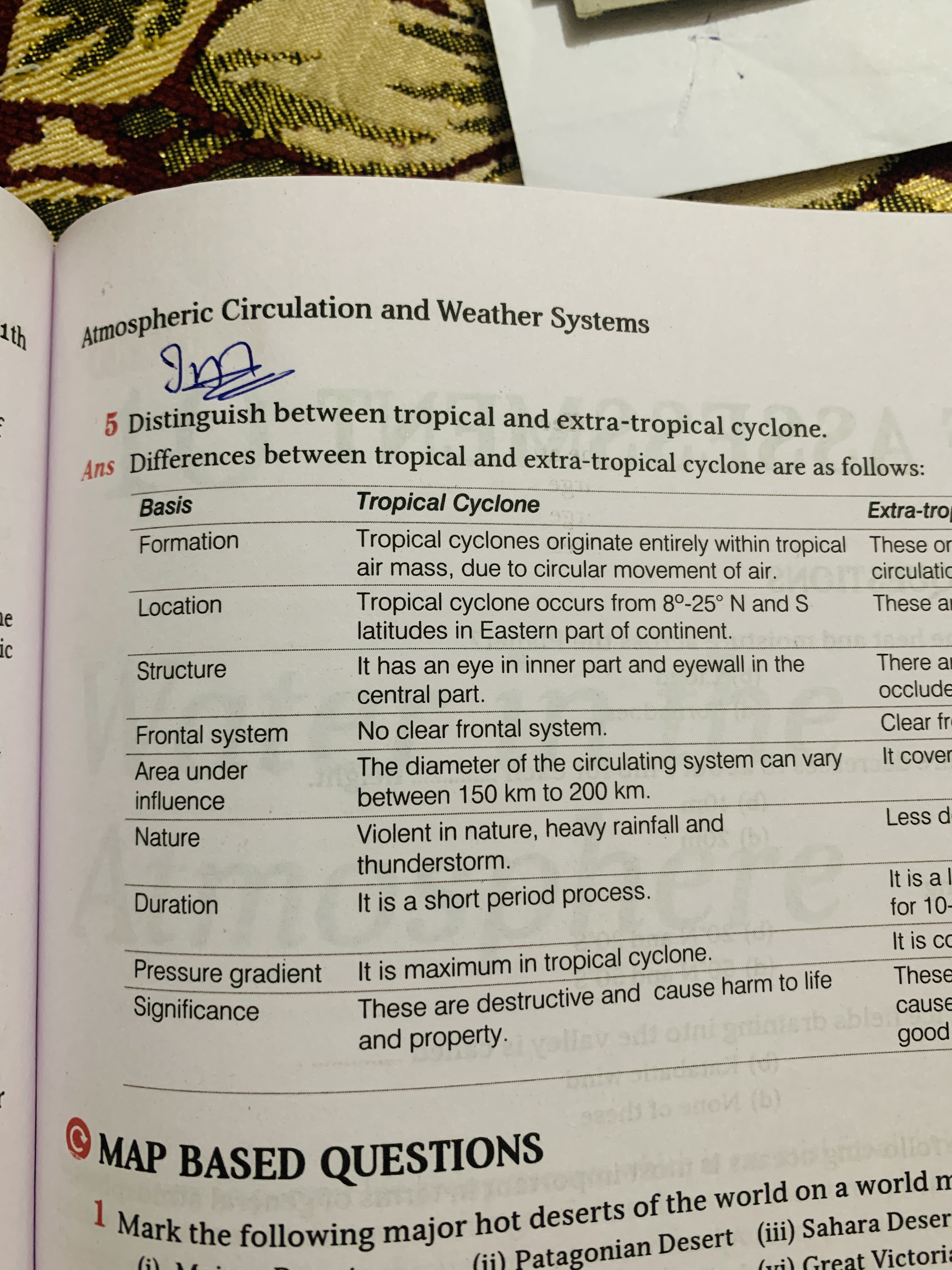
The question asks to differentiate between tropical and extra-tropical cyclones based on several criteria such as formation, location, structure, frontal system, area under influence, nature, duration, pressure gradient, and significance. This is a knowledge-based question related to atmospheric science and geography.
Answer
Tropical cyclones are warm-core, smaller, and form over tropical waters. Extratropical cyclones are cold-core, larger, and form over land and sea, often with fronts.
Tropical cyclones originate within a tropical air mass and occur between 8°-25° N and S latitudes. They have an eye and eyewall, lack a clear frontal system, typically span 150-200 km, are violent with heavy rain, and are short-lived, with maximum pressure gradient. These are destructive. Extratropical cyclones originate outside tropical air masses, occur at higher latitudes, have frontal systems, cover larger areas, are less destructive, and are longer lasting.
Answer for screen readers
Tropical cyclones originate within a tropical air mass and occur between 8°-25° N and S latitudes. They have an eye and eyewall, lack a clear frontal system, typically span 150-200 km, are violent with heavy rain, and are short-lived, with maximum pressure gradient. These are destructive. Extratropical cyclones originate outside tropical air masses, occur at higher latitudes, have frontal systems, cover larger areas, are less destructive, and are longer lasting.
More Information
Tropical cyclones are 'warm-core' in the troposphere, while extratropical cyclones are 'warm-core' in the stratosphere and 'cold-core' in the troposphere.
Tips
A common mistake is thinking that the terms tropical and extratropical refer only to the latitude at which they occur; temperature structure is also a key differentiator.
Sources
- Difference Between Extratropical and Tropical Cyclones - insightsonindia.com
- Extra-tropical Cyclone vs Tropical Cyclone - Hong Kong Observatory - hko.gov.hk
- What Is The Difference Between Tropical Cyclones & Extratropical ... - alabamawx.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information