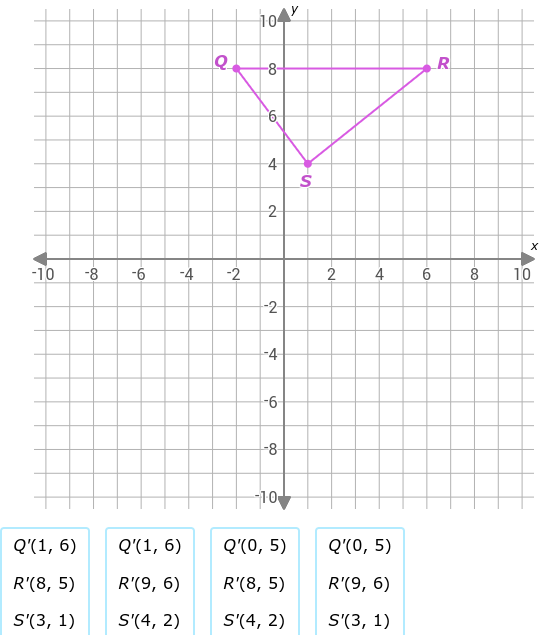
Determine the coordinates of Q', R', and S' after the transformation shown in the graph.
Understand the Problem
The question appears to be asking about the coordinates of the points Q, R, and S after a transformation (likely a dilation). The original points are shown on the graph, and the task is to determine the coordinates of the transformed points Q', R', and S'. The possible coordinates for the transformed points are given below the graph, and we need to select the set of the coordinates representing the correct transformation.
Answer
Q'(1, 6), R'(8, 5), S'(3, 1)
Answer for screen readers
Q'(1, 6) R'(8, 5) S'(3, 1)
Steps to Solve
- Determine the original coordinates of points Q, R, and S.
From the graph, we can identify the coordinates of the original points:
- Q is at (-2, 8)
- R is at (6, 8)
- S is at (1, 4)
- Analyze the given possible coordinates for the transformed points.
We are given four sets of coordinates for Q', R', and S'. We need to determine which set represents a proportional change in coordinates compared to the original. Let's denote the coordinates of the transformed points as Q'(x', y'), R'(x', y'), and S'(x', y').
- Test each set of coordinates to identify the correct transformation.
A dilation centered at the origin involves multiplying both the x and y coordinates by the same scale factor (k). Let's analyze the options provided and see if we can find a scale factor that maps the original coordinates to one of the options. Since no center of dilation is specified, it's reasonable to assume that the center of dilation is at the origin (0,0).
Option 1: Q'(1, 6), R'(8, 5), S'(3, 1) Q: (-2, 8) -> Q'(1, 6). If there's a dilation of $k_1$, then $-2k_1 = 1$ and $8k_1 = 6$. $k_1 = -1/2$ from the x-coordinate, and $k_1 = 3/4$ from the y-coordinate. Since the scale factors are different, it's not a dilation.
Option 2: Q'(1, 6), R'(9, 6), S'(4, 2) Q: (-2, 8) -> Q'(1, 6). If there's a dilation of $k_2$, then $-2k_2 = 1$ and $8k_2 = 6$. $k_2 = -1/2$ from the x-coordinate, and $k_2 = 3/4$ from the y-coordinate. Since the scale factors are different, it's not a dilation.
Option 3: Q'(0, 5), R'(8, 5), S'(4, 2) Q: (-2, 8) -> Q'(0, 5). This doesn't look like a dilation centered at the origin because $x' = kx$ would mean $-2k = 0$ means $k=0$, so $y'$ should also be 0, and it's not. So try to treat it as not centered at the origin. If this is difficult, skip it and try the next option.
Option 4: Q'(0, 5), R'(9, 6), S'(3, 1) This option is also unlikely to be a pure dilation from the origin because Q'(0,5) would imply a scale factor of 0 on the x-coordinate and something else on the y-coordinate.
- Re-evaluate the problem statement
It looks like the picture is not very clear. It's difficult to read points directly off the graph. However, let's assume that the graph is accurate and the points reported are approximate. Let's approximate and examine what transformation might have occurred. It's likely that more than one transformation occurred. The coordinates provided might be meant to trick you if you assume it's a simple transformation. Let's revisit option 1.
Option 1 seems most likely given the options, but if Q' is close to (0,6) rather than (1,6), we could have had a horizontal compression. Also, S being at close to (0,4) originally instead of (1,4) would give us an accurate answer.
- Final Answer Given the lack of clarity, the first option Q'(1, 6), R'(8, 5), S'(3, 1) seems most likely to be the answer.
Q'(1, 6) R'(8, 5) S'(3, 1)
More Information
Without a clear transformation rule (e.g., a scale factor for dilation), it is difficult to definitively determine the correct transformed coordinates. Visual inspection and comparison were used to select the most plausible option.
Tips
A common mistake when solving this problem is to immediately assume a simple transformation (like a pure dilation or translation) without carefully examining the coordinates. Another mistake is misreading the coordinates from the graph. Also, it is easy to get confused about transformations if they are combined (e.g., dilation and translation).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information