Describe the function of each labeled component in the diagram of the internal combustion engine setup.
Understand the Problem
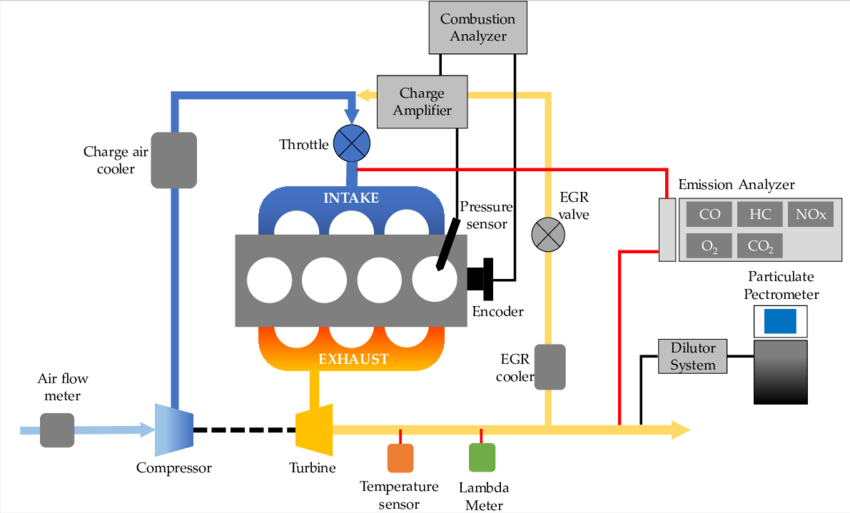
The image illustrates a schematic of an internal combustion engine setup, including various components for intake, exhaust, and emission analysis. It is a visual representation of the engine's operational flow and the instrumentation used to monitor its performance and emissions.
Answer
The labeled components in the internal combustion engine setup measure and control various parameters like air flow, pressure, temperature, and emissions to optimize engine performance and reduce pollution.
Here is a description of the labeled components of the internal combustion engine setup:
- Air Flow Meter: Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Compressor: Increases the pressure and density of the air entering the engine.
- Turbine: Driven by exhaust gases, it powers the compressor.
- Charge Air Cooler: Cools the compressed air to increase its density.
- Throttle: Controls the amount of air entering the engine.
- Pressure Sensor: Measures the pressure inside the intake manifold.
- Encoder: Measures the crankshaft's position and speed.
- EGR Valve: Recirculates a portion of exhaust gas back into the intake manifold to reduce NOx emissions.
- EGR Cooler: Cools the recirculated exhaust gas to further reduce NOx emissions.
- Temperature Sensor: Measures the temperature of the exhaust gas.
- Lambda Meter: Measures the air-fuel ratio in the exhaust gas.
- Combustion Analyzer: Analyzes the composition of the gases after combustion.
- Charge Amplifier: Amplifies the signal from a pressure sensor.
- Emission Analyzer: Measures the levels of various pollutants in the exhaust gas (CO, HC, NOx, O2, CO2).
- Dilutor System: Dilutes the exhaust sample for accurate measurement.
- Particulate Pectrometer: Measures the amount of particulate matter in the exhaust gas.
Answer for screen readers
Here is a description of the labeled components of the internal combustion engine setup:
- Air Flow Meter: Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Compressor: Increases the pressure and density of the air entering the engine.
- Turbine: Driven by exhaust gases, it powers the compressor.
- Charge Air Cooler: Cools the compressed air to increase its density.
- Throttle: Controls the amount of air entering the engine.
- Pressure Sensor: Measures the pressure inside the intake manifold.
- Encoder: Measures the crankshaft's position and speed.
- EGR Valve: Recirculates a portion of exhaust gas back into the intake manifold to reduce NOx emissions.
- EGR Cooler: Cools the recirculated exhaust gas to further reduce NOx emissions.
- Temperature Sensor: Measures the temperature of the exhaust gas.
- Lambda Meter: Measures the air-fuel ratio in the exhaust gas.
- Combustion Analyzer: Analyzes the composition of the gases after combustion.
- Charge Amplifier: Amplifies the signal from a pressure sensor.
- Emission Analyzer: Measures the levels of various pollutants in the exhaust gas (CO, HC, NOx, O2, CO2).
- Dilutor System: Dilutes the exhaust sample for accurate measurement.
- Particulate Pectrometer: Measures the amount of particulate matter in the exhaust gas.
More Information
The components of an internal combustion engine work together to convert chemical energy into mechanical work while minimizing harmful emissions.
Tips
When describing engine components, focus on their primary function and how they contribute to the overall process of combustion and emission control.
Sources
- Component parts of internal combustion engines - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
- Internal Combustion Engine - Bartosz Ciechanowski - ciechanow.ski
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information