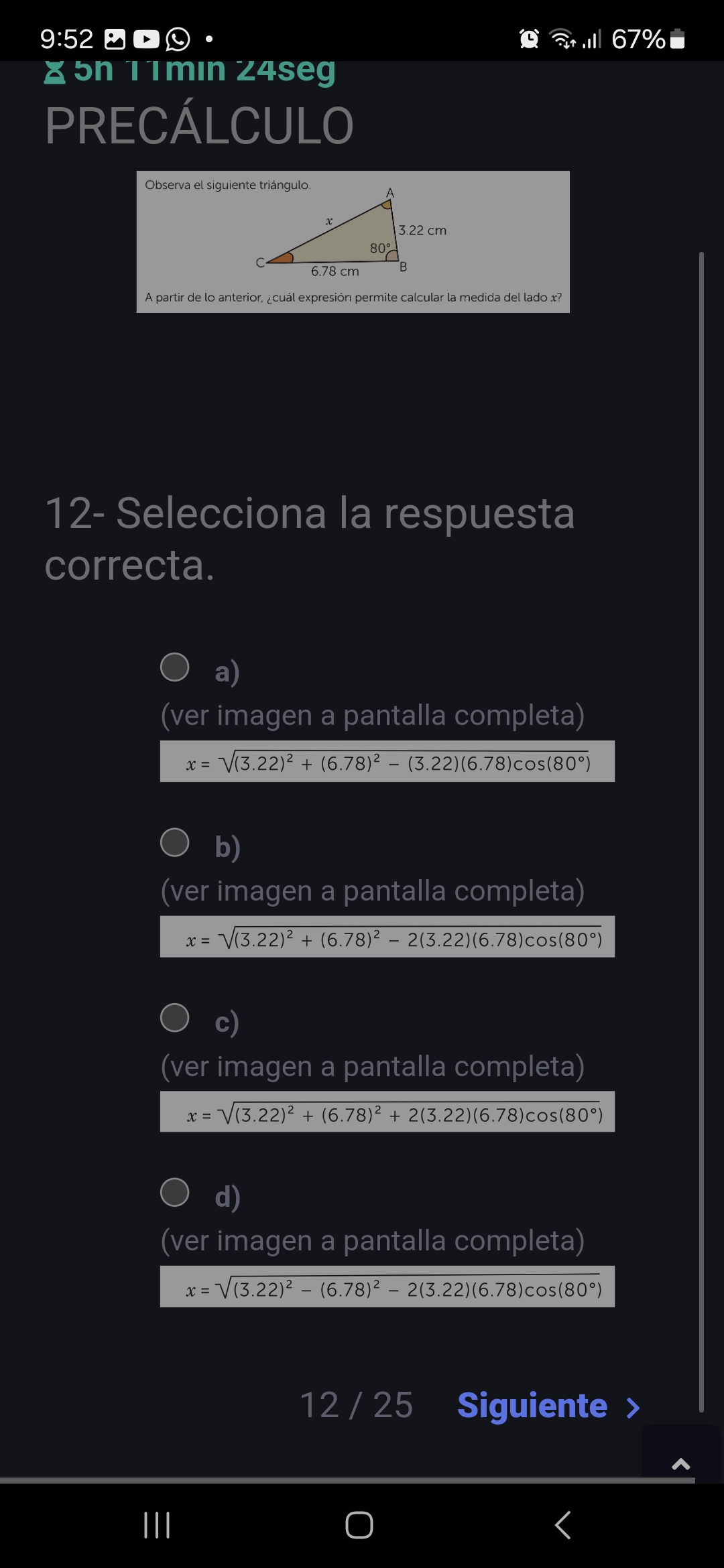
¿Cuál expresión permite calcular la longitud del lado x en el triángulo dado?
Understand the Problem
La pregunta presenta un triángulo con dos lados conocidos (3.22 cm y 6.78 cm) y el ángulo entre ellos (80 grados). Se pide identificar la expresión correcta para calcular la longitud del lado opuesto al ángulo dado, usualmente denotado como 'x'. Esto implica aplicar la ley de los cosenos.
Answer
$x = \sqrt{(3.22)^2 + (6.78)^2 - 2(3.22)(6.78)cos(80^\circ)}$
Answer for screen readers
b) $x = \sqrt{(3.22)^2 + (6.78)^2 - 2(3.22)(6.78)cos(80^\circ)}$
Steps to Solve
- Recall the Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines relates the sides and angles of a triangle. For a triangle with sides $a$, $b$, and $c$, and angle $C$ opposite side $c$, the Law of Cosines states: $c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(C)$
- Apply the Law of Cosines to the given problem
In our problem, we want to find side $x$, which is opposite the $80^\circ$ angle. The other two sides are 3.22 cm and 6.78 cm. Let $x = c$, $a = 3.22$, $b = 6.78$, and $C = 80^\circ$. Then, according to the Law of Cosines: $x^2 = (3.22)^2 + (6.78)^2 - 2(3.22)(6.78) \cos(80^\circ)$
- Solve for $x$
To find $x$, we take the square root of both sides of the equation from Step 2: $x = \sqrt{(3.22)^2 + (6.78)^2 - 2(3.22)(6.78) \cos(80^\circ)}$
b) $x = \sqrt{(3.22)^2 + (6.78)^2 - 2(3.22)(6.78)cos(80^\circ)}$
More Information
The Law of Cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem. When the angle $C$ is $90^\circ$, $\cos(C) = 0$, and the Law of Cosines reduces to $c^2 = a^2 + b^2$, which is the Pythagorean theorem.
Tips
- Forgetting the factor of 2 in the term $2ab\cos(C)$.
- Using the wrong sign before the $2ab\cos(C)$ term. It should be negative.
- Taking the square root prematurely or not at all.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information