Consider the reaction: $2Fe^{3+}_{(aq)} + Sn^{2+}_{(aq)} \rightarrow 2Fe^{2+}_{(aq)} + Sn^{4+}_{(aq)}$. What is the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$ if the rate of disappearance of... Consider the reaction: $2Fe^{3+}_{(aq)} + Sn^{2+}_{(aq)} \rightarrow 2Fe^{2+}_{(aq)} + Sn^{4+}_{(aq)}$. What is the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$ if the rate of disappearance of $Fe^{3+}$ is $9.00 \times 10^{-3} M/s$?
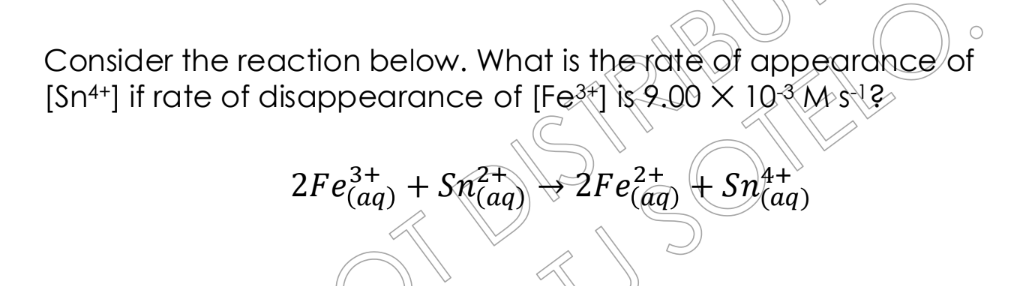
Understand the Problem
The question is asking us to determine the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$ given the rate of disappearance of $Fe^{3+}$ in the reaction: $2Fe^{3+}{(aq)} + Sn^{2+}{(aq)} \rightarrow 2Fe^{2+}{(aq)} + Sn^{4+}{(aq)}$. We need to use the stoichiometry of the reaction to relate the rates of change of the reactants and products.
Answer
$4.50 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$
Answer for screen readers
The rate of appearance of $[Sn^{4+}]$ is $4.50 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$.
Steps to Solve
- Relate the rates using stoichiometry The balanced equation $2Fe^{3+}{(aq)} + Sn^{2+}{(aq)} \rightarrow 2Fe^{2+}{(aq)} + Sn^{4+}{(aq)}$ shows that for every 2 moles of $Fe^{3+}$ that disappear, 1 mole of $Sn^{4+}$ appears. Therefore, the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$ is half the rate of disappearance of $Fe^{3+}$. We can write this as:
$$Rate_{Sn^{4+}} = -\frac{1}{2} Rate_{Fe^{3+}}$$
Note the negative sign on the rate of $Fe^{3+}$
- Substitute the given rate of disappearance We are given that the rate of disappearance of $Fe^{3+}$ is $9.00 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$. Since it is disappearing, its rate is negative. So, $Rate_{Fe^{3+}} = -9.00 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$.
$$Rate_{Sn^{4+}} = -\frac{1}{2} (-9.00 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1})$$
- Calculate the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$ Now, we can calculate the rate of appearance of $Sn^{4+}$:
$$Rate_{Sn^{4+}} = \frac{1}{2} (9.00 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}) = 4.50 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$$
The rate of appearance of $[Sn^{4+}]$ is $4.50 \times 10^{-3} M s^{-1}$.
More Information
The rate of appearance of a product is always positive, while the rate of disappearance of a reactant is always negative. The stoichiometric coefficients in a balanced chemical equation allow us to relate the rates of different reactants and products.
Tips
A common mistake is forgetting to account for the stoichiometric coefficients when relating the rates of different species in the reaction. Another mistake is not paying attention to the sign of the rate; reactants disappear (negative rate), and products appear (positive rate).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information