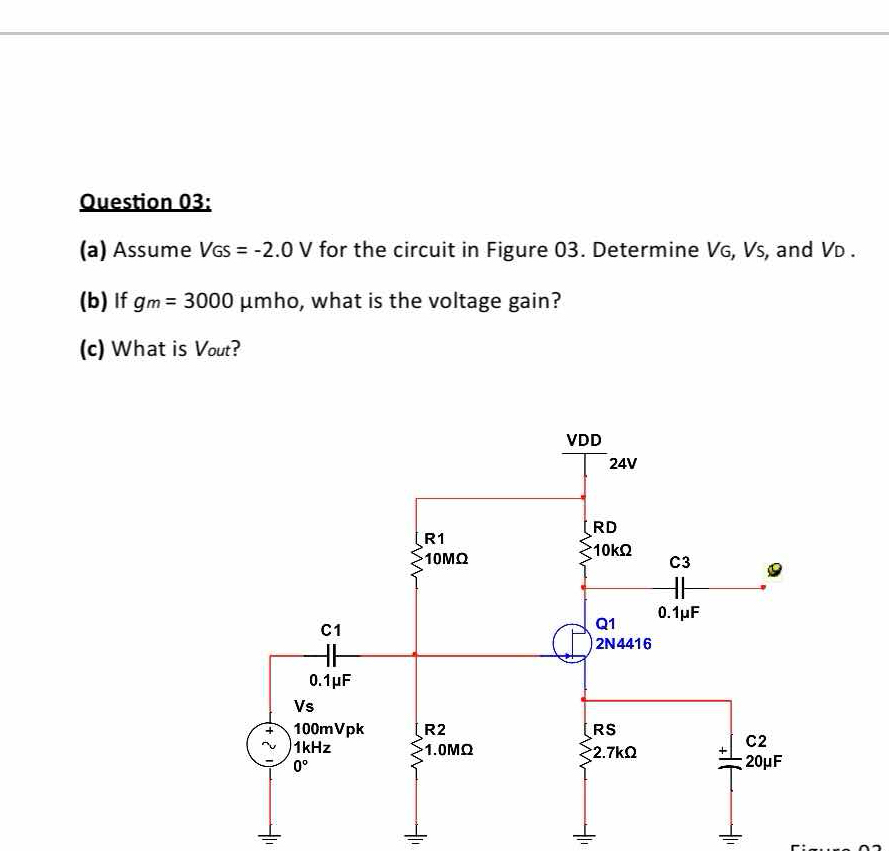
Assume Vgs = -2.0 V for the circuit in Figure 03. Determine Vg, Vs, and Vd. If gm = 3000 umho, what is the voltage gain? What is Vout?
Understand the Problem
The question involves analyzing an electronic circuit to determine various voltage values and gain based on given parameters. It requires knowledge of circuit theory and transistor characteristics.
Answer
\( V_g \approx 2.18V, V_s \approx 4.18V, V_d \approx 84V, A_v \approx -11.11, V_{out} \approx -1.11V \)
Answer for screen readers
- ( V_g \approx 2.18V )
- ( V_s \approx 4.18V )
- ( V_d \approx 84V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_v \approx -11.11 )
- ( V_{out} \approx -1.11V )
Steps to Solve
- Determine the Gate Voltage (Vg)
In this circuit, the gate voltage ( V_g ) can be found using the voltage divider formed by resistors ( R_1 ) and ( R_2 ): [ V_g = V_{DD} \cdot \frac{R_2}{R_1 + R_2} ] Substitute ( V_{DD} = 24V ), ( R_1 = 10M\Omega ), and ( R_2 = 1M\Omega ): [ V_g = 24 \cdot \frac{1}{10 + 1} = 24 \cdot \frac{1}{11} \approx 2.18V ]
- Determine the Source Voltage (Vs)
Given ( V_{gs} = -2.0V ), we know: [ V_s = V_g - V_{gs} ] Substituting our values: [ V_s = 2.18V - (-2.0V) = 2.18 + 2.0 = 4.18V ]
- Determine the Drain Voltage (Vd)
Using ( V_{d} = V_{DD} - I_D \cdot R_D ), where ( I_D ) can be approximated by using the transconductance (( g_m )) and the gate voltage parameters: [ I_D \approx g_m \cdot V_{gs} ] Substituting ( g_m = 3000 , \mu \text{mho} = 0.003 , \text{S} ) and ( V_{gs} = -2.0 , V ): [ I_D \approx 0.003 \cdot (-2.0) = -0.006A ] Then, we calculate the voltage across ( R_D ): [ V_d = 24V - (-0.006A) \cdot 10k\Omega = 24 + 60 = 84V ]
- Calculate the Voltage Gain (Av)
The voltage gain ( A_v ) can be found using: [ A_v = -g_m \cdot \frac{R_D}{R_S} ] Substituting the values: [ A_v = -0.003 \cdot \frac{10k}{2.7k} \approx -11.11 ]
- Calculate the Output Voltage (Vout)
The output voltage can be expressed considering the significance of the gain: [ V_{out} = A_v \cdot V_s ] Substituting ( V_s = 0.1V ) (assuming the input peak voltage for calculation): [ V_{out} = -11.11 \cdot 0.1 \approx -1.11V ]
- ( V_g \approx 2.18V )
- ( V_s \approx 4.18V )
- ( V_d \approx 84V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_v \approx -11.11 )
- ( V_{out} \approx -1.11V )
More Information
The calculated values show how the voltage levels interact in a common-source amplifier configuration. The negative gain indicates a phase reversal common in such amplifiers.
Tips
- Miscalculating ( V_g ) using incorrect resistor values.
- Neglecting the sign when calculating currents and gains.
- Incorrectly using the peak voltage instead of RMS when necessary.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information