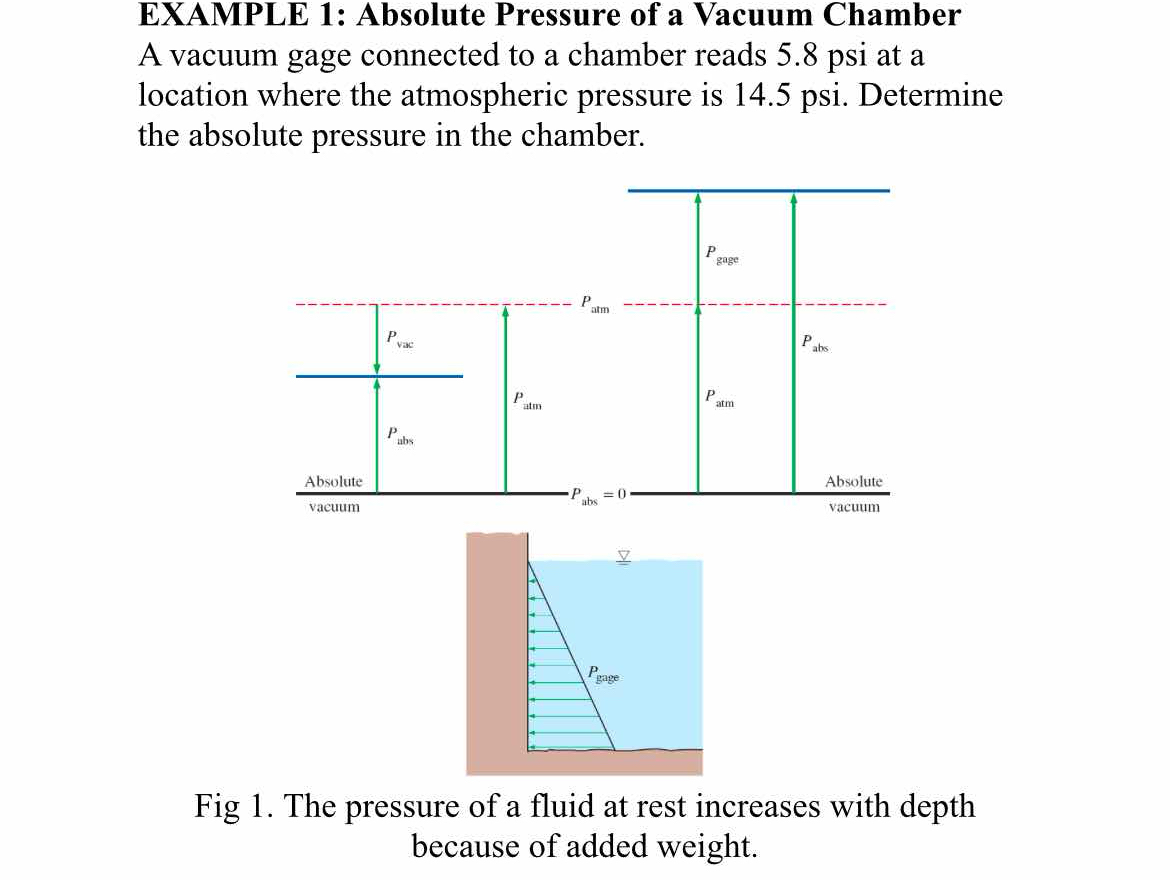
A vacuum gauge connected to a chamber reads 5.8 psi at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 14.5 psi. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the absolute pressure in a vacuum chamber using information from a vacuum gauge and atmospheric pressure. The high-level approach involves applying the formula for absolute pressure, which is the difference between atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure.
Answer
The absolute pressure in the chamber is \( 8.7 \, \text{psi} \).
Answer for screen readers
The absolute pressure in the chamber is ( P_{abs} = 8.7 , \text{psi} ).
Steps to Solve
- Identify the given values
From the problem, we have the following values:
- Atmospheric pressure, ( P_{atm} = 14.5 , \text{psi} )
- Gauge pressure, ( P_{gauge} = 5.8 , \text{psi} )
-
Understand the relationship between pressures
The absolute pressure in the chamber is calculated using the formula: $$ P_{abs} = P_{atm} - P_{gauge} $$ -
Substitute the values into the formula
Now, substitute the known values into the equation: $$ P_{abs} = 14.5 , \text{psi} - 5.8 , \text{psi} $$ -
Perform the calculation
Calculate ( P_{abs} ): $$ P_{abs} = 14.5 - 5.8 = 8.7 , \text{psi} $$
The absolute pressure in the chamber is ( P_{abs} = 8.7 , \text{psi} ).
More Information
The absolute pressure is an important measure in vacuum systems, directly affecting the performance of the equipment. Knowing the absolute pressure helps in calibrating instruments and ensuring proper functioning.
Tips
- Confusing absolute pressure with gauge pressure. Remember that gauge pressure does not account for atmospheric pressure.
- Not correctly subtracting the gauge pressure from atmospheric pressure. Ensure the arithmetic is accurate.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information