(a) Normalize ψ. (b) Determine the expectation values of x and x².
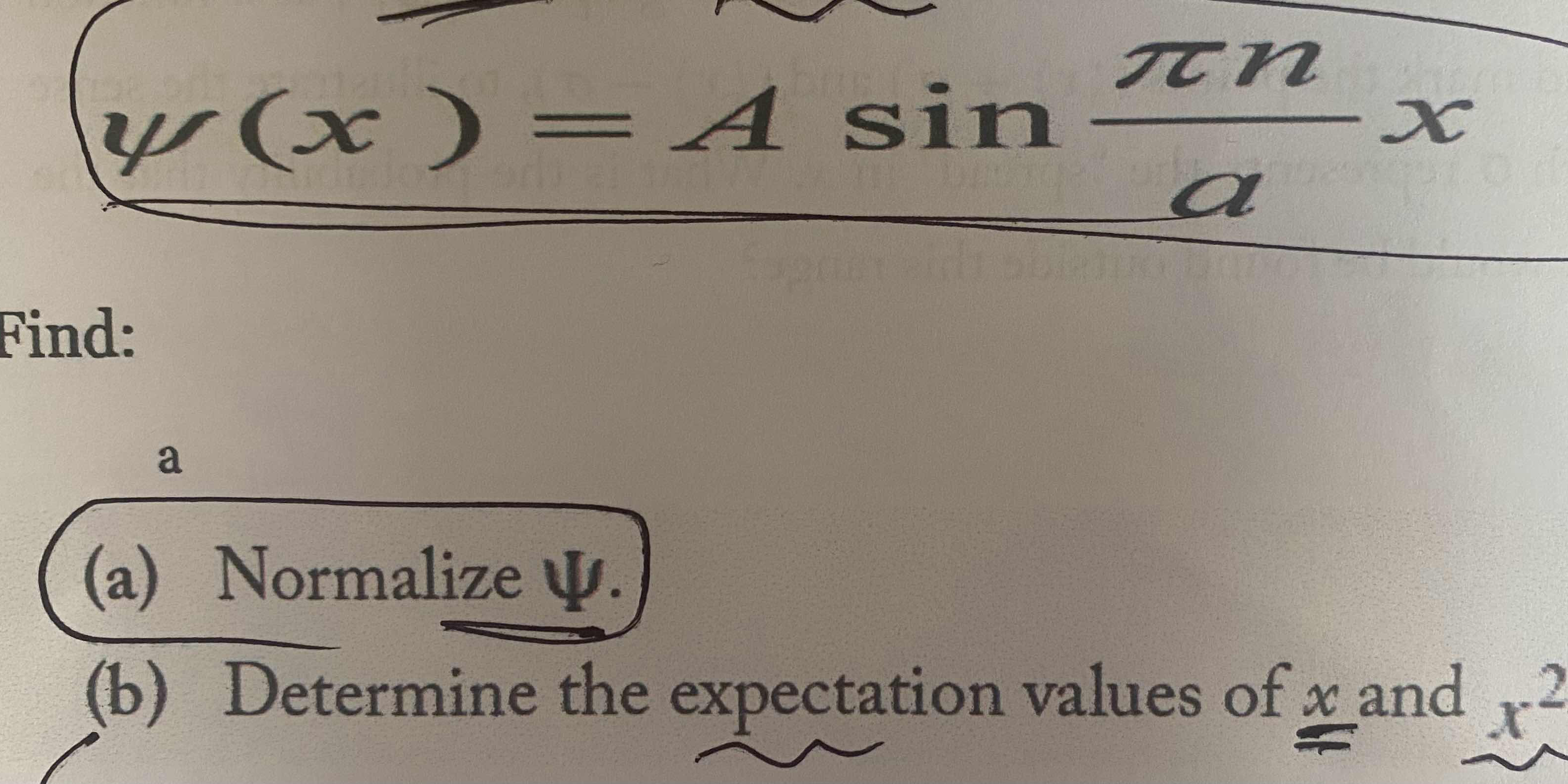
Understand the Problem
The question asks for two main tasks related to a wave function ψ(x). The first part requires normalizing the function, and the second part requires finding the expectation values for x and x². This is often associated with quantum mechanics and involves mathematical calculations.
Answer
The normalized wave function is $A = \sqrt{\frac{2}{a}}$. Expectation values depend on computed integrals.
Answer for screen readers
The normalized wave function is $A = \sqrt{\frac{2}{a}}$.
For the expectation values, you will generally need numerical evaluation or specific integral solutions as they can be complex.
Steps to Solve
- Normalizing the Wave Function
To normalize the wave function $\psi(x) = A \sin\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right)$, we need to ensure that the integral of the probability density over the domain equals 1:
$$ \int_{0}^{a} |\psi(x)|^2 , dx = 1 $$
Calculating the integral:
$$ \int_{0}^{a} |A \sin\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right)|^2 , dx = A^2 \int_{0}^{a} \sin^2\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) , dx $$
Using the identity $\sin^2(x) = \frac{1 - \cos(2x)}{2}$, we find:
$$ A^2 \int_{0}^{a} \sin^2\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) , dx = A^2 \cdot \frac{a}{2} $$
Setting this equal to 1 gives us:
$$ A^2 \cdot \frac{a}{2} = 1 \implies A^2 = \frac{2}{a} \implies A = \sqrt{\frac{2}{a}} $$
- Finding Expectation Values for x
The expectation value $\langle x \rangle$ is given by:
$$ \langle x \rangle = \int_{0}^{a} x |\psi(x)|^2 , dx $$
Substituting $\psi(x)$ into the integral:
$$ \langle x \rangle = \int_{0}^{a} x \left( A \sin\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) \right)^2 , dx = A^2 \int_{0}^{a} x \sin^2\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) , dx $$
This requires integration by parts or the use of integral tables to solve.
- Finding Expectation Value for x²
The expectation value $\langle x^2 \rangle$ is given by:
$$ \langle x^2 \rangle = \int_{0}^{a} x^2 |\psi(x)|^2 , dx $$
Substituting $\psi(x)$ into the integral:
$$ \langle x^2 \rangle = \int_{0}^{a} x^2 \left( A \sin\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) \right)^2 , dx = A^2 \int_{0}^{a} x^2 \sin^2\left(\frac{\pi n}{a} x\right) , dx $$
Again, use integration techniques to evaluate this integral.
The normalized wave function is $A = \sqrt{\frac{2}{a}}$.
For the expectation values, you will generally need numerical evaluation or specific integral solutions as they can be complex.
More Information
In quantum mechanics, wave functions describe the quantum state of a particle, and normalizing them ensures their probabilities are meaningful. Expectation values provide averages for observable properties of a particle, giving insights into its behavior.
Tips
- Forgetting to square the wave function while normalizing.
- Misapplying integration techniques or limits when calculating integrals.
- Not simplifying integrals using trigonometric identities, leading to more complex calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information