∫ 1/v^2 dv
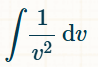
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to solve the integral of the function 1/v^2 with respect to v. This involves applying the rules of integration to find the antiderivative of the given function.
Answer
The integral is $ -\frac{1}{v} + C $.
Answer for screen readers
The final result of the integral is: $$ -\frac{1}{v} + C $$
Steps to Solve
-
Rewrite the Integral To facilitate integration, we can rewrite the integrand $ \frac{1}{v^2} $ as $ v^{-2} $.
-
Apply the Power Rule of Integration The power rule states that for any function $ v^n $, the integral is given by: $$ \int v^n , dv = \frac{v^{n+1}}{n+1} + C $$ for $ n \neq -1 $.
Here, $ n = -2 $, so: $$ \int v^{-2} , dv = \frac{v^{-2+1}}{-2+1} + C = \frac{v^{-1}}{-1} + C $$
- Simplify the Result Simplifying the above expression gives: $$ \int v^{-2} , dv = -\frac{1}{v} + C $$
The final result of the integral is: $$ -\frac{1}{v} + C $$
More Information
This integration result shows that the area under the curve of the function $ \frac{1}{v^2} $ decreases without bound as $ v $ approaches zero, reflecting the function's vertical asymptote.
Tips
- Forgetting to add the constant of integration $ C $.
- Misapplying the power rule, particularly forgetting that it applies only when $ n \neq -1 $.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information