1. Solve for x: 1/(3x - 1) + 2/(x - 3) 2. Rationalize the denominator: 2 / (x+1+√x)
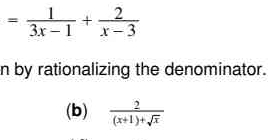
Understand the Problem
The image contains two math problems. The first problem is an equation involving fractions with algebraic expressions in the denominators. The second problem asks to rationalize the denominator of the expression 2 / (x+1+√x).
Answer
(a) $\frac{7x-5}{3x^2-10x+3}$ (b) $\frac{2(x+1-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1}$
Answer for screen readers
(a) $\frac{1}{3x-1} + \frac{2}{x-3} = \frac{7x-5}{3x^2 - 10x + 3}$ (b) $\frac{2}{(x+1)+\sqrt{x}} = \frac{2(x+1-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1}$
Steps to Solve
-
Solve the first equation Begin by finding a common denominator for the two fractions, which is $(3x-1)(x-3)$.
-
Combine the fractions Multiply the first fraction by $\frac{x-3}{x-3}$ and the second fraction by $\frac{3x-1}{3x-1}$. Combine the numerators: $$ \frac{1}{3x-1} + \frac{2}{x-3} = \frac{1(x-3) + 2(3x-1)}{(3x-1)(x-3)} $$
-
Simplify the numerator Expand and simplify the numerator: $$ \frac{x-3+6x-2}{(3x-1)(x-3)} = \frac{7x-5}{(3x-1)(x-3)} $$
-
Expand the denominator Expand the denominator to get: $$ \frac{7x-5}{3x^2 - 9x - x + 3} = \frac{7x-5}{3x^2 - 10x + 3} $$
-
Rationalize the denominator of the second expression The expression to rationalize is $\frac{2}{(x+1)+\sqrt{x}}$. To rationalize the denominator, multiply both the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator, which is $(x+1) - \sqrt{x}$.
-
Multiply by the conjugate $$ \frac{2}{(x+1)+\sqrt{x}} \cdot \frac{(x+1)-\sqrt{x}}{(x+1)-\sqrt{x}} $$
-
Simplify the denominator The denominator becomes $((x+1)+\sqrt{x})((x+1)-\sqrt{x}) = (x+1)^2 - (\sqrt{x})^2 = (x^2+2x+1) - x = x^2 + x + 1$.
-
Simplify the expression The expression simplifies to: $$ \frac{2((x+1)-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1} = \frac{2(x+1-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1} $$
-
Final Result Thus the original equations are $$ \frac{1}{3x-1} + \frac{2}{x-3} = \frac{7x-5}{3x^2 - 10x + 3} $$ $$ \frac{2}{(x+1)+\sqrt{x}} = \frac{2(x+1-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1} $$
(a) $\frac{1}{3x-1} + \frac{2}{x-3} = \frac{7x-5}{3x^2 - 10x + 3}$ (b) $\frac{2}{(x+1)+\sqrt{x}} = \frac{2(x+1-\sqrt{x})}{x^2+x+1}$
More Information
Rationalizing the denominator is a technique used to eliminate radical expressions from the denominator of a fraction, making it easier to work with.
Tips
A common mistake while rationalizing the denominator is not correctly multiplying by the conjugate. Also people might forget to distribute in the numerator after multiplying by the conjugate. Don't forget to expand $(x+1)^2$ correctly when rationalizing as well.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information