Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the kidneys within the urinary system?
What is the primary function of the kidneys within the urinary system?
- Transporting urine to the bladder
- Regulating blood pressure
- Producing urine (correct)
- Filtering blood for nutrients
Which of the following components is NOT part of the urinary system?
Which of the following components is NOT part of the urinary system?
- Spleen (correct)
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
Where is the renal artery located and what is its primary function?
Where is the renal artery located and what is its primary function?
- It branches off the aorta, supplying oxygenated blood to the kidney. (correct)
- It connects the renal pelvis to the bladder.
- It carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidney.
- It exits the kidney carrying oxygenated blood.
What structure within the nephron is responsible for filtering blood?
What structure within the nephron is responsible for filtering blood?
Which layer of the kidney is situated directly outside the renal medulla?
Which layer of the kidney is situated directly outside the renal medulla?
What is the primary role of active vitamin D in the body?
What is the primary role of active vitamin D in the body?
Which muscle type is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
Which muscle type is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
What is the primary composition of the renal medulla?
What is the primary composition of the renal medulla?
Which statement about the sphincters in the urinary system is correct?
Which statement about the sphincters in the urinary system is correct?
What is the role of calyces in the kidneys?
What is the role of calyces in the kidneys?
Which electrolyte is primarily adjusted by the kidneys to maintain balance?
Which electrolyte is primarily adjusted by the kidneys to maintain balance?
What triggers the reflex action for urination?
What triggers the reflex action for urination?
At what volume of urine does one typically begin to feel the urge to urinate?
At what volume of urine does one typically begin to feel the urge to urinate?
What is the primary role of the efferent arteriole in the kidney's filtering process?
What is the primary role of the efferent arteriole in the kidney's filtering process?
Which renal structure is responsible for enclosing the glomerulus?
Which renal structure is responsible for enclosing the glomerulus?
What predominantly happens in the peritubular capillaries?
What predominantly happens in the peritubular capillaries?
What is the average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) per minute?
What is the average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) per minute?
Which process in urine formation involves the selective return of useful substances to the bloodstream?
Which process in urine formation involves the selective return of useful substances to the bloodstream?
What effect does aldosterone have on kidney function?
What effect does aldosterone have on kidney function?
Which of the following substances is primarily involved in tubular secretion?
Which of the following substances is primarily involved in tubular secretion?
What is the primary outcome of tubular reabsorption?
What is the primary outcome of tubular reabsorption?
What triggers the release of renin from the kidneys?
What triggers the release of renin from the kidneys?
Which hormones increase water reabsorption in the kidney?
Which hormones increase water reabsorption in the kidney?
What represents a normal specific gravity range for urine?
What represents a normal specific gravity range for urine?
What change occurs in kidney function as individuals age?
What change occurs in kidney function as individuals age?
Which of the following is a waste product eliminated by the kidneys?
Which of the following is a waste product eliminated by the kidneys?
Which structure serves as the entry point for the renal artery into the kidney?
Which structure serves as the entry point for the renal artery into the kidney?
What role does the renal cortex primarily play within the kidney's anatomy?
What role does the renal cortex primarily play within the kidney's anatomy?
Which process occurs within the nephron and is essential for urine formation?
Which process occurs within the nephron and is essential for urine formation?
What is the significance of the efferent arteriole being smaller than the afferent arteriole?
What is the significance of the efferent arteriole being smaller than the afferent arteriole?
What is the primary role of the renal pyramids within the kidneys?
What is the primary role of the renal pyramids within the kidneys?
Which component of the nephron directly interacts with blood vessels to facilitate filtration?
Which component of the nephron directly interacts with blood vessels to facilitate filtration?
What does the renal fascia do in relation to the kidneys?
What does the renal fascia do in relation to the kidneys?
Within the nephron, what is primarily filtered into the Bowman's capsule?
Within the nephron, what is primarily filtered into the Bowman's capsule?
What process primarily occurs in Bowman's capsule during urine formation?
What process primarily occurs in Bowman's capsule during urine formation?
How does increased fluid intake affect the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
How does increased fluid intake affect the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Which structure does urine flow into after the collecting tubules?
Which structure does urine flow into after the collecting tubules?
Which of the following processes does NOT occur in the distal convoluted tubules?
Which of the following processes does NOT occur in the distal convoluted tubules?
What is the primary function of peritubular capillaries in the nephron?
What is the primary function of peritubular capillaries in the nephron?
Which hormone promotes potassium excretion from the kidneys?
Which hormone promotes potassium excretion from the kidneys?
Which of the following substances is NOT typically reabsorbed during tubular reabsorption?
Which of the following substances is NOT typically reabsorbed during tubular reabsorption?
What is the typical composition of normal urine?
What is the typical composition of normal urine?
What role does angiotensin II play in the renal system?
What role does angiotensin II play in the renal system?
Which portion of the nephron is primarily involved in the secretion of hydrogen ions?
Which portion of the nephron is primarily involved in the secretion of hydrogen ions?
What consequence does aging have on the function of the kidneys?
What consequence does aging have on the function of the kidneys?
Which component of urine is specifically influenced by dietary habits?
Which component of urine is specifically influenced by dietary habits?
What marks the threshold level in active transport during tubular reabsorption?
What marks the threshold level in active transport during tubular reabsorption?
What is the primary function of the renal corpuscle within the nephron?
What is the primary function of the renal corpuscle within the nephron?
Which structures connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
Which structures connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder?
What role do the renal pyramids play in the kidneys?
What role do the renal pyramids play in the kidneys?
What maintains the high pressure in the glomerulus for filtration?
What maintains the high pressure in the glomerulus for filtration?
Which layer of the kidney contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules?
Which layer of the kidney contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules?
What structure facilitates the exit of urine from the kidneys?
What structure facilitates the exit of urine from the kidneys?
Which ion is primarily conserved or excreted to maintain acid-base balance in the body?
Which ion is primarily conserved or excreted to maintain acid-base balance in the body?
Which component carries oxygenated blood to the kidneys?
Which component carries oxygenated blood to the kidneys?
What is the primary function of glomerular filtration?
What is the primary function of glomerular filtration?
Which process primarily occurs in the proximal convoluted tubules?
Which process primarily occurs in the proximal convoluted tubules?
What is the average range of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) per minute?
What is the average range of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) per minute?
Which substance is NOT typically reabsorbed during tubular reabsorption?
Which substance is NOT typically reabsorbed during tubular reabsorption?
What happens to urine volume with increased fluid intake?
What happens to urine volume with increased fluid intake?
Which hormone decreases sodium reabsorption and increases urination?
Which hormone decreases sodium reabsorption and increases urination?
What describes the role of the peritubular capillaries in kidney function?
What describes the role of the peritubular capillaries in kidney function?
What effect does aging have on kidney function?
What effect does aging have on kidney function?
How does aldosterone influence kidney function?
How does aldosterone influence kidney function?
What is the process called that involves the removal of waste products from the blood into urine?
What is the process called that involves the removal of waste products from the blood into urine?
Which structure prevents blood cells from passing into Bowman's capsule?
Which structure prevents blood cells from passing into Bowman's capsule?
Which characteristic is NOT normal for urine composition?
Which characteristic is NOT normal for urine composition?
What role does the detrusor muscle play in the bladder?
What role does the detrusor muscle play in the bladder?
What is the main function of the renin-angiotensin system?
What is the main function of the renin-angiotensin system?
Which is a common outcome when renin is released by the kidneys?
Which is a common outcome when renin is released by the kidneys?
What happens to the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) if blood flow decreases significantly?
What happens to the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) if blood flow decreases significantly?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the renal tubules?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the renal tubules?
What is the role of aldosterone in renal function?
What is the role of aldosterone in renal function?
During tubular secretion, which of the following substances is commonly eliminated from the body?
During tubular secretion, which of the following substances is commonly eliminated from the body?
What effect does a decrease in renal blood flow have on urine concentration?
What effect does a decrease in renal blood flow have on urine concentration?
Which component of urine formation primarily involves moving substances from the renal tubules to the blood?
Which component of urine formation primarily involves moving substances from the renal tubules to the blood?
What initiates the renin-angiotensin system when blood pressure drops?
What initiates the renin-angiotensin system when blood pressure drops?
Which of the following contributes to the concentration of urine by promoting water reabsorption?
Which of the following contributes to the concentration of urine by promoting water reabsorption?
What is the typical composition of normal urine concerning water content?
What is the typical composition of normal urine concerning water content?
What is the outcome of aging on kidney function?
What is the outcome of aging on kidney function?
What is the primary function of the nephrons within the kidneys?
What is the primary function of the nephrons within the kidneys?
Which structure is responsible for collecting urine before it enters the ureter?
Which structure is responsible for collecting urine before it enters the ureter?
Which component of the renal corpuscle plays a crucial role in the filtration of blood?
Which component of the renal corpuscle plays a crucial role in the filtration of blood?
What characteristic of the renal pyramids aids in the kidneys' urine production?
What characteristic of the renal pyramids aids in the kidneys' urine production?
What role does the renal fascia serve for the kidneys?
What role does the renal fascia serve for the kidneys?
Which of the following processes primarily occurs in the renal cortex?
Which of the following processes primarily occurs in the renal cortex?
What maintains the high pressure in the glomerulus necessary for filtration?
What maintains the high pressure in the glomerulus necessary for filtration?
Which layer of the kidney is involved in urine collection after it leaves the renal pyramids?
Which layer of the kidney is involved in urine collection after it leaves the renal pyramids?
Which of the following correctly describes a function of the nephron?
Which of the following correctly describes a function of the nephron?
What separates the renal cortex from the renal medulla?
What separates the renal cortex from the renal medulla?
Flashcards
Nephron location
Nephron location
The nephron is the functional unit within the kidney.
Kidney function
Kidney function
Kidneys remove waste, regulate blood volume, electrolytes, and pH, and filter blood to maintain homeostasis.
Urinary system components
Urinary system components
The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, and the urethra.
Renal corpuscle job
Renal corpuscle job
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal corpuscle structure
Renal corpuscle structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney location
Kidney location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal blood flow
Renal blood flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney support structure
Kidney support structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin D activation
Vitamin D activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter function
Ureter function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder function
Bladder function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex urination
Reflex urination
Signup and view all the flashcards
External urethral sphincter
External urethral sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arteriole Size
Efferent Arteriole Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubules
Renal Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting Tubule
Collecting Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation Steps
Urine Formation Steps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Filtration Amounts
Kidney Filtration Amounts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Urine Output
Normal Urine Output
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Corpuscle Component
Renal Corpuscle Component
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arteriole Size
Efferent Arteriole Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Location
Kidney Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Blood Flow
Renal Blood Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubules Components
Renal Tubules Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubules
Renal Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation Steps
Urine Formation Steps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Filtration Amounts
Kidney Filtration Amounts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Urine Output
Normal Urine Output
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting Tubule
Collecting Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arteriole
Efferent Arteriole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubules
Renal Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Corpuscle
Renal Corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubules
Renal Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting Tubule
Collecting Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Corpuscle
Renal Corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Arteriole Size
Efferent Arteriole Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation
Urine Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main function of the kidneys?
What is the main function of the kidneys?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two main tissue layers of the kidney?
What are the two main tissue layers of the kidney?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the nephron?
What is the nephron?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the renal corpuscle?
What is the renal corpuscle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the glomerulus?
What is the glomerulus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Bowman's capsule?
What is the function of Bowman's capsule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is pressure maintained in the glomerulus for filtration?
How is pressure maintained in the glomerulus for filtration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the renal tubules?
What is the role of the renal tubules?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main steps in urine formation?
What are the main steps in urine formation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldosterone
Aldosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
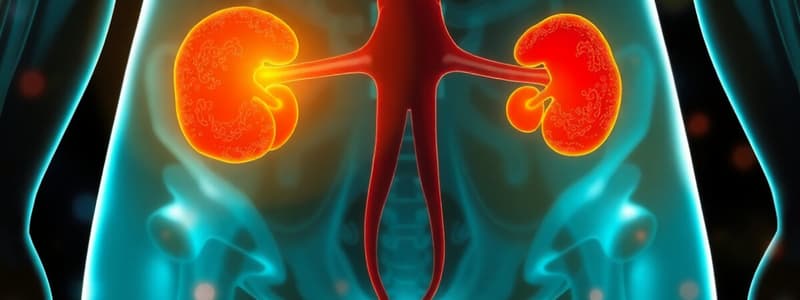
Urinary System
- The urinary system, a vital system for the body, is comprised of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra.
- The primary function of the kidneys is to produce urine, while the other parts of the system act as conduits for urination.
- Kidneys perform various functions, including:
- Waste product elimination (e.g., urea, creatinine, ammonia)
- Blood volume regulation (through water retention/excretion)
- Electrolyte balance (by adjusting sodium, potassium levels)
- Acid-base balance via excretion or conservation of ions like H+ (acid) and HCO3 (bicarbonate, alkaline)
- Regulation of tissue fluid (fluid surrounding cells)
- The kidneys are located in the upper abdominal cavity on either side of the vertebral column behind the peritoneum.
- The upper part of each kidney sits near the rib cage, with a layer of adipose tissue (fat) acting as a cushion.
- Renal fascia, a strong fibrous connective tissue, holds the kidneys in place.
- Each kidney has an indentation called a hilus, where the renal artery enters and the renal vein and ureter exit.
- The renal artery branches off the aorta, carrying oxygenated blood to the kidney.
- The renal vein carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidney and empties into the inferior vena cava.
- The ureter connects the kidney to the bladder.
- Each kidney has two tissue layers:
- The renal cortex (outer layer): Contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules.
- The renal medulla (inner layer): Composed of loops of Henle and collecting tubules.
- The renal medulla also contains wedge-shaped structures called renal pyramids.
- The apex of each pyramid is the renal pelvis, an expansion of the ureter within the kidney.
- Calyces are funnel-shaped extensions of the renal pelvis.
- Urine flows from the renal pyramids into the calyx and then to the renal pelvis before exiting through the ureter.
Nephrons
- The nephron, the functional and structural unit of the kidney, plays a critical role in urine formation.
- Each kidney contains approximately a million nephrons.
- Nephrons are closely associated with blood vessels.
- The nephron consists of:
- The renal corpuscle
- The renal tubules
Renal Corpuscle
- Contains a glomerulus, a network of capillaries, surrounded by Bowman's capsule.
- The glomerulus receives blood from an afferent arteriole and empties into an efferent arteriole.
- The efferent arteriole is smaller than the afferent arteriole, maintaining high pressure in the glomerulus for filtration.
- Bowman's capsule is the expanded end of a renal tubule that encloses the glomerulus.
Renal Tubules
- These tubules continue after Bowman's capsule:
- Proximal convoluted tubules (closer to the renal corpuscle)
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubules (further from the renal corpuscle)
- Distal convoluted tubules from several nephrons empty into a collecting tubule.
- Several collecting tubules merge to form a papillary duct that empties into the calyx (the gutter-like structure in the renal pelvis).
Blood Vessels in the Kidney
- Blood flows from the abdominal aorta through the renal artery, then to the afferent arterioles, and finally to the glomerulus, where filtration occurs.
- Blood then flows through the efferent arterioles, peritubular capillaries, the veins of the kidney, and finally the renal vein.
- Two sets of capillaries in the kidney are crucial for filtration and reabsorption:
- Glomerulus: This is the first set involved in filtration.
- Peritubular capillaries: These are the second set involved in reabsorption of nutrients and substances.
Urine Formation
- Urine formation involves three main processes:
- Glomerular filtration:
- The high pressure in the glomerulus forces plasma, dissolved substances, and small proteins out of the capillaries and into Bowman's capsule, forming renal filtrate.
- Only blood cells and large proteins cannot pass through the filtration barrier.
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): The amount of filtrate produced by both kidneys per minute.
- Average GFR: 100-125 ml per minute.
- GFR is directly proportional to blood flow, meaning more fluid intake leads to a higher GFR and vice versa.
- Tubular reabsorption:
- Essential substances (e.g., glucose, water, amino acids, electrolytes) are reabsorbed from the renal tubules into the peritubular capillaries, which return the substances to circulation.
- Tubular secretion:
- Waste products and excess substances are secreted from the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules for elimination in urine.
- Glomerular filtration:
Kidney Function
- Kidneys filter blood and produce urine
- In a 24-hour period, kidneys filter 150 to 180 liters of blood, but only 1 to 2 liters is excreted as urine.
- Reabsorption is the process of returning useful substances back into the blood from the filtrate in the nephron.
- Occurs in the proximal convoluted tubules, distal convoluted tubules, and collecting tubules.
- Reabsorption involves active transport and passive transport processes.
- Active transport requires energy (ATP) and is used to reabsorb glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and positive ions (e.g., sodium). This has a threshold level, meaning if there is excess of a substance, it may not be fully reabsorbed.
- Passive transport involves movement along concentration gradients and includes:
- Osmosis: The reabsorption of water (see Chapter 2 for more details)
- Pinocytosis: The reabsorption of small proteins that are too large for active transport.
- Tubular secretion is the process of removing waste products and excess substances from the blood and excreting them into the urine.
- Occurs in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting tubules.
- Examples of secreted substances:
- Hydrogen: Helps regulate blood pH levels
- Ammonia: Nitrogenous waste product
- Creatinine: Waste product from muscle metabolism
- Medications: Excess medications may be excreted by the kidneys.
Hormones that influence kidney function
- Aldosterone: Promotes sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion, increasing blood volume and pressure.
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP): Decreases sodium reabsorption, increasing urination and lowering blood volume and pressure.
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): Increases water reabsorption, concentrating urine and retaining water in the body.
Urine formation
- Glomerular filtration: The first step of urine formation.
- Occurs in the glomerulus of the nephron.
- Blood is filtered through the glomerular capillaries, pushing water, glucose, amino acids, small proteins, minerals, and waste products into Bowman's capsule.
- Large proteins and blood cells remain in the capillaries.
- Tubular reabsorption: The selective reabsorption of useful substances from the filtrate back into the blood.
- Tubular secretion: The removal of waste products and excess substances from the blood and secretion into the urine.
Urine Characteristics
- Normal urinary output: 1 to 2 liters per 24 hours.
- Color: Yellow (Dark yellow: concentrated, light yellow: dilute).
- Specific gravity: 1.010 to 1.025 (Measure of dissolved materials in the urine).
- pH: 4.6 to 8.0 (Influenced by diet, blood pH).
- Composition: 95% water, nitrogenous wastes (urea, creatinine, uric acid).
Aging and Urinary System
- With age, nephrons are lost, decreasing the ability to concentrate urine.
- Glomerular filtration rate decreases due to arteriosclerosis (hardening of arteries).
- Bladder decreases in size, tone decreases, leading to frequent urination.
- Urinary incontinence is not a normal consequence of aging.
Other Kidney Functions
- Renin-angiotensin system: Regulates blood pressure
- When blood pressure drops, cells in the afferent arterioles release renin.
- Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which is then converted to angiotensin II.
- Angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) and the release of aldosterone.
- This increases blood pressure by raising blood volume and decreasing blood loss.
- Erythropoietin production: Released by the kidneys when blood oxygen levels decrease.
- Stimulates red bone marrow to produce more red blood cells.
- Increases oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
- Vitamin D activation: The kidneys convert inactive vitamin D to its active form.
- Active vitamin D increases calcium and phosphorus absorption in the small intestine.
Urinary Tract
- Ureters: Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Smooth muscle contracts in peristaltic waves to propel urine.
- Bladder: Muscular sac that stores urine.
- Contains detrusor muscle (smooth muscle that contracts to empty the bladder).
- Urethra: Carries urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body.
- Contains internal and external urethral sphincters.
- Internal sphincter: Not under voluntary control.
- External sphincter: Under voluntary control.
Micturition (Urination)
- Reflex urination: The involuntary process of urination.
- When the bladder fills with urine, stretch receptors send signals to the spinal cord.
- The spinal cord triggers relaxation of the internal sphincter and contraction of the detrusor muscle, expelling urine.
- Voluntary control: Can be exerted through the external urethral sphincter.
- The bladder can hold approximately 800 milliliters of urine.
- The urge to urinate is often felt when the bladder is about 200-400 milliliters full.
- When the bladder is full enough, urine flow cannot be prevented.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.