Podcast
Questions and Answers
भूकंप किसके द्वारा प्राकृतिक आपदाएँ उत्पन्न कर सकते हैं?
भूकंप किसके द्वारा प्राकृतिक आपदाएँ उत्पन्न कर सकते हैं?
- अंधवास्तु
- बिजली गिरना
- तूफान
- मानव सतह पर ऊर्जा का छोड़ना (correct)
मौसम का क्या मतलब है?
मौसम का क्या मतलब है?
- हवाई माहौल (correct)
- मौसम की मान्यता
- वर्षा की मात्रा
- क्षेत्र में दिन की सुबह
मृदा में क्या परिणामकारी हो सकते हैं?
मृदा में क्या परिणामकारी हो सकते हैं?
- पेड़-पौधों की मौत
- समुंद्री तट
- पेड़-पौधों की वृद्धि (correct)
- स्थल परिपन्थी
तापमान के प्रकार क्या होते हैं?
तापमान के प्रकार क्या होते हैं?
प्राकृतिक आपदाएं किसके कारण हो सकती है?
प्राकृतिक आपदाएं किसके कारण हो सकती है?
'जल-संहार' में किस प्रकार से प्रकोप हुआ?
'जल-संहार' में किस प्रकार से प्रकोप हुआ?
भूगर्भिक बल क्या है जो पृथ्वी की सतह को आकर्षित करने में मदद करता है?
भूगर्भिक बल क्या है जो पृथ्वी की सतह को आकर्षित करने में मदद करता है?
किस प्रकार के प्राकृतिक तत्वों द्वारा धरती की सतह की अलग-अलग रुपरेखाएँ बनती हैं?
किस प्रकार के प्राकृतिक तत्वों द्वारा धरती की सतह की अलग-अलग रुपरेखाएँ बनती हैं?
किस समुद्र में सागर प्रवाहों की महत्वपूर्ण गति होती है?
किस समुद्र में सागर प्रवाहों की महत्वपूर्ण गति होती है?
किन प्राकृतिक प्रक्रियाओं द्वारा पुन:सृजित भूमि के संरचन हो सकते हैं?
किन प्राकृतिक प्रक्रियाओं द्वारा पुन:सृजित भूमि के संरचन हो सकते हैं?
किन क्रियाओं द्वारा प्रकृति पर प्रकोप से निरंतर प्रभावित होती है?
किन क्रियाओं द्वारा प्रकृति पर प्रकोप से निरंतर प्रभावित होती है?
किस प्रकार के हवाई क्रियाओं प्रमुख भू-प्रक्रिया हो सकते हैं?
किस प्रकार के हवाई क्रियाओं प्रमुख भू-प्रक्रिया हो सकते हैं?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Physical Geography
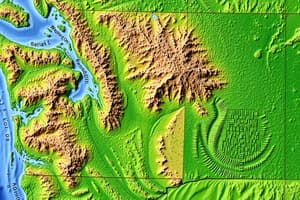
Physical geography focuses on understanding the Earth's landforms, bodies of water, climate, soil conditions, plant life, and animal species—all aspects related to the planet's natural environment. It involves studying various physical phenomena like weather patterns, plate tectonics, erosion, volcanic activity, and ocean currents. By examining these elements and their interactions, physical geographers gain insights into the Earth's past, present, and potential future states.
Land Formation
Land formation refers to the process by which land features are created through geological forces such as plate tectonics, erosion, and sedimentation. These forces shape the Earth's surface, forming mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and other landmarks.
Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is a significant factor in shaping the Earth's surface. When magma rises to the surface, it creates new land forms and can alter existing ones. For instance, the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in Italy formed the famous Pompeii ruins.
Erosion
Erosion, caused by wind, rain, glaciers, or other agents, breaks down rocks and other materials over time, changing the shapes of landforms and creating new ones. Examples include the Grand Canyon, carved by the Colorado River, or sand dunes shaped by wind.
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is the study of the large pieces of the Earth's crust called plates. Their movement and interaction cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as mountain ranges and other significant geological features.
Climate
Climate refers to the average atmospheric conditions in a region over a long period, typically 30 years. These conditions include temperature, precipitation (rainfall, snowfall, etc.), humidity, cloudiness, and other factors that influence weather and climate.
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of the degree of hotness or coldness of a place. It can be seasonal, daily, or even hourly and is influenced by factors such as altitude, proximity to bodies of water, and latitude.
Rainfall
Rainfall is the amount of precipitation that falls in a given area over a specified period. It varies greatly around the world, influencing the growth of plants, the availability of water, and the occurrence of natural disasters like floods and droughts.
Soil
Soil is the upper layer of the Earth's crust that is suitable for plant growth. It is made up of organic matter, water, and minerals, and its properties determine its ability to support plant life and retain water.
Earthquakes
An earthquake is a sudden movement of the Earth's surface caused by a release of energy in the Earth's crust. Earthquakes can cause damage to buildings and infrastructure, as well as triggering other natural disasters like tsunamis and landslides.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters are events that cause widespread damage and destruction, often resulting from extreme weather or geological events. Examples include hurricanes, tornadoes, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes.
In summary, physical geography encompasses the study of Earth's natural environment, including its features, processes, and phenomena. By understanding these elements, we can gain insights into the Earth's past and present conditions, as well as predict future changes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.