Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
- 12
- 7 (correct)
- 5
- 4
Which part of a typical vertebra is the weight-bearing portion?
Which part of a typical vertebra is the weight-bearing portion?
- Body (correct)
- Laminae
- Vertebral Arch
- Spinous process
What is the collective name for the 5 fused vertebrae in the lower part of the spine?
What is the collective name for the 5 fused vertebrae in the lower part of the spine?
- Thoracic
- Coccyx
- Sacrum (correct)
- Lumbar
Which vertebrae type has a body that is small but wider from side to side?
Which vertebrae type has a body that is small but wider from side to side?
Which structure contains the spinal cord?
Which structure contains the spinal cord?
What forms the intervertebral foramina?
What forms the intervertebral foramina?
Which type of vertebrae has a heart-shaped body?
Which type of vertebrae has a heart-shaped body?
How is the vertebral foramen of lumbar vertebrae described?
How is the vertebral foramen of lumbar vertebrae described?
Which vertebrae type has a short and bifid spinous process for C2-C6?
Which vertebrae type has a short and bifid spinous process for C2-C6?
Which vertebrae have transverse processes that extend posterolaterally?
Which vertebrae have transverse processes that extend posterolaterally?
In lumbar vertebrae, how are the superior facets of articular processes directed?
In lumbar vertebrae, how are the superior facets of articular processes directed?
Which type of vertebrae has a mammillary process on the posterior surface of each superior articular process?
Which type of vertebrae has a mammillary process on the posterior surface of each superior articular process?
Which vertebrae have a bifid spinous process?
Which vertebrae have a bifid spinous process?
Which vertebrae are known for their heart-shaped bodies?
Which vertebrae are known for their heart-shaped bodies?
What is a unique feature of the vertebral foramen in lumbar vertebrae?
What is a unique feature of the vertebral foramen in lumbar vertebrae?
Which vertebra is referred to as the 'vertebra prominens'?
Which vertebra is referred to as the 'vertebra prominens'?
Where do the transverse processes of T1-T10 have an articulation facet?
Where do the transverse processes of T1-T10 have an articulation facet?
Which vertebrae have superior facets directed posteromedially?
Which vertebrae have superior facets directed posteromedially?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
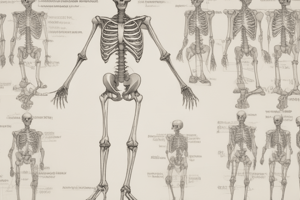
Regional Vertebrae
- The human spine consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 5 fused sacrum vertebrae, and 4 fused coccyx vertebrae.
Typical Vertebrae
- A typical vertebra has a body, which is the anterior, weight-bearing portion.
- The vertebral arch is located posterior to the body and contains the vertebral foramen, which houses the spinal cord.
- Pedicles are short, thick supports for the vertebral arch.
- Laminae are the plates extending posteriorly from the pedicles.
- Transverse processes are lateral projections for muscle attachment.
- The spinous process is a single posterior projection for muscle attachment.
- Superior articular facets are two superior surfaces on the vertebral arch.
- Inferior articular facets are two inferior surfaces on the vertebral arch.
- Intervertebral foramina are openings formed by the superior and inferior vertebral notches.
Cervical Vertebrae
- Cervical vertebrae have a small body, but are wider from side to side.
- The superior surface of the body is concave, with a more anterior-posterior orientation.
Thoracic Vertebrae
- No specific details mentioned about thoracic vertebrae.
Cervical Vertebrae
- Articular process: superior facets directed superoposteriorly, inferior facets directed inferoanteriorly, with some being horizontal.
- Spinous process: short (C3-C6), bifid (C2-C6), with C7 being longer and known as the "vertebrae prominens".
Thoracic Vertebrae
- Body: heart-shaped, with one or two costal facets that articulate with the head of a rib.
- Vertebral foramen: circular and smaller than those in cervical and lumbar vertebrae.
- Transverse processes: long, strong, and extend posterolaterally, with length diminishing from T1-T7 and T1-T10 having articulation with the rib.
- Articular processes: superior facets directed posteriorly and slightly laterally, inferior facets directed anteriorly and slightly medially.
- Spinous processes: long, sloping posteroinferiorly, with tips extending to the level of the vertebral body below.
Lumbar Vertebrae
- Body: kidney-shaped when viewed superiorly.
- Vertebral foramen: triangular, larger than in thoracic vertebrae and smaller than in cervical vertebrae.
- Transverse processes: superior facets directed posteromedially, inferior facets directed anterodorsally, with a mammillary process on the posterior surface of each superior articular process.
- Spinous process: short, sturdy, thick, broad, and hatchet-shaped.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.