Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the direction of blood flow in the cardiovascular system?
What is the direction of blood flow in the cardiovascular system?
- In a circular motion, with no pressure gradient
- Randomly, with no direction
- From high pressure to low pressure (correct)
- From low pressure to high pressure
What is the primary reason for the higher pressure in arteries compared to veins?
What is the primary reason for the higher pressure in arteries compared to veins?
- Arteries have a thicker wall than veins
- Arteries are closer to the heart than veins (correct)
- Arteries have a lower elasticity than veins
- Arteries have a smaller diameter than veins
What is the term for the high pressure in arteries when the heart's ventricles contract?
What is the term for the high pressure in arteries when the heart's ventricles contract?
- Mean arterial pressure
- Blood pressure gradient
- Diastolic pressure
- Systolic pressure (correct)
What is the characteristic of arteries that allows them to snap back into place after stretching?
What is the characteristic of arteries that allows them to snap back into place after stretching?
What is the term for the average pressure in the arteries throughout the cardiac cycle?
What is the term for the average pressure in the arteries throughout the cardiac cycle?
What is the purpose of the heart's contraction in the cardiovascular system?
What is the purpose of the heart's contraction in the cardiovascular system?
What is the characteristic of arteries that allows them to withstand high pressure?
What is the characteristic of arteries that allows them to withstand high pressure?
What is the direction of pressure change as blood flows through the arterioles, capillaries, and veins?
What is the direction of pressure change as blood flows through the arterioles, capillaries, and veins?
What is the medical relevance of the higher pressure in arteries compared to veins?
What is the medical relevance of the higher pressure in arteries compared to veins?
What is the primary function of capillaries?
What is the primary function of capillaries?
What is the main difference between arteries and veins?
What is the main difference between arteries and veins?
What is the function of arterioles?
What is the function of arterioles?
What is the purpose of the sympathetic division in arterioles?
What is the purpose of the sympathetic division in arterioles?
What percentage of blood volume is stored in veins at any given point?
What percentage of blood volume is stored in veins at any given point?
What is a key feature of capillary walls?
What is a key feature of capillary walls?
What is the purpose of valves in veins?
What is the purpose of valves in veins?
What is the effect of the small diameter of capillaries on blood flow?
What is the effect of the small diameter of capillaries on blood flow?
What is a key feature of arteries?
What is a key feature of arteries?
What is the relationship between the structural and functional features of blood vessels?
What is the relationship between the structural and functional features of blood vessels?
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their characteristics:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their characteristics:
Match the following terms related to blood pressure with their definitions:
Match the following terms related to blood pressure with their definitions:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their functions:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their functions:
Match the following characteristics of arteries with their benefits:
Match the following characteristics of arteries with their benefits:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their locations:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their locations:
Match the following pressure changes with their locations in the cardiovascular system:
Match the following pressure changes with their locations in the cardiovascular system:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects on blood flow:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects on blood flow:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following blood vessels with their characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their functions:
Match the following blood vessels with their functions:
Match the following blood vessels with their wall composition:
Match the following blood vessels with their wall composition:
Match the following blood vessels with their diameter characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their diameter characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their pressure characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their pressure characteristics:
Match the following blood vessels with their primary location:
Match the following blood vessels with their primary location:
Match the following blood vessels with their unique features:
Match the following blood vessels with their unique features:
Match the following blood vessels with their roles in blood flow:
Match the following blood vessels with their roles in blood flow:
Match the following blood vessels with their branching patterns:
Match the following blood vessels with their branching patterns:
What are the two upper chambers of the heart that contract to push blood down into the ventricles?
What are the two upper chambers of the heart that contract to push blood down into the ventricles?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves in the heart?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves in the heart?
What is the term for the hole in the heart that normally closes after birth?
What is the term for the hole in the heart that normally closes after birth?
What is the purpose of the semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the purpose of the semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the result of defective heart valves, infections, or septal defects?
What is the result of defective heart valves, infections, or septal defects?
What is the characteristic of the ventricles that allows them to pump blood out of the heart?
What is the characteristic of the ventricles that allows them to pump blood out of the heart?
What is the relationship between the valves and the 'lub-dup' sound in the heart?
What is the relationship between the valves and the 'lub-dup' sound in the heart?
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves in the heart?
Match the following heart chambers with their descriptions:
Match the following heart chambers with their descriptions:
Match the following heart valves with their locations:
Match the following heart valves with their locations:
Match the following heart sounds with their causes:
Match the following heart sounds with their causes:
Match the following fetal heart structures with their effects after birth:
Match the following fetal heart structures with their effects after birth:
Match the following heart valve functions with their effects:
Match the following heart valve functions with their effects:
Match the following heart structures with their characteristics:
Match the following heart structures with their characteristics:
What is the primary function of myoglobin in heart muscle tissue?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in heart muscle tissue?
What is the result of blockage of the coronary arteries?
What is the result of blockage of the coronary arteries?
What can an ECG reveal in a heart attack patient?
What can an ECG reveal in a heart attack patient?
What is the purpose of oxygen supplementation in heart attack treatment?
What is the purpose of oxygen supplementation in heart attack treatment?
What is the function of creatine kinase and troponin in diagnosing heart attack?
What is the function of creatine kinase and troponin in diagnosing heart attack?
What is the primary reason for administering aspirin in heart attack treatment?
What is the primary reason for administering aspirin in heart attack treatment?
What is a long-term treatment for heart attack patients?
What is a long-term treatment for heart attack patients?
What is the primary effect of a blocked coronary artery?
What is the primary effect of a blocked coronary artery?
What is the consequence of necrosis of heart tissue?
What is the consequence of necrosis of heart tissue?
What is the purpose of nitroglycerin in heart attack treatment?
What is the purpose of nitroglycerin in heart attack treatment?
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following consequences of a heart attack with their effects:
Match the following consequences of a heart attack with their effects:
Match the following heart attack treatments with their effects:
Match the following heart attack treatments with their effects:
Match the following cardiac components with their characteristics:
Match the following cardiac components with their characteristics:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following heart attack symptoms with their effects:
Match the following heart attack symptoms with their effects:
Match the following cardiac components with their effects:
Match the following cardiac components with their effects:
Match the following heart attack treatments with their effects:
Match the following heart attack treatments with their effects:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their effects:
Which type of cardiac muscle cells can depolarize spontaneously and produce pacemaker potentials?
Which type of cardiac muscle cells can depolarize spontaneously and produce pacemaker potentials?
What is the function of intercalated discs and gap junctions in cardiac muscle cells?
What is the function of intercalated discs and gap junctions in cardiac muscle cells?
What is unique about the contraction of cardiac muscle cells compared to skeletal muscle cells?
What is unique about the contraction of cardiac muscle cells compared to skeletal muscle cells?
Where does the electrical conduction system of the heart start?
Where does the electrical conduction system of the heart start?
What is the function of the atrioventricular node in the electrical conduction system?
What is the function of the atrioventricular node in the electrical conduction system?
What is the role of autorhythmicity cells in the heart?
What is the role of autorhythmicity cells in the heart?
What is the characteristic of cardiac muscle cells that allows for coordinated contraction?
What is the characteristic of cardiac muscle cells that allows for coordinated contraction?
What is the purpose of the long refractory period in cardiac muscle cells?
What is the purpose of the long refractory period in cardiac muscle cells?
What is the role of the sinoatrial node in the electrical conduction system?
What is the role of the sinoatrial node in the electrical conduction system?
What is the difference between cardiac muscle contraction and skeletal muscle contraction?
What is the difference between cardiac muscle contraction and skeletal muscle contraction?
What is the primary function of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)?
What is the primary function of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)?
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
What is a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute classified as?
What is a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute classified as?
What is characterized by a lack of coordination in the conduction system, resulting in irregular heart rhythms?
What is characterized by a lack of coordination in the conduction system, resulting in irregular heart rhythms?
What is the treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
What is the treatment for ventricular fibrillation?
What is characterized by a complete lack of electrical activity in the heart?
What is characterized by a complete lack of electrical activity in the heart?
What is the result of damage to the AV node?
What is the result of damage to the AV node?
What is the treatment for AV node block?
What is the treatment for AV node block?
What is the consequence of atrial fibrillation?
What is the consequence of atrial fibrillation?
What is the characteristic of ventricular fibrillation?
What is the characteristic of ventricular fibrillation?
Match the following ECG waves with their corresponding heart activity:
Match the following ECG waves with their corresponding heart activity:
Match the following arrhythmias with their characteristics:
Match the following arrhythmias with their characteristics:
Match the following cardiac muscle cells with their characteristics:
Match the following cardiac muscle cells with their characteristics:
Match the following treatments with their corresponding arrhythmias:
Match the following treatments with their corresponding arrhythmias:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle contraction with their descriptions:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle contraction with their descriptions:
Match the following heart rates with their corresponding classifications:
Match the following heart rates with their corresponding classifications:
Match the following heart conditions with their effects on the body:
Match the following heart conditions with their effects on the body:
Match the following components of the electrical conduction system with their locations:
Match the following components of the electrical conduction system with their locations:
Match the following characteristics of normal cardiac muscle cells with their descriptions:
Match the following characteristics of normal cardiac muscle cells with their descriptions:
Match the following components of the electrical conduction system with their functions:
Match the following components of the electrical conduction system with their functions:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following components of the heart with their functions:
Match the following ECG components with their measurements:
Match the following ECG components with their measurements:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle with their descriptions:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle with their descriptions:
Match the following components of the heart with their effects:
Match the following components of the heart with their effects:
Match the following ECG uses with their purposes:
Match the following ECG uses with their purposes:
Match the following heart conditions with their treatments:
Match the following heart conditions with their treatments:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle contraction with their effects:
Match the following characteristics of cardiac muscle contraction with their effects:
Match the following components of the heart with their characteristics:
Match the following components of the heart with their characteristics:
What is the sequence of events in the cardiac cycle if we start with relaxation of the heart?
What is the sequence of events in the cardiac cycle if we start with relaxation of the heart?
What does the term systole refer to in the cardiac cycle?
What does the term systole refer to in the cardiac cycle?
What is the term for the relaxation of the ventricles?
What is the term for the relaxation of the ventricles?
What is the term for the pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are contracting?
What is the term for the pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are contracting?
What is the sequence of events in the cardiac cycle if we start with contraction of the atria?
What is the sequence of events in the cardiac cycle if we start with contraction of the atria?
What is the cardiac cycle?
What is the cardiac cycle?
What does the term diastole refer to in the cardiac cycle?
What does the term diastole refer to in the cardiac cycle?
What is the primary difference between systole and diastole?
What is the primary difference between systole and diastole?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
-
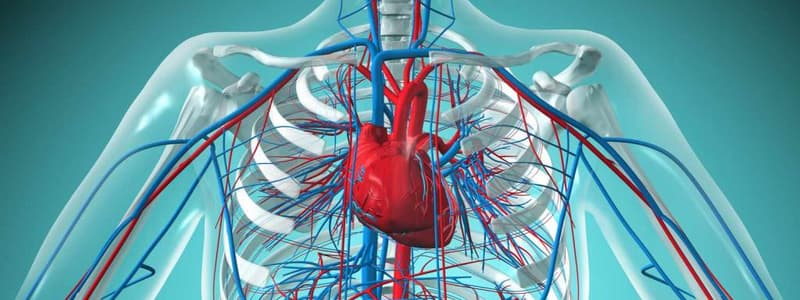
The cardiovascular system consists of a closed system of vessels connecting to the heart, where the heart pumps blood out into arteries, which then branch out into smaller arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and eventually back to the heart.
-
Blood always flows from high pressure to low pressure, following a pressure gradient, similar to chemical and electrochemical gradients in the body.
-
The heart's contraction creates high pressure, forcing blood out into the arteries, which have a higher pressure than veins, and the pressure drops as it flows through the arterioles, capillaries, and finally veins.
-
The arteries have a higher pressure than veins due to their proximity to the heart, and this pressure is medically relevant in diagnosing wounds or injuries.
-
There are two important terms related to blood pressure: systolic pressure, referring to the high pressure in arteries when the heart's ventricles contract, and diastolic pressure, referring to the pressure in arteries when the ventricles relax.
-
Mean arterial pressure is the average pressure in the arteries throughout the cardiac cycle.
-
Arteries have a larger diameter, thick walls, and a smooth muscle layer, allowing them to withstand high pressure and function for rapid transit.
-
Arteries are distensible, meaning they can stretch, and highly elastic, allowing them to snap back into place after stretching.
-
Arteries serve as a pressure reservoir, expanding and then snapping back into place to continue pushing blood through the cardiovascular system during diastole.
-
Veins have a larger diameter, especially those closest to the heart, but thinner walls with less smooth muscle and connective tissue, allowing for low resistance and accommodating low pressure.
-
Veins have valves that prevent backflow and ensure blood returns to the heart, and they are distensible, allowing them to stretch and accommodate a large amount of blood.
-
Veins serve as a blood reservoir, storing about two-thirds of the blood volume at any given point.
-
Arterioles have a smaller diameter, resulting in more resistance to blood flow, and they have smooth muscle within their walls regulated by the sympathetic division.
-
The sympathetic division controls arteriole diameter, causing vasoconstriction or vasodilation, which affects blood distribution throughout the body.- Blood vessels play a crucial role in controlling blood direction in the body.
-
Capillaries are the narrowest type of blood vessel, forming a highly branched network with a large surface area.
-
The small diameter of capillaries creates resistance to slow down blood flow, allowing for efficient exchange of substances.
-
Capillary walls are only one layer thick, composed of simple squamous epithelial tissue, permitting maximum diffusion of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other molecules.
-
The structural features of capillaries, including their small diameter, thin walls, and extensive branching, promote exchange, which is their primary function.
-
The close relationship between structural and functional features of blood vessels is essential for their effectiveness.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.