Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which factor is LEAST likely to influence the volume and direction of travel between tourist generating and destination regions?
Which factor is LEAST likely to influence the volume and direction of travel between tourist generating and destination regions?
- The specific routes taken by tourists when traveling.
- The availability and convenience of transit routes connecting the regions.
- The modes of transportation available for reaching the destination.
- The number of tourists traveling between the regions. (correct)
A country with few direct flights to another country experiences low tourist volume between them. Which strategy would MOST directly address this issue to increase tourism?
A country with few direct flights to another country experiences low tourist volume between them. Which strategy would MOST directly address this issue to increase tourism?
- Lobbying for the establishment of more direct flight routes. (correct)
- Investing in the development of luxury resorts and accommodations.
- Promoting the country's cultural attractions through social media campaigns.
- Offering visa waivers to citizens of the other country.
Which of the following best describes how 'push' and 'pull' factors interact in tourism?
Which of the following best describes how 'push' and 'pull' factors interact in tourism?
- Push factors create a desire to leave a generating region, while pull factors make a destination attractive. (correct)
- Push factors attract tourists to generating regions, while pull factors encourage them to stay longer.
- Push and pull factors both operate independently to influence a tourist's decision to travel.
- Push factors are marketing strategies used by destinations, while pull factors are personal motivations of tourists.
A densely populated city with high levels of pollution is MOST likely to act as which of the following in the context of tourism?
A densely populated city with high levels of pollution is MOST likely to act as which of the following in the context of tourism?
Which of the following scenarios exemplifies the interdependence of tourists and businesses in a tourism system?
Which of the following scenarios exemplifies the interdependence of tourists and businesses in a tourism system?
How does community-based tourism MOST directly contribute to the local economy?
How does community-based tourism MOST directly contribute to the local economy?
A decrease in tourist arrivals due to an economic downturn in generating regions can lead to which of the following impacts on tourism destination regions?
A decrease in tourist arrivals due to an economic downturn in generating regions can lead to which of the following impacts on tourism destination regions?
Which of the following is the MOST significant way that tourists contribute to the positive environmental impact in a destination like Antarctica?
Which of the following is the MOST significant way that tourists contribute to the positive environmental impact in a destination like Antarctica?
What is the MOST direct effect of increased disposable income on the growth of tourism?
What is the MOST direct effect of increased disposable income on the growth of tourism?
How have innovations in communication technologies like the Internet MOST significantly contributed to lowering the costs of travel?
How have innovations in communication technologies like the Internet MOST significantly contributed to lowering the costs of travel?
Which of the following factors has LEAST contributed to increased mobility in travel to tourist destinations?
Which of the following factors has LEAST contributed to increased mobility in travel to tourist destinations?
What is the MOST significant impact of commercial air travel on tourism?
What is the MOST significant impact of commercial air travel on tourism?
Which stage of tourism destination development is characterized by a rapid increase in tourist numbers, construction of man-made attractions, and heavy advertising?
Which stage of tourism destination development is characterized by a rapid increase in tourist numbers, construction of man-made attractions, and heavy advertising?
In the context of tourism destination development, what does the term 'rejuvenation' refer to?
In the context of tourism destination development, what does the term 'rejuvenation' refer to?
Which stage of the tourism destination lifecycle is MOST likely to see locally owned businesses being replaced by multinational corporations?
Which stage of the tourism destination lifecycle is MOST likely to see locally owned businesses being replaced by multinational corporations?
According to the spectrum of personality characteristics, what is a defining trait of 'Dependable' tourists?
According to the spectrum of personality characteristics, what is a defining trait of 'Dependable' tourists?
Which of the following actions would be MOST effective for a tourism board aiming to attract 'Venturer' tourists?
Which of the following actions would be MOST effective for a tourism board aiming to attract 'Venturer' tourists?
How can personality characteristics of tourists MOST directly influence the development of a tourist destination?
How can personality characteristics of tourists MOST directly influence the development of a tourist destination?
If a destination is in the 'exploration' stage, it probably appeals MOST to what kind of tourist?
If a destination is in the 'exploration' stage, it probably appeals MOST to what kind of tourist?
In the context of tourism, what constitutes a 'tourist generating region'?
In the context of tourism, what constitutes a 'tourist generating region'?
What distinguishes international tourism from domestic tourism?
What distinguishes international tourism from domestic tourism?
What is the role of tour agencies in both tourist generating and tourist destination regions?
What is the role of tour agencies in both tourist generating and tourist destination regions?
Complete the following analogy: Push factors are to generating regions as ____ are to destination regions.
Complete the following analogy: Push factors are to generating regions as ____ are to destination regions.
What is the relevance of United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) in the context of global tourism?
What is the relevance of United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) in the context of global tourism?
Refer to the image of the graph 'China-GDP-per-capita-disposable-income-and-number-of-outbound-tourist-growth-trends'. According to the graph, which factor showed the LEAST growth between 2009-2018?
Refer to the image of the graph 'China-GDP-per-capita-disposable-income-and-number-of-outbound-tourist-growth-trends'. According to the graph, which factor showed the LEAST growth between 2009-2018?
Flashcards
Who are tourists?
Who are tourists?
People who travel and stay outside their usual environment for more than 24 hours but not more than 1 consecutive year for travel purpose.
Domestic Tourism
Domestic Tourism
Tourism within a tourist's own country.
International Tourism
International Tourism
Tourism outside of a tourist's own country.
Tourist generating regions
Tourist generating regions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tourist destination regions
Tourist destination regions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transit routes
Transit routes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Push factors
Push factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pull Factors
Pull Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tourists, Businesses and Organizations
Tourists, Businesses and Organizations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motivation to travel
Motivation to travel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ability to Travel
Ability to Travel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lesser-known tourist destinations
Lesser-known tourist destinations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mobility to Travel
Mobility to Travel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dependables vs Venturers
Dependables vs Venturers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stages of tourism development
Stages of tourism development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exploration Stage
Exploration Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Involvement Stage
Involvement Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Development Stage
Development Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Consolidation Stage
Consolidation Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stagnation Stage
Stagnation Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decline stage
Decline stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rejuvenation
Rejuvenation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Tourists travel and stay outside their usual environment for >24 hours, but <1 year, for any purpose.
Types of Tourism
- Domestic tourism involves tourism activities within a tourist's country.
- International tourism involves tourism activities outside a tourist's country.
Tourism System Components
- Tourist generating regions: Areas where tourists originate.
- Tourist destination regions: Areas that attract tourists.
- Transit routes: Pathways connecting tourist generating and destination regions.
- These components are interconnected.
Tourism System Examples
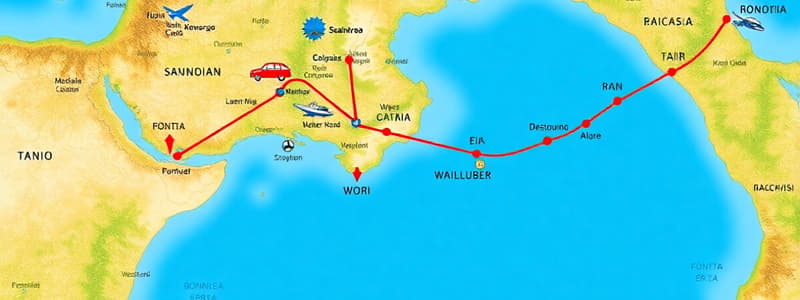
- A Singapore executive flying to Manchester exemplifies how tourist generating regions send people to tourist destination regions via transit routes.
- The 40-year-old executive: The tourist
- Singapore: The tourist generating region
- Manchester, England: The tourist destination region
- Air travel: The transit route
Volume and Direction of Travel
- Transit routes influence travel volume and direction between regions.
- More transit routes provide more options and increase travel.
- Additional options can result in shorter travel times.
- Volume refers to the number of traveling tourists.
- Direction refers to the specific route taken.
- Fewer direct flights between Singapore and Brazil results in fewer tourists.
Tourism Regions
- Tourism generating regions source tourists and host significant tourism production sectors.
- Tourism destination regions attract tourists, experience tourism's consequences, and house primary production elements.
- Transit routes facilitate tourist passage to destinations.
Relationship Between Tourist Regions
- Tourist movement relies on push and pull factors.
- Push factors exist in generating regions.
- Pull factors exist in destination regions.
Interdependence
- Interdependence exists between tourists, businesses, and organizations in both generating and destination regions.
Push and Pull Factors
- Tourist movement depends on generating regions' "push" and destination regions' "pull".
Push Factors at Generating Regions
- Factors that cause tourists to leave:
- Stressful work environment
- Unpleasant living conditions including overcrowding and pollution
- Lack of recreational options
Pull Factors at Destination Regions
- Qualities that attract tourists:
- Scenic beauty
- Special events (concerts, festivals)
- Attractions, facilities, and amenities
Push/Pull Interplay
- An interplay between push and pull factors develops the need and motivation to travel.
- People in fast-paced environments may seek relaxing nature getaways.
Mutual Dependence
- Tourists, businesses, and organizations are interdependent in tourism.
- Tourists need accommodations in destination regions.
- Businesses rely on tourists for revenue, creating mutual dependence.
- Tour agencies assist with bookings and provide guides.
- Tour agencies rely on tourists for revenue and can benefit hotels by directing tourists to them.
Tourist Organizations
- Tourist organizations are critical as they recommend businesses to potential tourists.
- The BHA provides recommendations and accreditations for places to stay.
- Accreditations enable tourists to select accommodations based on their needs, benefiting businesses.
Tourism and the Environment
- Tourism interacts with nature, communities, and economies.
- Businesses that are tourism-related affect nature.
Positive Impacts
- New opportunities for services arise, benefiting local populations.
- Local economies benefit from tourist arrivals due to interactions with nature and communities.
- In Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, tourists interact with natural limestone formations and local communities.
- Community based tourism lets locals participate in the tourism sector.
- Local employment and income increase, growing economies.
- Minimizing the impact on wildlife or pollution of ecosystems is crucial.
- Environmental awareness may arise.
- Scientific and conservation projects may get funding from travelers.
Negative impacts
- Tourist destinations may face degradation of the natural environment.
- A degraded environment results in less tourism.
- Decreased local incomes due to fewer tourists.
- Locals may lose income, and have their livelihoods negatively affected.
- Economic downturns in tourist generating regions, lead to less tourism activity.
- Loss of income and jobs may occur in tourist destination regions as a result.
- Business that directly rely on tourism may be impacted and reduced demand may occur.
Motivation to Travel
- Satisfying needs through travel, driven by a mix of push/pull factors increases the growth of Tourism.
Statistic
- International tourist arrivals grew from 25 million (1950) to 1.5 billion (2019)
Relaxation and Travel
- Hectic lifestyles have increased people the need to seek relaxation through travel.
- Coastal landscapes in Phuket, Thailand, provide tranquility for relaxation.
- Theme parks enable escape from stress and worries.
Self-Fulfillment
- The desire for personal growth has increased travel.
- Culinary Tourism: Balinese cooking classes
- Spiritual Tourism: Mecca pilgrimage for Muslims
- Challenging Activities: Mountain climbing and skydiving
Examples
- Climbing Mount Everest for personal challenge.
New Experiences
- Experiencing unique environments and cultures is a part of traveling.
Examples
- Hiking in remote forests and seeing glacial landscapes
- Sharing travel experiences on social media raises interest in unique destinations.
Global Impact
- Globalization improves accessibility via transport networks.
- Remote areas are impacted by rising rates tourism as a result.
Unique Destinations
- Antarctica offers a sense of adventure and exclusivity away from mainstream tourism.
Eco-Tourism
- Increased environmental awareness motivates travel to destinations emphasizing sustainability.
Growth in Tourism
- Growth in disposable income and increased leisure time facilitate travel, supported by tourism industry innovations.
- Increased disposable income, rather than necessity is a large motivation.
Statistics
- China's outbound travelers reached ~155 million in 2019, triple the 2010 figure.
- This growth is as a result of increased income.
Leisure Time
- Paid leave and more free time facilitates the chance for travel.
- More financial stability results while having time away from work.
Example
- More travel and domestic tourism arose due to Chinese government encouraging half-day Fridays.
Innovation
- Business innovations, lower transport costs, and reduced accommodation costs contribute to growth.
- More fuel-efficient modes and communication advancements also contribute.
- Tour operators are increasingly replaced by websites and applications.
Examples
- Website allowing comparisons of accommodation.
Impact of Air Transportation in Tourism
- Air transport has become increasingly affordable.
- Increased carrying capacity reduces costs.
Statistics
- Airbus A-380 carries 853 passengers while the Boeing 747 initially held 853.
- Communication and Innovations in travel are driving down the cost of flights.
Options
- There are more websites and applications that lower prices and provide convenience.
- Budget airlines offer affordable travel options.
Mobility
- There are more routes for public transport and private vehicle ownership.
- More airports, roads, and railways are being constructed to improve transport.
- Changi Airport created Terminal 4 to allow more flights.
- Expanded bus and train routes facilitate ease of use.
Example
- The Downtown MRT line in Singapore improves accessibility to attractions with multilingual maps.
New Modes of Travel
- Development of faster, further, transit.
Example
- Conventional trains from Tokyo to Osaka took 6 hrs 40 minutes.
- Bullet trains cut the trip to 3 hrs 10 minutes.
- Lower traveling times and convenience has been seen in new aircraft post 1950s.
Examples
- Singapore to London used to take 2-4 days, whereas now this is only 14 hours.
Private Car Ownership
- Private cars improve convenience to locations.
- Increased car ownership to visit spots may gain spiritual enlightenment.
Tourism Development
- Tourism destinations evolve and change over time.
- The key features and tourist arrivals evolve.
- Destinations grow in popularity when investors and tour operators enter newly discovered locations.
- Over time popularity declines if the location isn't looked after.
- Destinations go through different stages, these stages may not occur in a linear fashion.
Tourism Stages Overview
- Destinations progress through six stages relating to tourism development.
Six Stages of Tourism Development
- exploration
- involvement
- development
- consolidation
- stagnation
- decline OR rejuvenation
Exploration Stage
- A small number of individual tourists visit destinations that may not always be active year-round.
- The destination relies on natural attractions without many facilities.
Example
- Jaco Island in Timor Leste.
Tourists
- Are few international travelers due to limited tourism facilities and location.
- Are often attracted to Houses of national parks with coastlines.
Involvement Stage
- There is an increase in advertisements and publicity in tourist arrivals for various seasons.
- The local economy starts to rise.
- There are goods and services provided via the locals for a destination that boasts rise in goods, services and facilities to cater to tourists.
Authority Intervention
- Local Authorities that are usually in charge of the facilities that are requested in an attraction.
Example
- Kuang Si waterfalls improve facilities through investments such as roads and transportation, the rise of travel agencies and the construction of car parks and bathrooms.
Development Stage
- Tourist numbers increase rapidly as the destination gains man-made attractions and foreign labor
- There are a higher amount of tourism jobs and workers than before that benefit the economy.
- Heavy advertising helps drive the economic success and the recognition of tourist destinations.
Example
- Vietnam's Phu Quoc Island
Consolidation Stage
- More tourists than locals often make up the number of the visiting attraction.
- Tourist jobs increase rapidly as numbers of tourists climb to new heights.
Example
- Most of the hotels and facilities are in the hands of multi-nationalists.
- Tourism in Goa and India have a wide display of buildings that feature architecture and Portuguese culture.
Impact
- There is an increased investment in the tourism sector by the Government as well as higher employment opportunity and economic growth which are impacted by growing tourist numbers.
5. Stagnation Stage
- Destinations face limited numbers as tourist arrivals stop based of carrying capacity.
6. Decline Stage
- No revival will result negatively on previous economic growth as facilities and attractions see a lower rate of tourists and a negative impact on the local community.
7. Rejuvenation Stage
- Destinations gain more attractions and facilities as there is new investment to attract new and old tourists that result in re-branding.
Personalities Affecting Tourism
- Individual travel choices are influenced by spectrum of individual personalities, thus travel desitnations are impacted.
- Tourist types: Dependables versus Venturers
Tourist Classifications
- Tourists are classified as pure Venturer or Dependables
- It is found this is only 2-4% of the population.
- There is 62% of people that are in the middle with leanings to one side or the other as greater numbers for that spectrum fit near the near-venturer or near-dependable scale.
- 16% of tourists fall in that range.
- Venturers:
- This type of tourist often likes to spend their money more readily and reach out to find and explore the world.
- Dependables:
- This type of tourist often is more cautious when spending money and want to try and make their daily lives predictable.
Travel
- Venturers:
- Are always planning their own trips and activities for a mass tourism base
- Dependables:
- Tend to prefer structure and routine travel choices.
Choice Factors
- Personality influences preferences, destinations, and activities.
- Mongolia being underdeveloped attracts Venturer-type tourists who can tolerate less accommodations.
- Tourists tend to influence decisions as tourist destination evolve over time. The way a location caters to a tourist base that it wants will develop personality over time.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.