Podcast
Questions and Answers
¿Cuál de los siguientes derechos NO está consagrado en la Constitución española?
¿Cuál de los siguientes derechos NO está consagrado en la Constitución española?
- Derecho a la integridad física y moral
- Derecho a la educación
- Derecho a la propiedad privada (correct)
- Derecho a la vida
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre la organización del Estado español es FALSA?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre la organización del Estado español es FALSA?
- El sistema político español se basa en el pluralismo político
- La soberanía nacional pertenece al pueblo español
- El rey es el jefe de Estado y ostenta el poder ejecutivo (correct)
- España es una monarquía parlamentaria
¿Qué principio fundamental NO se menciona en la Constitución española?
¿Qué principio fundamental NO se menciona en la Constitución española?
- Justicia
- Igualdad
- Supremacía racial (correct)
- Libertad
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre los derechos sociales en la Constitución española es FALSA?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre los derechos sociales en la Constitución española es FALSA?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre la protección del medio ambiente en la Constitución española es VERDADERA?
¿Cuál de las siguientes afirmaciones sobre la protección del medio ambiente en la Constitución española es VERDADERA?
¿Cuál es la función principal de la rama judicial en el sistema político español?
¿Cuál es la función principal de la rama judicial en el sistema político español?
¿Cuál es la principal diferencia entre las comunidades autónomas y otras regiones en España?
¿Cuál es la principal diferencia entre las comunidades autónomas y otras regiones en España?
¿Cuál es el papel del gobierno central en el sistema político español?
¿Cuál es el papel del gobierno central en el sistema político español?
¿Cuál es el proceso para enmendar la Constitución española?
¿Cuál es el proceso para enmendar la Constitución española?
¿Cuál es el objetivo principal de la Constitución española?
¿Cuál es el objetivo principal de la Constitución española?
Study Notes
Title: Understanding the Spanish Constitution: Fundamental Rights, Organization of the State, Distribution of Powers, and Territorial Organization
Fundamental Rights
The Spanish Constitution proclaims itself as a social and democratic state, founded on the principles of freedom, justice, equality, and political pluralism. It establishes a series of fundamental rights designed to protect individuals and promote a fair society. Some key aspects of these rights include:
- Protection of human rights, such as the right to life and physical and moral integrity.
- Abolition of the death penalty.
- Right to education, including access to a quality education and vocational training.
- Right to work and receive adequate wages, with consideration given to unemployment benefits.
- Provisions for social assistance, such as pensions for the elderly, disabled, orphans, and widows.
- Right to health care, with the state responsible for providing medical care to low-income populations.
The constitution stresses the importance of environmental protection, requiring citizens to preserve the environment and prohibiting actions that could cause serious damage to it.
Organization of the State
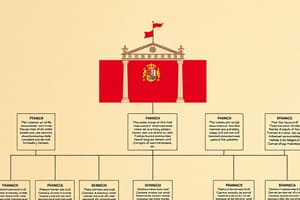
According to the Spanish Constitution, Spain is a parliamentary monarchy where national sovereignty belongs to the Spanish people. The organization of the state includes several branches:
- Legislative branch: The Cortes Generales, consisting of the Congress of Deputies and the Senate, is responsible for legislative functions.
- Executive branch: The government, headed by the President, exercises executive authority and legislative power through administrative regulations.
- Judicial branch: The judiciary, including courts and tribunals, ensures respect for the Constitution and applies laws to resolve conflicts and disputes.
Distribution of Powers
The Spanish Constitution outlines the distribution of powers between central authorities and regional governments, ensuring that power remains balanced and decentralized:
- Central government: Responsible for foreign relations, defense, national security, fiscal policy, monetary policy, and other domestic matters.
- Autonomous communities: Empowered to manage their cultural, educational, and economic affairs within the framework of general state law.
Territorial Organization
The Spanish Constitution recognizes and guarantees the right to autonomy for different nationalities and regions, allowing them to govern themselves within the general framework of the state:
- Autonomous communities: These are territories with a high degree of self-government and representation in the Cortes Generales.
- Other regions: Some areas without autonomy have certain special statuses defined by law and participate in regional councils.
Constitutional Amendments
Procedures for constitutional amendment involve the Cortes Generales proposing changes with a two thirds majority, followed by ratification by the Spanish people through a referendum.
In conclusion, the Spanish Constitution aims to establish a social and democratic state based on the rule of law, protecting human rights, promoting equality, and ensuring territorial organization. It provides a comprehensive legal framework for governing Spain while respecting the autonomy of its diverse regions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the fundamental rights, organization of the state, distribution of powers, and territorial organization as outlined in the Spanish Constitution. Learn about key principles, branches of government, powers of central and regional authorities, and procedures for constitutional amendments.