Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a common initial symptom of rosacea?
What is a common initial symptom of rosacea?
- Permanent redness
- Development of rhinophyma
- Thickening of skin
- Intermittent flushing (correct)
Which treatment is primarily used for papules and pustules in rosacea?
Which treatment is primarily used for papules and pustules in rosacea?
- Topical antibiotics (correct)
- Pulsed dye laser
- Oral steroids
- Surgical removal
What happens to the skin in the later stages of rosacea?
What happens to the skin in the later stages of rosacea?
- It remains unchanged
- It thickens and may develop rhinophyma (correct)
- It becomes less sensitive
- It starts peeling
What role do the prescribed antibiotics play in treating rosacea?
What role do the prescribed antibiotics play in treating rosacea?
What is the most effective treatment for individuals mainly troubled by flushing due to rosacea?
What is the most effective treatment for individuals mainly troubled by flushing due to rosacea?
Which demographic is more commonly affected by rosacea?
Which demographic is more commonly affected by rosacea?
How does the pulsed dye laser treatment work for rosacea?
How does the pulsed dye laser treatment work for rosacea?
Which symptom is common to the second phase of rosacea?
Which symptom is common to the second phase of rosacea?
What is the first step in treating Raynaud’s phenomenon?
What is the first step in treating Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Which phases are classically described in Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Which phases are classically described in Raynaud’s phenomenon?
What is the most common underlying disease associated with secondary Raynaud’s?
What is the most common underlying disease associated with secondary Raynaud’s?
Which of the following treatments is often recommended for Raynaud's phenomenon?
Which of the following treatments is often recommended for Raynaud's phenomenon?
What typical symptoms may accompany Raynaud’s phenomenon?
What typical symptoms may accompany Raynaud’s phenomenon?
In addition to checking for symptoms, what lab test is helpful in the evaluation of a patient with Raynaud’s?
In addition to checking for symptoms, what lab test is helpful in the evaluation of a patient with Raynaud’s?
What is a common demographic feature of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
What is a common demographic feature of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Which of the following describes the potential severity of Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Which of the following describes the potential severity of Raynaud’s phenomenon?
Which desmoglein proteins are primarily affected in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Which desmoglein proteins are primarily affected in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
What is the primary reason for the fragility of blisters in Pemphigus disorders?
What is the primary reason for the fragility of blisters in Pemphigus disorders?
Which medication is considered most effective for treating Pemphigus?
Which medication is considered most effective for treating Pemphigus?
Pemphigus Foliaceous primarily affects which of the following?
Pemphigus Foliaceous primarily affects which of the following?
Which immune response mechanism is involved in Pemphigus disorders?
Which immune response mechanism is involved in Pemphigus disorders?
What is a potential benefit of using azathioprine over prednisone in the treatment of Pemphigus?
What is a potential benefit of using azathioprine over prednisone in the treatment of Pemphigus?
In which demographic is Pemphigus Foliaceous more likely to be found?
In which demographic is Pemphigus Foliaceous more likely to be found?
What causes the erosion observed in severe cases of Pemphigus?
What causes the erosion observed in severe cases of Pemphigus?
What is the primary goal of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis in resistant lupus cases?
What is the primary goal of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis in resistant lupus cases?
Which type of cutaneous lupus is almost exclusively seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus?
Which type of cutaneous lupus is almost exclusively seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus?
How does subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) typically present?
How does subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) typically present?
What percentage of patients with chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE) typically have systemic lupus?
What percentage of patients with chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE) typically have systemic lupus?
What is thought to cause the photo-related nature of cutaneous lupus lesions?
What is thought to cause the photo-related nature of cutaneous lupus lesions?
Which immune responses are involved in lupus as an autoimmune disease?
Which immune responses are involved in lupus as an autoimmune disease?
Which treatment is commonly associated with improvement of cutaneous lupus in patients with systemic lupus?
Which treatment is commonly associated with improvement of cutaneous lupus in patients with systemic lupus?
What is a defining characteristic of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE) lesions?
What is a defining characteristic of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE) lesions?
What is the most common initial approach to treating erythema nodosum (EN)?
What is the most common initial approach to treating erythema nodosum (EN)?
What is the primary treatment for mild cutaneous lupus?
What is the primary treatment for mild cutaneous lupus?
What underlying condition is NOT typically associated with erythema nodosum?
What underlying condition is NOT typically associated with erythema nodosum?
Which of the following is theorized to be a potential cause of erythema nodosum?
Which of the following is theorized to be a potential cause of erythema nodosum?
Which factor is most effective for preventing flares in patients with systemic lupus?
Which factor is most effective for preventing flares in patients with systemic lupus?
What is the typical duration of nodules associated with erythema nodosum?
What is the typical duration of nodules associated with erythema nodosum?
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE) is most common in which demographic?
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE) is most common in which demographic?
Where does PMLE typically present on the body?
Where does PMLE typically present on the body?
Which treatment is considered if initial management of erythema nodosum is ineffective?
Which treatment is considered if initial management of erythema nodosum is ineffective?
What is a common characteristic of the onset of PMLE?
What is a common characteristic of the onset of PMLE?
What is one theory regarding the pathogenesis of PMLE?
What is one theory regarding the pathogenesis of PMLE?
Which treatment has been found to be effective for PMLE?
Which treatment has been found to be effective for PMLE?
What demographic is more likely to experience Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)?
What demographic is more likely to experience Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)?
Flashcards
Rosacea Symptoms
Rosacea Symptoms
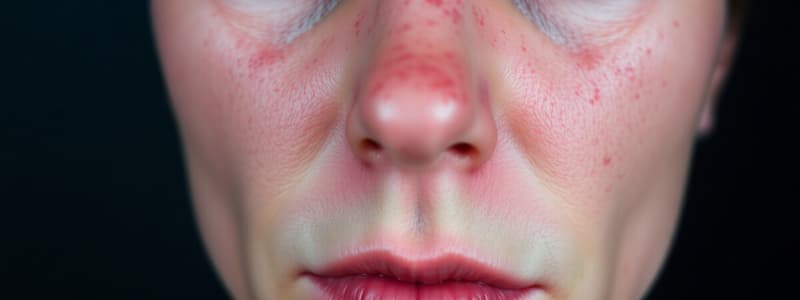
Rosacea presents with intermittent flushing, facial redness, and sometimes facial telangiectasias (small blood vessels on the surface of the skin), papules, and pustules. Severe cases can lead to rhinophyma (enlarged nose).
Rosacea Triggers
Rosacea Triggers
Certain factors can trigger rosacea flares, such as hot drinks, alcohol, caffeine, spicy food, wind, and sunlight.
Rosacea Treatment (mild)
Rosacea Treatment (mild)
Topical antibiotics like metronidazole and clindamycin are commonly used for papules and pustules. Avoiding triggers is a key strategy for managing flushing.
Rosacea Treatment (severe)
Rosacea Treatment (severe)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rosacea Rhinophyma Treatment
Rosacea Rhinophyma Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rosacea Theory
Rosacea Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Livedo Reticularis (LR)
Livedo Reticularis (LR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rosacea Inflammatory Center
Rosacea Inflammatory Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
Raynaud's phases
Raynaud's phases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Raynaud's cause (sympathetic)
Raynaud's cause (sympathetic)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Raynaud's
Primary Raynaud's
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Raynaud's
Secondary Raynaud's
Signup and view all the flashcards
Raynaud's symptoms
Raynaud's symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Raynaud's treatment
Raynaud's treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Raynaud's causes
Secondary Raynaud's causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosis of Raynaud's
Diagnosis of Raynaud's
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV)
Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pemphigus Foliaceous (PF)
Pemphigus Foliaceous (PF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intraepidermal blisters
Intraepidermal blisters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Desmoglein proteins
Desmoglein proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Desmoglein 1
Desmoglein 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Desmoglein 3
Desmoglein 3
Signup and view all the flashcards
Immunosuppressive medications
Immunosuppressive medications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prednisone
Prednisone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutaneous Lupus
Cutaneous Lupus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutaneous Lupus Flare Triggers
Cutaneous Lupus Flare Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutaneous Lupus Treatment (Mild)
Cutaneous Lupus Treatment (Mild)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutaneous Lupus Treatment (Severe)
Cutaneous Lupus Treatment (Severe)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE)
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PMLE Presentation
PMLE Presentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
PMLE Treatment
PMLE Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ACLE)
Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ACLE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE)
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE)
Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of sunlight in cutaneous lupus?
What is the role of sunlight in cutaneous lupus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What types of immune responses are involved in lupus?
What types of immune responses are involved in lupus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does treatment for systemic lupus affect cutaneous lupus?
How does treatment for systemic lupus affect cutaneous lupus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is UVB more damaging than UVA in cutaneous lupus?
Why is UVB more damaging than UVA in cutaneous lupus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Erythema Nodosum (EN)?
What is Erythema Nodosum (EN)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
EN and Systemic Disorders
EN and Systemic Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
EN during Pregnancy
EN during Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
EN and Hypersensitivity
EN and Hypersensitivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial EN Treatment
Initial EN Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Rosacea
- Very common in individuals with light skin, especially those of Irish or Scottish descent
- Often begins with intermittent flushing triggered by hot drinks, alcohol, caffeine, spicy food, wind, or sunlight, leading to facial warmth and redness.
- Redness can become permanent, and facial telangiectasias may develop.
- Next phase includes red papules and pustules, mainly on cheeks, nose, and forehead.
- Third phase involves thickening of the nose (rhinophyma) often after years of other symptoms
- Poorly understood, likely a component of facial cutaneous vasculature hyperresponsiveness.
- One theory suggests excess vasodilation causing skin edema and inflammation
- Primarily treated with topical antibiotics (e.g., metronidazole, clindamycin) to treat papules and pustules, though not general redness or rhinophyma, due to their supposed anti-inflammatory effects rather than microbial killing.
- Oral antibiotics (e.g., doxycycline) for severe cases, also work as anti-inflammatory agents
- Flushing triggers should be avoided
- For erythema and telangiectasias, pulsed dye laser treatment is often most effective due to its focus on hemoglobin and blood vessel destruction.
- Rhinophyma surgically treated for excess tissue.
Livedo Reticularis (LR)
- A bluish/violet, net-like pattern on the skin, usually on the legs.
- Usually no palpable component or symptoms.
- Mostly caused by skin exposure to cold temperature; resolves with warming
- Can be persistent and unrelated to cold exposure, presenting with skin "aching" if unrelated to cold, which warrants a review of systems.
- Represents increased deoxygenated blood in cutaneous venules, visible through skin.
- Any process increasing blood or reducing oxygen in venules can cause it:
- Cold-related: arterial vasoconstriction and slower blood flow causing more deoxygenation.
- Persistent: Increased viscosity (e.g., lupus anticoagulant, cryoglobulinemia) or vasodilation causes (e.g., neurologic or endocrine disorders).
- Usually does not require treatment unless persistent; assess for underlying causes if not resolving.
- Associated with lupus anticoagulant in women.
Raynaud's Phenomenon
- Relatively common in young women.
- Vasospastic disorder affecting the hands.
- Triggers (e.g., cold exposures):
- Skin color change (white, then blue, then red)
- Numbness or tingling
- Swelling and burning/aching.
- Severe cases may cause gangrene or ulcers.
- Possible causes:
- Sympathetic nervous system control of digital vessels issues
- Blood hyperviscosity
- Abnormalities or blockages in digital vessels, or local overproduction of vasoconstrictors/underproduction of vasodilators
- Primary Raynaud's (80-90%) has no underlying medical issues, while secondary Raynaud's is associated with an underlying disease.
- Diagnosis requires a review of systems and general examination. Checking for ANA and ESR in patients with Raynaud's could be useful; abnormalities of capillaries on the proximal nail folds might indicate systemic sclerosis as possible underlying disease
- Treatments:
- Maintain warm extremities
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., nifedipine or diltiazem)
Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) and Pemphigus Foliaceous (PF)
-
Rare, autoimmune blistering diseases usually impacting 30s, 40s, or 50s
-
More common in Jewish or Mediterranean people
-
Often involves oral and cutaneous erosions/blisters (potentially severe, life-threatening)
-
Differentiated based on affected desmoglein:
- PV involves desmoglein 1 and 3, leading to oral and cutaneous involvement
- PF involves only desmoglein 1 and hence primarily cutaneous involvement
-
Treatment includes immunosuppressants (e.g. prednisone) and sometimes intravenous immunoglobulin or plasmapheresis in resistant cases.
Cutaneous Lupus
- Systemic autoimmune disorder, more common in women.
- Presents in three forms:
- Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ACLE): Malar rash (cheeks and nasal bridge), erythema and edema.
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE): Wide spread, erythematous, scaly, photo-distributed rash which avoids the face
- Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE) or discoid lupus: 1-3 cm lesions (atropy, dilated pores), scaling, and pigmentary changes (hypo- or hyper-pigmentation). Primarily affects the conchal bowl of the ear
- Photo-related, and related to sun exposure damages to cells.
- Treatment emphasizes sun protection and sometimes systemic steroids, antimalarials (e.g. hydroxychloroquine and quinacrine) if severe, or other immunosuppressants
Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE)
- Often affects upper chest, arms, upper back (temporarily).
- Symptoms often appear in spring.
- Papules/plaques, erythematous and edematous, without scales.
- Mild, self-resolving, & rarely seeking medical attention
- Treatment generally combines sun protection and antimalarial medications, potentially low-intensity UV exposures to reduce symptoms
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
- Uncommon. More often found in men in their 40s, typically.
- Skin lesions (e.g. fragility, blisters, scarring, milia) affecting sun-exposed skin
- Deficiency in uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD) enzyme causes build-up of uroporphyrins that cause damage. This damage also is related to sun exposure.
- Often associated with liver disease (hemochromatosis, alcoholism, hepatitis C).
- Treated with phlebotomy (blood removal) and, if necessary, other immunosuppresants
Erythema Nodosum (EN)
- Inflammation in subcutaneous fat, producing painful red nodules on shins.
- Common in 20s, 30s, or 40s.
- Often associated with systemic disorders like sarcoidosis, infections, and medications.
- Treatment typically includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), elevation, rest. Systemic steroids may be used if symptoms persist.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.