Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements best encapsulates the role of operations within an organization?
Which of the following statements best encapsulates the role of operations within an organization?
- Operations are important in public sector but not paramount in private sector.
- Operations primarily serve to uphold the organization's public image and marketing efforts.
- Operations are confined to specific departments, focusing on day-to-day tasks.
- Operations are integral to an organization's success, influencing its overall performance and encompassing a range of functions. (correct)
Within the context of operations, what is the primary function of transforming inputs?
Within the context of operations, what is the primary function of transforming inputs?
- To minimize the cost of raw materials and energy consumption.
- To standardize products and services in order to appeal to a wider market.
- To convert basic inputs such as materials, energy, and customer requirements into outputs for the end customer. (correct)
- To streamline internal processes and reduce the need for skilled labor.
In the basic operations system model, what role does 'feedback' primarily serve?
In the basic operations system model, what role does 'feedback' primarily serve?
- To ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- To inform stakeholders about the financial performance of the organization.
- To relay customer information to the marketing department.
- To provide data for process improvement and adjustments. (correct)
According to Stakeholder Theory, what is the role of an entrepreneur or manager in creating value?
According to Stakeholder Theory, what is the role of an entrepreneur or manager in creating value?
What is the core principle of social value creation in a business context?
What is the core principle of social value creation in a business context?
In the context of organizational design, what best describes the role of senior-level managers within a firm?
In the context of organizational design, what best describes the role of senior-level managers within a firm?
What is the fundamental purpose of designing an organization?
What is the fundamental purpose of designing an organization?
What is the primary implication of the statement: 'what they achieve detracts from what you could’ve taken from the value chain'?
What is the primary implication of the statement: 'what they achieve detracts from what you could’ve taken from the value chain'?
Which of the following factors is LEAST likely to influence an organization's ideal structure?
Which of the following factors is LEAST likely to influence an organization's ideal structure?
In a vertical organizational structure, how is authority typically distributed?
In a vertical organizational structure, how is authority typically distributed?
Which of the following characterizes a key advantage of a vertical organizational structure?
Which of the following characterizes a key advantage of a vertical organizational structure?
What is an implication of a vertical structure being 'dependent on a strong leader at the top'?
What is an implication of a vertical structure being 'dependent on a strong leader at the top'?
In a horizontal organizational structure, how do employees' roles and responsibilities typically differ from those in a vertical structure?
In a horizontal organizational structure, how do employees' roles and responsibilities typically differ from those in a vertical structure?
What is a potential drawback of a horizontal organizational structure?
What is a potential drawback of a horizontal organizational structure?
Why might a small business opt for a horizontal organizational structure?
Why might a small business opt for a horizontal organizational structure?
What is a key difference between vertically and horizontally integrated organizations in terms of their approach to managing their business?
What is a key difference between vertically and horizontally integrated organizations in terms of their approach to managing their business?
What is a primary trend emerging in organizational structures?
What is a primary trend emerging in organizational structures?
According to 'Designing Organizations to Create Value (2003)', what can result from a poor organizational design?
According to 'Designing Organizations to Create Value (2003)', what can result from a poor organizational design?
Which of the following is described as a characteristic of leadership?
Which of the following is described as a characteristic of leadership?
What is the ultimate responsibility of senior-level managers within the firm regarding stakeholders?
What is the ultimate responsibility of senior-level managers within the firm regarding stakeholders?
Under what scenarios is it most important for businesses to redesign organizational culture?
Under what scenarios is it most important for businesses to redesign organizational culture?
Compared to other organizational structures, what advantages does horizontal integration have?
Compared to other organizational structures, what advantages does horizontal integration have?
Which element is likely found in a basic operations system?
Which element is likely found in a basic operations system?
What is the role of the CEO in creating value for stakeholders?
What is the role of the CEO in creating value for stakeholders?
Which of the following contributes the LEAST to having the best organizational structure?
Which of the following contributes the LEAST to having the best organizational structure?
What are the consequences of a lack of clarity in defining roles and responsibilities within a horizontal company?
What are the consequences of a lack of clarity in defining roles and responsibilities within a horizontal company?
What is the primary role of feedback in the basic operations system model?
What is the primary role of feedback in the basic operations system model?
What is a possible impact for the introduction of technology in emerging trends?
What is a possible impact for the introduction of technology in emerging trends?
How do vertically integrated companies handle component parts and value-added improvements?
How do vertically integrated companies handle component parts and value-added improvements?
In the context of operations, what constitutes a transformation input?
In the context of operations, what constitutes a transformation input?
How does Apple’s thinking relate to vertically integrated companies?
How does Apple’s thinking relate to vertically integrated companies?
Why do organizations undergo restructuring processes?
Why do organizations undergo restructuring processes?
What factor would make implementation of horizontal companies the most challenging compared to other organizational designs?
What factor would make implementation of horizontal companies the most challenging compared to other organizational designs?
Flashcards
Operations
Operations
Activities that transform inputs into outputs for the end customer, spanning various sectors and organizational departments.
Basic Operations System
Basic Operations System
An operations model with inputs being transformed through processes into outputs, incorporating feedback for continuous improvement.
Stakeholder Theory
Stakeholder Theory
The concept where entrepreneurs or managers create value by aligning and capturing the joint interests of all stakeholders involved.
Value Creation
Value Creation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Value Creation Definition
Value Creation Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organization Design
Organization Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical Structure
Vertical Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of Vertical Structures
Advantages of Vertical Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of Vertical Structures
Disadvantages of Vertical Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Structure
Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of Horizontal Structure
Advantages of Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of Horizontal Structure
Disadvantages of Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emerging Trends in Structures
Emerging Trends in Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Need to Restructure
Need to Restructure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Need to Restructure
Need to Restructure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Characteristics of Leadership
Characteristics of Leadership
Signup and view all the flashcards
Characteristics of Leadership
Characteristics of Leadership
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Understanding Operations
- Operations occur in all sectors: manufacturing, services, private, and public.
- An organization's operations performance determines how it is judged.
- Operations encompass a wide range of functions, not limited to a specific department.
- Operations transform basic inputs (materials, energy, customer requirements, information, skills, finance) into outputs for the end customer.
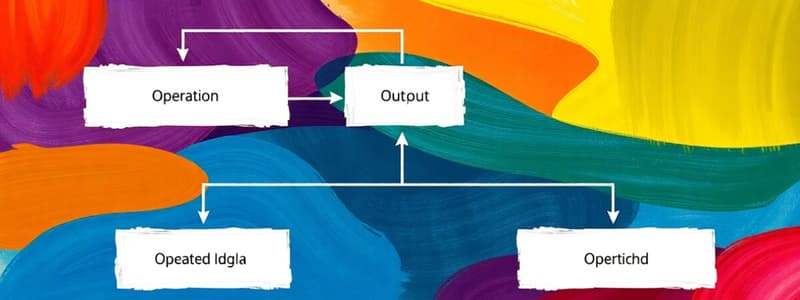
- A basic operations system involves inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback.
The Basic Operations System Explained
- Inputs include materials and customer information.
- Transformation involves capital, technology, energy, know-how, and experience, adding value throughout the process from basic inputs to finished goods and services.
- Outputs are the final, completed product/service offering.
- Outputs consist of tangible and intangible elements.
- Outputs combine physical and psychological effects and benefits for the customer in the final transaction.
- Services and production operations have become linked.
The Leader/Stakeholder Theory and Value Creation
- Entrepreneurs/managers create value by capturing the joint interests of stakeholders.
- Stakeholder interests may conflict but should be shaped in the same direction over time.
- Successful businesses create value for various stakeholders: customers, suppliers, employees, communities, financiers, shareholders, banks.
- Social value satisfies many stakeholders through collaboration.
- Value is what stakeholders seek in a relationship with an organization.
- Value creation starts with creating goods valued by consumers, meeting their needs more fully amid competition.
- Key result area of a CEO involves satisfying existing market needs and exploiting opportunities for potential market segments.
- Best use of resources and leveraging resources are requirements in value creation.
- Senior-level managers are responsible for a range of stakeholders within the firm and its external connections.
- Value creation consists of devising/implementing processes and creating competitive advantage.
Why Design an Organization
- Organizational design arranges people and jobs to meet goals.
- Graphically, it is represented via an organizational chart.
- Organizational design features assignment of responsibilities, reporting structures, communication channels, and relationships.
- Comprises organizational components (units), hierarchy, and their relationships
- Design portrays where formal authority and power are located, and how authority/accountability flows.
- Provides a home and identity for employees
- Design must define what the positions are, and how they are grouped.
- Design establishes the reporting sequence.
- Determines what each person and unit is responsible for
Best Structures and Vertical/Tall Structure
- The best structure depends on the type of work (skilled labor or professionals), size in terms of employees, revenue, geographic dispersion of facilities, and range of business.
- Two types of structures exist: vertical (tall) and horizontal (flat).
- Vertical structures have a chain of management with the CEO at the top making decisions and delegating them down to lower levels.
- Power in a vertical structure emanates from the top down.
- Vertical structures feature a well-defined chain of command.
- In vertical structures the person at the top of the organizational chart has the most power.
- In vertical structures employees report to the person directly above them.
- With vertical structures each person is responsible for a specific area or set of duties.
- Advantages of vertical structures include efficiency and quick decision-making.
- Responsibility lies with people highest in the chain of command.
- Employees have clearly defined duties in each position, which involves specialized tasks, with little need to learn new tasks and skills.
- Vertical Structure enables better task designation to employees or departments with well-defined responsibilities for employees.
- Vertical Structures are generally easier to manage
Disadvantages of Vertical Structure
- Vertical structures can be rigid with many rules.
- Vertical structures are dependent on a strong leader at the top.
- Weak leadership means successive hierarchical structures may be frustrated by poor decision-making by superiors.
- Vertical structures lack the transparency of horizontal companies because each layer complicates information more and more.
- Some employees may feel stifled or unheard in this kind of structure.
Horizontal Structure
- Horizontal structures have a less-defined chain of command.
- In Horizontal Structures, employees across lines have similar input into how the organization is run.
- Instead of defined duties, employees may work in teams where everyone has input.
- Horizontal Structures consist of employees performing many different functions, reporting to several supervisors.
- Project managers or team leaders report to teams of supervisors, with team members essentially equal in terms of power.
- Horizontal Structures typically have almost no middle managers.
- High-level managers in Horizontal Structures handle day-to-day tasks and interact with customers and front-line employees personally.
- Horizontal Structures typically cost less to run because there are less managers.
- Compared to vertical, Horizontal Structures have less rules and more power in the hands of employees, increasing employee satisfaction.
- Employees in horizontal organizations may have a stronger sense of identification with the team.
- Disadvantages include less efficiency and taking more time and resources to make decisions.
- Workers must learn more skills, which can increase job stress, or be more interesting.
- Horizontal companies are much harder to implement than vertical companies, especially as the business grows and the business must foster a culture of teamwork.
- In horizontal structures Employees may be less sure about their roles/responsibilities within the company.
- Project managers can be frustrated by the lack of authority
- In an increasingly globalized world, all companies should implement the best of both a horizontal and vertical structure
Horizontal vs Vertical Integration
- Frank Ostroff in 2013 stated that, businesses will become more horizontally structured.
- Most new and small businesses opt to be horizontally structured due the lack of a large amount of employees and resources.
- Horizontal organisations usually need more coordination than vertical
- Vertically integrated businesses have more control, the ability to dictate component parts
- Horizontally integrated businesses have less control, and are dependent on others to "play their part"
- Vertically businesses usually leverage higher benefits for their success.
- Horizontally integrated businesses are able to benefit from the success of everyone in the value chain.
- Vertically integrated businesses usually have a scarcity mentality when approaching partnerships
- Horizontally integrated businesses usually have an abundance mentality when approaching partnerships
Emerging Trends
- Trends include the interdependence of different departments.
- Trends consist of responding to rapid changes in the environment.
- It is important to streamline organizations to improve communication and decision-making.
- Technological rises have made virtual organizations boundary-less.
- There has been a trend to establish self-directed work teams as the basic production group.
- Motiviation techniques involve expanding the scope of jobs, and workers being involved in problem solving, planning, and fostering open communications
Need to Restructure
- Designing Organizations to Create Value (2003) writes that a poor design can lead to lost profits or failure.
- There is a need to reduce costs by removing layers of bureaucracy, improve competitiveness, and reorient the organizational culture and behaviors to enhance productivity and profits.
- Important to respond to competition, and respond to Jit
Characteristics of Leadership
- Leadership involves flexibility, tenaciousness, empathy, transparency, compassion, communication, and decisiveness.
- More characteristics involve conflict resolution, clear vision, passion, protection, understanding, and problem-solving.
- Negotiation is another important skill for leadership.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.