Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary distinction between climate and weather?
What is the primary distinction between climate and weather?
- Climate is studied by meteorologists, while weather is studied by climatologists.
- Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, and climate is the long-term average of these conditions. (correct)
- Climate refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, whereas weather describes long-term patterns.
- Weather includes temperature, while climate includes humidity and air pressure.
On what basis did Wladimir Köppen primarily categorize Earth's climate zones?
On what basis did Wladimir Köppen primarily categorize Earth's climate zones?
- Average annual temperature and precipitation levels.
- Proximity to major geographical features like mountains and oceans.
- Prevailing wind patterns and air pressure systems.
- Types of native vegetation present in different regions. (correct)
According to the Köppen climate classification system, how many major climate groups are recognized?
According to the Köppen climate classification system, how many major climate groups are recognized?
- Seven
- Four
- Five (correct)
- Three
Which of the following best characterizes the Group A climate zone?
Which of the following best characterizes the Group A climate zone?
The 'dry' climate group in the Köppen classification system is designated as:
The 'dry' climate group in the Köppen classification system is designated as:
Regions classified as Group C climates are described as 'humid middle latitude with mild winters'. Where are these regions located relative to the equator?
Regions classified as Group C climates are described as 'humid middle latitude with mild winters'. Where are these regions located relative to the equator?
If a region is described as having consistent warm temperatures throughout the year, high humidity, and is home to rainforests, which Köppen climate group would it most likely belong to?
If a region is described as having consistent warm temperatures throughout the year, high humidity, and is home to rainforests, which Köppen climate group would it most likely belong to?
Which of the following sequences correctly orders the Köppen climate groups as you move from the equator towards the Polar Regions?
Which of the following sequences correctly orders the Köppen climate groups as you move from the equator towards the Polar Regions?
Which characteristic is NOT a primary factor in classifying a climate as 'humid middle latitude with mild winters'?
Which characteristic is NOT a primary factor in classifying a climate as 'humid middle latitude with mild winters'?
If a region is classified as 'humid middle latitude with severe winters,' what two factors are most influential in determining this classification?
If a region is classified as 'humid middle latitude with severe winters,' what two factors are most influential in determining this classification?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes Group E climates from all other climate classifications?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes Group E climates from all other climate classifications?
A climatologist is comparing two regions: one in central South America and another in northern Canada. Which of the following climate characteristics would they likely use to differentiate between the two?
A climatologist is comparing two regions: one in central South America and another in northern Canada. Which of the following climate characteristics would they likely use to differentiate between the two?
Which of the following locations would most likely be classified as a Group D climate?
Which of the following locations would most likely be classified as a Group D climate?
Why are there so many sub-classifications (14) within the major climate groups?
Why are there so many sub-classifications (14) within the major climate groups?
Imagine a region described as having moist air, being in the middle latitudes, but experiencing extremely cold and prolonged winters. Which climate classification would this region MOST likely fall under?
Imagine a region described as having moist air, being in the middle latitudes, but experiencing extremely cold and prolonged winters. Which climate classification would this region MOST likely fall under?
Flashcards
Climate
Climate
The long-term patterns of meteorological conditions, including temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind, and precipitation.
Wladimir Köppen
Wladimir Köppen
A climatologist who created a system categorizing Earth's climates into five major groups.
Köppen Climate Classification
Köppen Climate Classification
Categorizes Earth's climates into five major groups based on native vegetation.
Group A: Humid Tropical
Group A: Humid Tropical
Signup and view all the flashcards
Group B: Dry
Group B: Dry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Group C: Mid-Latitude, Mild Winter
Group C: Mid-Latitude, Mild Winter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Climate Definition
Climate Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Köppen's Climate Basis
Köppen's Climate Basis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humid Middle Latitude with Mild Winters
Humid Middle Latitude with Mild Winters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humid Middle Latitude with Severe Winters
Humid Middle Latitude with Severe Winters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polar Climate
Polar Climate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major Climate Classifications
Major Climate Classifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Climate Sub-classifications
Climate Sub-classifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Middle Latitudes
Middle Latitudes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polar Regions
Polar Regions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Climate constitutes long-term weather patterns of an area, considering temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind, and precipitation.
- Weather represents the day-to-day variations of these conditions.
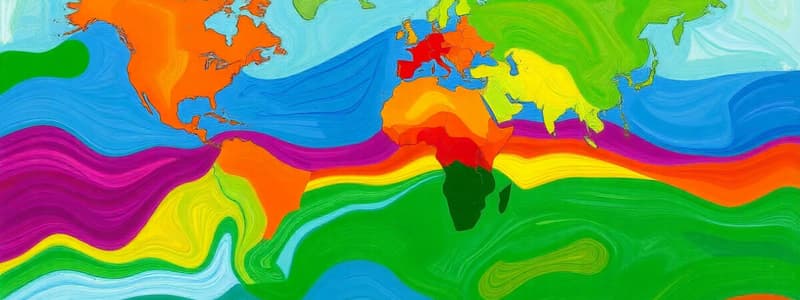
Köppen Climate Classification
- The Köppen Climate Classification system, developed in 1884 by Wladimir Köppen, categorizes Earth's climates into five major groups based on native vegetation.
- Vegetation serves as a representative of local temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables.
- The classifications are based on the equator outwards to the polar regions, labeled as A, B, C, D, and E.
Group A: Humid Tropical
- Located along the equator, characterized by consistently warm temperatures year-round.
- Features rainforests like the Amazon.
Group B: Dry
- Situated north and south of the equator.
- Characterized by minimal moisture, encompassing major deserts such as the Sahara and the Great Victoria.
- Temperatures remain relatively constant with limited seasonal changes.
Group C: Humid Middle Latitude with Mild Winters
- Located mid-way between the equator and the polar region.
- Features seasonal changes with tolerable winters
- Found in regions like the central U.S., southern Europe, and central South America.
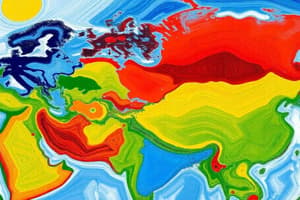
Group D: Humid Middle Latitude with Severe Winters
- Located closer to the poles than Group C, characterized by severe winters.
- Includes regions such as northern Canada and Siberia.
Group E: Polar
- Located at the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
- Experiences consistent cold temperatures throughout the year.
Climate Sub-classifications
- The major climate groups can be further divided into more specific classifications based on temperature ranges and rainfall amounts.
- There are 14 sub-classifications used to describe Earth's climates.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the difference between climate and weather. Discover the Köppen Climate Classification system, which divides climates into five major groups (A-E) based on vegetation, temperature, and precipitation patterns from the equator to the poles.