Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the most recognizable part of a sound in audio production?
What is the most recognizable part of a sound in audio production?
- Frequency
- Compression phase
- Amplitude
- Waveform (correct)
Which part of an audio waveform is referred to as the compression phase?
Which part of an audio waveform is referred to as the compression phase?
- The ascending part of the waveform
- The silent part of the waveform
- The horizontal line indicating zero energy
- When energy reaches its peak and then goes back down (correct)
What does a sine wave look like?
What does a sine wave look like?
- Smooth curve (correct)
- Sharp spikes
- Irregular zig-zag
- Straight line
Which common feature do different waveforms share in terms of energy?
Which common feature do different waveforms share in terms of energy?
What behavior is seen in all naturally occurring audio waveforms?
What behavior is seen in all naturally occurring audio waveforms?
How would a silent audio waveform appear on a graph?
How would a silent audio waveform appear on a graph?
What does amplitude refer to in sound waves?
What does amplitude refer to in sound waves?
How are waveforms with greater amplitude represented visually in a waveform?
How are waveforms with greater amplitude represented visually in a waveform?
What is the unit of measurement for amplitude?
What is the unit of measurement for amplitude?
At what range of Decibels does sound become painful for humans?
At what range of Decibels does sound become painful for humans?
Which measurement is used to assess the amplitude of sound traveling through the air?
Which measurement is used to assess the amplitude of sound traveling through the air?
What term can be used interchangeably with amplitude?
What term can be used interchangeably with amplitude?
What does loudness deal with in relation to sound?
What does loudness deal with in relation to sound?
What is needed to properly record or reproduce a sound using digital audio?
What is needed to properly record or reproduce a sound using digital audio?
Analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion refers to which process in the recording of audio?
Analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion refers to which process in the recording of audio?
What is the term used to describe the part of an audio wave where the air pressure increases?
What is the term used to describe the part of an audio wave where the air pressure increases?
What does a sound's waveform represent?
What does a sound's waveform represent?
What is the term used to describe one period of compression followed by one period of rarefaction in a sound wave?
What is the term used to describe one period of compression followed by one period of rarefaction in a sound wave?
How is frequency measured in sound waves?
How is frequency measured in sound waves?
What frequency range is generally considered for human beings?
What frequency range is generally considered for human beings?
Which term is used to describe the decrease in high-end frequency sensitivity over time in humans?
Which term is used to describe the decrease in high-end frequency sensitivity over time in humans?
What represents a low-frequency sound compared to a high-frequency sound?
What represents a low-frequency sound compared to a high-frequency sound?
What does a sine wave represent in terms of sound?
What does a sine wave represent in terms of sound?
'Two cycles of a sine wave' represents what aspect of sound?
'Two cycles of a sine wave' represents what aspect of sound?
'Different animals can hear different frequencies.' What enables this phenomenon?
'Different animals can hear different frequencies.' What enables this phenomenon?
According to the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, how many samples per second are needed to accurately record or reproduce a sound?
According to the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, how many samples per second are needed to accurately record or reproduce a sound?
What happens when there are less than two samples per cycle when recording a sound?
What happens when there are less than two samples per cycle when recording a sound?
What is the Nyquist frequency when recording at a 44.1 kHz sample rate?
What is the Nyquist frequency when recording at a 44.1 kHz sample rate?
Why is a high-frequency distortion near the Nyquist frequency audible in digital recordings?
Why is a high-frequency distortion near the Nyquist frequency audible in digital recordings?
What is the significance of a 16-bit audio in terms of amplitude representation?
What is the significance of a 16-bit audio in terms of amplitude representation?
Which bit depth allows for a more accurate measurement of amplitude in digital audio?
Which bit depth allows for a more accurate measurement of amplitude in digital audio?
What is the Nyquist frequency when recording at a 96 kHz sample rate?
What is the Nyquist frequency when recording at a 96 kHz sample rate?
What is the maximum number of amplitude levels represented by 24-bit audio?
What is the maximum number of amplitude levels represented by 24-bit audio?
How does increasing bit depth affect the dynamic range in audio recording?
How does increasing bit depth affect the dynamic range in audio recording?
What is the maximum dynamic range of a 24-bit audio file?
What is the maximum dynamic range of a 24-bit audio file?
How does a 24-bit audio file compare to a 16-bit audio file in terms of dynamic range?
How does a 24-bit audio file compare to a 16-bit audio file in terms of dynamic range?
What is the difference in file size between one minute of 16-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio and one minute of 24-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio?
What is the difference in file size between one minute of 16-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio and one minute of 24-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio?
What happens to file size when the sample rate is doubled for mono audio files?
What happens to file size when the sample rate is doubled for mono audio files?
Which bit depth option in Pro Tools is considered substantially different from fixed point depths?
Which bit depth option in Pro Tools is considered substantially different from fixed point depths?
What impact do higher sample rates and bit depths have on Digital Audio Workstations?
What impact do higher sample rates and bit depths have on Digital Audio Workstations?
How much storage space does one minute of 32-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio require?
How much storage space does one minute of 32-bit/44.1 kHz mono audio require?
What valuable resources are recommended for those interested in diving deeper into digital audio science as per the text?
What valuable resources are recommended for those interested in diving deeper into digital audio science as per the text?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
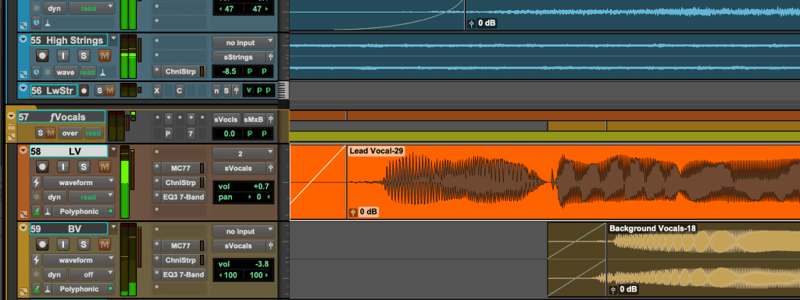
Audio Basics
- The three critical parts of audio are:
- Waveform: the shape of a sound
- Frequency: the pitch of a sound
- Amplitude: the energy level of a sound
Waveform
- A waveform represents the tone or timbre of a sound
- Waveforms have a compression phase and a rarefaction phase
- A compression phase is when the energy increases, and a rarefaction phase is when the energy decreases
- The combination of compression and rarefaction phases creates a cycle
- A waveform with a shorter compression phase and a longer rarefaction phase will have a different tone than a waveform with a longer compression phase and a shorter rarefaction phase
- Examples of waveforms include:
- Sine wave: a simple and pure sound
- Square wave: a sound with a more complex waveform
- Triangle wave: a sound with a triangular waveform
Frequency
- Frequency refers to the pitch of a sound
- It is measured in Hertz (Hz) and represents the number of cycles per second
- A higher frequency means a higher pitch, while a lower frequency means a lower pitch
- The human range of hearing is from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
- Different animals can hear different frequencies
- The frequency range of human hearing can vary depending on age and listening habits
Amplitude
- Amplitude refers to the energy level of a sound
- It is visually represented in a waveform by its height
- A sound with a greater amplitude will be a taller waveform, while a sound with a lower amplitude will be a shorter waveform
- Amplitude can be affected by the force of a sound, such as hitting a drum harder or softer
- The unit of measurement for amplitude is Decibel (dB)
- The human range of hearing is from 0 dB (silent) to 120-130 dB (painful)
Audio in the Digital Domain
- Audio can be recorded and stored on a digital medium
- The process of converting analog audio to digital audio is called analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion
- The process of converting digital audio back to analog audio is called digital-to-analog (D/A) conversion
Samples and Sample Rates
- A sample is an instantaneous measurement of an audio signal
- A sample rate is the number of samples taken per second
- Common sample rates include:
- 44.1 kHz (44,100 samples per second)
- 48 kHz (48,000 samples per second)
- 88.2 kHz (88,200 samples per second)
- 96 kHz (96,000 samples per second)
- The sample rate must be at least twice the highest frequency of the sound to accurately record or reproduce it
- The Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem states that the sample rate must be at least twice the highest frequency of the sound
Bit Depth
- Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to measure the amplitude of a sound
- Common bit depths include:
- 16-bit: 65,536 possible amplitude values
- 24-bit: 16,777,216 possible amplitude values
- A higher bit depth allows for more accurate measurements of amplitude and a greater dynamic range
- The formula for calculating the dynamic range of a bit depth is: 6 dB per bit
- 16-bit audio has a maximum dynamic range of 96 dB, while 24-bit audio has a maximum dynamic range of 144 dB
The Impact of Sample Rate and Bit Depth on File Size
- The choices of sample rate and bit depth will influence the file size of a digital audio file
- A higher sample rate and bit depth will result in a larger file size
- The following chart lists sample rates, bit depths, and their corresponding file sizes for a mono, one-minute audio file:
- 44.1 kHz, 16-bit: 5.3 MB
- 48 kHz, 16-bit: 5.8 MB
- 88.2 kHz, 16-bit: 10.6 MB
- 96 kHz, 16-bit: 11.5 MB
- 176.4 kHz, 16-bit: 21.1 MB
- 192 kHz, 16-bit: 23.0 MB
- 44.1 kHz, 24-bit: 7.9 MB
- 48 kHz, 24-bit: 8.6 MB
- 88.2 kHz, 24-bit: 15.9 MB
- 96 kHz, 24-bit: 17.2 MB
- 176.4 kHz, 24-bit: 31.8 MB
- 192 kHz, 24-bit: 34.6 MB
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.