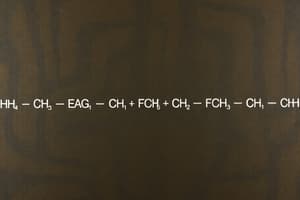Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do complex carbohydrates consist of?
What do complex carbohydrates consist of?
- Nucleotides
- Single monomers
- Two or more monomers (correct)
- Amino acids
What are proteins formed by linking together?
What are proteins formed by linking together?
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleotides
- Monomers
- Amino acids (correct)
What is the atomic number of an element?
What is the atomic number of an element?
- The number of nuclei in an atom
- The number of neutrons in an atom
- The number of electrons in an atom
- The number of protons in the nucleus of each of its atoms (correct)
Which subatomic particle has a positive charge?
Which subatomic particle has a positive charge?
What are isotopes?
What are isotopes?
What is the main difference between organic and inorganic compounds?
What is the main difference between organic and inorganic compounds?
Which of the following is an example of an inorganic compound?
Which of the following is an example of an inorganic compound?
What is the purpose of a chemical formula?
What is the purpose of a chemical formula?
Which of the following is an example of a chlorinated hydrocarbon?
Which of the following is an example of a chlorinated hydrocarbon?
What are monomers in the context of organic polymers?
What are monomers in the context of organic polymers?
Which of the following is an example of a simple carbohydrate?
Which of the following is an example of a simple carbohydrate?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Biomolecules
- Complex carbohydrates are composed of two or more monomers, including starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin.
- Proteins are formed by linking together monomers of amino acids.
- Nucleic acids are made by linking sequences of monomers called nucleotides, including DNA and RNA.
Atomic Structure
- Atomic structure consists of three subatomic particles: protons (positive), neutrons (uncharged), and electrons (negative).
- Atomic number is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which determines the chemical element in the periodic system.
Isotopes and Elements
- Isotopes are forms of an element having the same atomic number but different mass number.
- Each atom has an equal number of positively charged protons inside its nucleus and negatively charged electrons outside its nucleus, but they have different numbers of uncharged neutrons.
Compounds
- Organic compounds contain at least two carbon atoms combined with each other and with atoms of one or more other elements (e.g., H, O, N, S, P, Cl, Fl).
- Inorganic compounds lack carbon-hydrogen bonds and may consist of heavy metals and toxic elements (e.g., lead, mercury, chromium, arsenic, etc.).
Chemical Formula
- Chemical formula shows the number of atoms (ions) of each type of compound (e.g., H2O, O2, O3, N2, N2O, H2S, NH3, H2SO4, CH4, C6H12O6).
Types of Organic Compounds
- Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen atoms (e.g., methane).
- Chlorinated hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and chlorine atoms (e.g., pesticide DDT, chloroform).
- Simple carbohydrates are simple sugars, consisting of compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (e.g., glucose).
- Organic polymers are larger and more complex organic compounds consisting of a number of basic structural or molecular units called monomers linked by chemical bonds.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.