Podcast
Questions and Answers
A healthy, balanced ecosystem has _______.
A healthy, balanced ecosystem has _______.
more producers than consumers
If predators A and B prey upon the same species and predator A is eliminated, the population of predator B will likely __________.
If predators A and B prey upon the same species and predator A is eliminated, the population of predator B will likely __________.
- Remain the same
- Decrease
- Be eliminated
- Increase (correct)
Quaternary consumers are not _______.
Quaternary consumers are not _______.
- Animals
- Consumers
- Prey (correct)
- Predators
Explain how trees can be producers and yet the smallest trophic level in a pyramid of numbers.
Explain how trees can be producers and yet the smallest trophic level in a pyramid of numbers.
Explain why quaternary consumers occupy the top position in the pyramid of energy.
Explain why quaternary consumers occupy the top position in the pyramid of energy.
Explain how the elimination of a predator from an ecosystem might result in starvation amongst its prey species.
Explain how the elimination of a predator from an ecosystem might result in starvation amongst its prey species.
In order to look for their prey, owls _______.
In order to look for their prey, owls _______.
Explain the importance of decomposers to a food web and their interaction with quaternary consumers.
Explain the importance of decomposers to a food web and their interaction with quaternary consumers.
Explain what distinguishes primary and secondary consumers.
Explain what distinguishes primary and secondary consumers.
Rabbits are best described as _______.
Rabbits are best described as _______.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
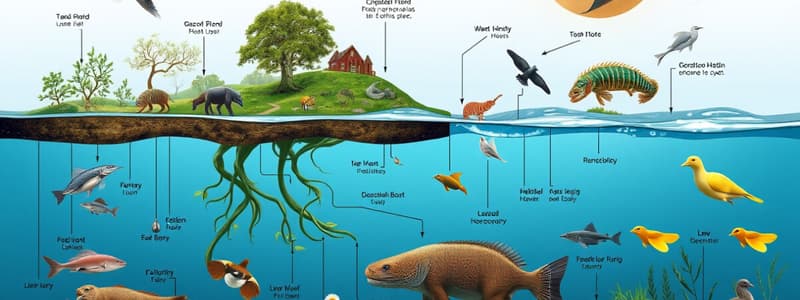
Trophic Levels and Food Webs
-
A healthy ecosystem typically has more producers than consumers, providing the foundational energy source for consumers.
-
If predator A is removed, predator B's population is likely to increase due to reduced competition for the same prey.
Quaternary Consumers
-
Quaternary consumers are not prey; they occupy the top position in the food chain and have no natural predators.
-
Energy decreases at each trophic level; when quaternary consumers feed on tertiary consumers, only 10-15% of the energy is retained.
Producers and Biomass
-
Trees, despite being fewer in number, are significant producers due to their large biomass, supporting numerous smaller organisms.
-
Trees hold the producer level in the trophic pyramid due to their extensive energy and nutrient contribution, despite being outnumbered.
Impact of Predator Elimination
-
Eliminating a primary predator can lead to overpopulation of prey species, leading to resource depletion and potential starvation.
-
Competition for limited food supplies increases as the prey population rises unchecked, thereby impacting ecosystem balance.
Owl Behavior
- Owls actively locate their prey by turning their heads, which enhances their ability to hunt efficiently.
Role of Decomposers
-
Decomposers are crucial in nutrient recycling within a food web, breaking down dead organic material and returning nutrients to the ecosystem.
-
This recycling processes impact all trophic levels, including quaternary consumers, ensuring sustainability in the ecosystem.
Consumers Distinctions
-
Primary consumers are primarily herbivores that feed directly on producers, while secondary consumers are carnivores that prey on primary consumers.
-
The main distinction lies in their dietary habits, shaping their roles within the trophic hierarchy.
Rabbit Classification
- Rabbits are classified as primary consumers, primarily feeding on plants and forming an essential part of the herbivore category.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.