Podcast
Questions and Answers
According to estimations, what proportion of global tobacco-related deaths could potentially be avoided within 30 years if adult tobacco consumption decreases by 50% by 2020?
According to estimations, what proportion of global tobacco-related deaths could potentially be avoided within 30 years if adult tobacco consumption decreases by 50% by 2020?
- One-third (correct)
- Two-thirds
- One-half
- One-quarter
Approximately what percentage of the global population currently has access to comprehensive tobacco cessation services?
Approximately what percentage of the global population currently has access to comprehensive tobacco cessation services?
- 5%
- 15% (correct)
- 50%
- 30%
Which of the following is NOT a recommendation for integrating brief tobacco interventions?
Which of the following is NOT a recommendation for integrating brief tobacco interventions?
- Integrating them into existing healthcare systems
- Focusing primarily on specialist treatment centers (correct)
- Making them available throughout a country's health system
- Prioritizing implementation within primary care settings
Why are oral health professionals considered to be in a unique position to assist tobacco users?
Why are oral health professionals considered to be in a unique position to assist tobacco users?
In developed countries, approximately what percentage of tobacco users visit their dentist or dental hygienist annually?
In developed countries, approximately what percentage of tobacco users visit their dentist or dental hygienist annually?
What is the primary reason that integrating brief tobacco interventions into oral health programs within primary care settings is considered cost-effective?
What is the primary reason that integrating brief tobacco interventions into oral health programs within primary care settings is considered cost-effective?
If a country aims to align with the WHO FCTC Article 14 guidelines, which strategy would represent the most comprehensive initial step towards developing a national tobacco treatment system?
If a country aims to align with the WHO FCTC Article 14 guidelines, which strategy would represent the most comprehensive initial step towards developing a national tobacco treatment system?
What does the 'A' in the 5A's model for tobacco intervention primarily focus on?
What does the 'A' in the 5A's model for tobacco intervention primarily focus on?
According to the STAR method, what is the recommended timeframe for setting a quit date?
According to the STAR method, what is the recommended timeframe for setting a quit date?
Which of the following is NOT a key element of practical counseling within the 5A's model?
Which of the following is NOT a key element of practical counseling within the 5A's model?
What would be the MOST effective initial strategy for implementation, according to the guidelines, when integrating brief tobacco interventions into oral health programs?
What would be the MOST effective initial strategy for implementation, according to the guidelines, when integrating brief tobacco interventions into oral health programs?
A patient, who has been smoking for 20 years, expresses reluctance to quit due to fear of weight gain and social isolation. Integrating the 5A's and the STAR methods, what is the MOST appropriate FIRST step?
A patient, who has been smoking for 20 years, expresses reluctance to quit due to fear of weight gain and social isolation. Integrating the 5A's and the STAR methods, what is the MOST appropriate FIRST step?
According to the 5As model, what is the FIRST step oral health providers should take when addressing tobacco use with patients?
According to the 5As model, what is the FIRST step oral health providers should take when addressing tobacco use with patients?
Which of the following best exemplifies how oral health providers should approach the 'Ask' step of the 5As model?
Which of the following best exemplifies how oral health providers should approach the 'Ask' step of the 5As model?
In the context of the 5As model, what does the 'Advise' component primarily entail?
In the context of the 5As model, what does the 'Advise' component primarily entail?
When implementing the 'Assist' component of the 5As model, what is a key action that oral health providers should take?
When implementing the 'Assist' component of the 5As model, what is a key action that oral health providers should take?
What does the 'Arrange' component of the 5As model involve?
What does the 'Arrange' component of the 5As model involve?
Which of the following is a critical consideration when tailoring advice during the 'Advise' stage of the 5As model?
Which of the following is a critical consideration when tailoring advice during the 'Advise' stage of the 5As model?
Suppose a patient is hesitant about quitting tobacco, expressing doubts about their ability to succeed. How should an oral health provider MOST appropriately handle the 'Assess' stage?
Suppose a patient is hesitant about quitting tobacco, expressing doubts about their ability to succeed. How should an oral health provider MOST appropriately handle the 'Assess' stage?
An oral health provider has a patient who is ready to quit. They have assisted the patient with a quit plan and provided information on specialist support. What SPECIFIC action should the provider take to fulfill the 'Arrange' stage effectively?
An oral health provider has a patient who is ready to quit. They have assisted the patient with a quit plan and provided information on specialist support. What SPECIFIC action should the provider take to fulfill the 'Arrange' stage effectively?
A patient presents for an oral health appointment. Upon asking about tobacco use, the patient reveals they smoke and are interested in quitting. After advising and assisting this patient, what is the MOST critical element that separates a good 'Arrange' strategy from an excellent one?
A patient presents for an oral health appointment. Upon asking about tobacco use, the patient reveals they smoke and are interested in quitting. After advising and assisting this patient, what is the MOST critical element that separates a good 'Arrange' strategy from an excellent one?
Why is it important to record a patient's tobacco use status in their dental treatment card?
Why is it important to record a patient's tobacco use status in their dental treatment card?
What key elements should be included in advice given to tobacco users to encourage them to quit?
What key elements should be included in advice given to tobacco users to encourage them to quit?
Which of the following statements embodies 'clear' advice regarding tobacco cessation?
Which of the following statements embodies 'clear' advice regarding tobacco cessation?
What makes advice 'personalized' in the context of tobacco cessation?
What makes advice 'personalized' in the context of tobacco cessation?
According to the recommendations, what is sufficient advice to provide someone who uses tobacco?
According to the recommendations, what is sufficient advice to provide someone who uses tobacco?
What is the MOST effective way to ensure that a dental practice consistently addresses tobacco use with all patients?
What is the MOST effective way to ensure that a dental practice consistently addresses tobacco use with all patients?
What is the PRIMARY goal of dental professionals asking patients about their tobacco use?
What is the PRIMARY goal of dental professionals asking patients about their tobacco use?
A 28-year-old female patient expresses concern about stained teeth and bad breath. How would you personalize your advice regarding tobacco cessation, based on the cues in the text?
A 28-year-old female patient expresses concern about stained teeth and bad breath. How would you personalize your advice regarding tobacco cessation, based on the cues in the text?
A dentist routinely advises patients to quit smoking but rarely follows up or offers concrete support beyond the initial recommendation. According to the guidelines, what crucial element of effective intervention is missing?
A dentist routinely advises patients to quit smoking but rarely follows up or offers concrete support beyond the initial recommendation. According to the guidelines, what crucial element of effective intervention is missing?
Imagine a healthcare system implements electronic medical records (EMRs) but fails to include a mandatory field for tobacco use status. What potential negative consequence could arise from this oversight, considering the principles outlined?
Imagine a healthcare system implements electronic medical records (EMRs) but fails to include a mandatory field for tobacco use status. What potential negative consequence could arise from this oversight, considering the principles outlined?
When a patient expresses disinterest in quitting tobacco, which intervention should be delivered according to the guidelines?
When a patient expresses disinterest in quitting tobacco, which intervention should be delivered according to the guidelines?
What is the primary purpose of asking a patient, 'What do you not like about being a smoker?'
What is the primary purpose of asking a patient, 'What do you not like about being a smoker?'
A patient responds 'Unsure' to both 'Would you like to be a non-tobacco user?' and 'Do you think you have a chance of quitting successfully?'. According to the guidelines, what action should be taken?
A patient responds 'Unsure' to both 'Would you like to be a non-tobacco user?' and 'Do you think you have a chance of quitting successfully?'. According to the guidelines, what action should be taken?
What is the next step after determining a patient is ready to make a quit attempt?
What is the next step after determining a patient is ready to make a quit attempt?
Which of the following best describes the 'Assess' step in the context of tobacco cessation?
Which of the following best describes the 'Assess' step in the context of tobacco cessation?
A dentist asks a patient 'What do you not like about being a tobacco user?' The patient responds, 'It makes my teeth yellow.' Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate follow-up?
A dentist asks a patient 'What do you not like about being a tobacco user?' The patient responds, 'It makes my teeth yellow.' Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate follow-up?
In the context of assessing a patient's readiness to quit, what does 'self-efficacy' refer to?
In the context of assessing a patient's readiness to quit, what does 'self-efficacy' refer to?
A patient states they are unsure if they want to quit tobacco use but believes they have a good chance of quitting successfully. How should the healthcare provider proceed, and why?
A patient states they are unsure if they want to quit tobacco use but believes they have a good chance of quitting successfully. How should the healthcare provider proceed, and why?
What is the underlying psychological principle behind asking a patient 'What do you not like about being a smoker?'?
What is the underlying psychological principle behind asking a patient 'What do you not like about being a smoker?'?
Assume a study reveals that patients who clearly articulate at least three dislikes about their tobacco use are statistically more likely to attempt quitting within 30 days. How would this influence your clinical approach when using the 'Assess' strategy?
Assume a study reveals that patients who clearly articulate at least three dislikes about their tobacco use are statistically more likely to attempt quitting within 30 days. How would this influence your clinical approach when using the 'Assess' strategy?
Flashcards
Impact of Tobacco Reduction
Impact of Tobacco Reduction
Reducing adult tobacco use by 50% by 2020 could prevent about one-third of tobacco-related deaths in 30 years.
Access to Cessation Services
Access to Cessation Services
Only 15% of the world population has access to complete tobacco cessation services.
Brief Interventions Importance
Brief Interventions Importance
Integrating brief tobacco interventions into healthcare systems, especially primary care, is recommended as a first step.
Primary Care Advantage
Primary Care Advantage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Health Programs' Role
Oral Health Programs' Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dentists' Unique Position
Dentists' Unique Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental Visit Reach
Dental Visit Reach
Signup and view all the flashcards
5A's: Ask
5A's: Ask
Signup and view all the flashcards
5A's: Advise
5A's: Advise
Signup and view all the flashcards
5A's: Assess
5A's: Assess
Signup and view all the flashcards
5A's: Assist
5A's: Assist
Signup and view all the flashcards
5A's: Arrange
5A's: Arrange
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the 5A's Model?
What is the 5A's Model?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ask ALL patients
Ask ALL patients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Friendly Tone
Friendly Tone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tailored advice
Tailored advice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assist (in 5 A's)
Assist (in 5 A's)
Signup and view all the flashcards
STAR Method
STAR Method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Practical Counseling
Practical Counseling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Danger Situations (Relapse)
Danger Situations (Relapse)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coping Skills
Coping Skills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Document Tobacco Use
Document Tobacco Use
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tobacco Use Indicators
Tobacco Use Indicators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advise to Quit
Advise to Quit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Personalized Advice
Personalized Advice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tie advice to demographics
Tie advice to demographics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Address Fertility Concerns
Address Fertility Concerns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sexual health effects on men
Sexual health effects on men
Signup and view all the flashcards
Focus on Immediate Benefits
Focus on Immediate Benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health condition
Health condition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Illness as Opportunity
Illness as Opportunity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elicit Dislikes
Elicit Dislikes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detailed Issue Response
Detailed Issue Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
5 R's Trigger
5 R's Trigger
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assess Readiness
Assess Readiness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance and Self-Efficacy
Importance and Self-Efficacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance Question
Importance Question
Signup and view all the flashcards
Self-Efficacy Question
Self-Efficacy Question
Signup and view all the flashcards
Next Steps: Ready to Quit
Next Steps: Ready to Quit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gauge Patient Belief
Gauge Patient Belief
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elicit, Build, and Suggest
Elicit, Build, and Suggest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Chapter explores integrating brief tobacco interventions into oral health programs in primary care.
- Objectives are to describe how oral health professionals can support users to quit and propose effective system changes for tobacco cessation services.
Introduction
- Adverse associations exist between tobacco and oral disease, including direct tobacco use and second-hand smoke linked to oral cancer, periodontal diseases, dental caries, and tooth loss.
- National oral health programs should actively support tobacco control efforts at both clinical and community levels.
WHO Oral Health Programme Tobacco Control Policy
- Goals of WHO Global Oral Health Programme have been reoriented for disease prevention and health promotion.
- There is emphasis on global policies in oral health promotion and oral disease prevention, coordinated with other programs and external partners.
- WHO recommends oral health programs embrace "the common risk factor approach" to integrate oral health promotion into broader health promotion.
- Tobacco use is a common risk factor between oral and chronic non-communicable diseases, justifying national oral health programs to support tobacco control.
- The WHO Oral Health Programme aims to ensure oral health professionals routinely increase patient awareness of tobacco risks and help them avoid all forms of tobacco.
- Programme collaborates with WHO Tobacco Free Initiative (TFI) and works with organizations to encourage WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) ratification.
- Promoting oral health professionals' involvement in tobacco cessation is a priority, with national programs urged to identify and treat tobacco users, integrating cessation services into routine practice.
WHO Policy on Tobacco Cessation
- Supporting users to quit is part of a comprehensive tobacco control package, consistent with Article 14 of the WHO FCTC.
- This aims to achieve voluntary global targets related to tobacco use and reduce premature mortality.
- Supporting current users to quit and population-level tobacco control measures can change the prevalence of tobacco use and death in the short- to medium-term.
- Reducing adult tobacco consumption by 50% by 2020 could avoid about one-third of global tobacco-related deaths within 30 years.
- Only 15% of the world population has access to tobacco cessation services, and 97 countries provide cessation support in primary care facilities with some cost coverage.
- Technical help for WHO Member States to improve national tobacco cessation and treatment systems is needed.
- Guidelines integrating brief tobacco interventions into health care systems are a first step for Parties to develop comprehensive treatment systems.
- Primary care setting should be the main focus because it can reach most tobacco users and has low service delivery costs.
- National oral health programs are a priority platform for integrating brief tobacco interventions due to oral health professionals' unique position to help tobacco users, especially the young.
The Unique Role of Oral Health Professionals in Helping Tobacco Users
- They can reach many users and persuade them to quit.
- In developed countries over 60% of users visit a dentist/hygienist yearly.
- Ethical, moral, and practical reasons exist for oral health professionals to play a role in helping users quit.
- Oral health professionals are concerned about tobacco's effects in the oropharyngeal area.
- They have access to children/caregivers, influencing individuals to quit or not start tobacco use.
- They have more time with patients than other health professionals, integrating tobacco cessation interventions into practice.
- They often treat women of childbearing age, explaining the potential harm to babies from tobacco use.
- They are as effective as other health professionals in quitting.
- They can build patient interest in stopping tobacco use by showing actual tobacco effects in the mouth.
What Should a National Oral Health Programme Do to Promote Tobacco Cessation?
- National oral health programs can promote tobacco cessation both within and outside the clinical setting.
- Clinical setting programs should strengthen the health care service to identify and provide every patient who uses tobacco with intervention.
- Outside the clinical setting oral health professionals can actively support tobacco control measures and increase the demand for cessation services through professional associations.
Oral Health Professionals Should Routinely Offer Brief Tobacco Interventions to All Tobacco Users in Primary Care
- Effective treatments for tobacco dependence include brief advice, intensive behavioral support, and pharmacological treatments.
- WHO recommends that health professionals deliver brief interventions as part of routine services, following WHO FCTC Article 14 guidelines.
- Behavioral counseling by oral health professionals with an oral exam can increase tobacco abstinence rates by 70% at six months or longer. Helping patients quit smoking as part of routine practice takes three-to-five minutes and is feasible, effective, and efficient, using the 5As and the 5Rs model.
- Every health care provider should educate about second-hand smoke dangers and encourage patients to avoid exposure and create a smoke-free home.
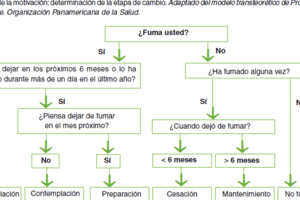
The 5As Model to Help Patients Ready to Quit
- Several models can deliver brief tobacco interventions.
- The 5As and 5Rs are the most widely used for brief intervention in primary care.
- The 5As (Ask, Advise, Assess, Assist, Arrange) summarize activities for providers to help a tobacco user make a quit attempt within three-to-five minutes, with "Ask" needing to be asked of all patients to make it part of the routine.
5As Defined
- Ask: Systematically identify all tobacco users at every visit.
- Advise: Advise all tobacco users that they need to quit.
- Assess: Determine readiness to make a quit attempt.
- Assist: Assist the patient with a quit plan/provide information on specialist support.
- Arrange: Schedule follow-up contacts/referral to specialist support.
The 5As in Detail
- Advice should be clear and positive, and tailored to the patient's circumstances.
- Assessment will be determined on whether the patient is ready to quit, then the patient will need assistance.
- Arranging for a follow up can cement a commitment to quitting.
- The 5As model can guide providers to talk about tobacco use and deliver advice to patients who are ready to quit.
- The 5As are systematically identify all tobacco users at every visit, persuade all users that to quit, and determining readiness.
Table 1
-
Strategies for implementation include the fact that tobacco use is a friendly way to ask patients, "Do you smoke cigarettes?".
-
Nicotine use status should be recorded, using the implementation methods of asking patients if they smoke cigarettes.
-
Asking, "Do you use any tobacco products?".
-
Persuade all tobacco users that they need to quit, they should be told a clear, strong and personalized manner.
-
The Clear implementation strategy is saying, “It is important that you quit smoking, if you are ill, if will not be enough.”
-
Strength is important for implementation, dentists need to inform patients that there is a duty to protect patient health both now and in the future.
-
Asking about any demographics, such as women being more susceptible to fertility affects.
-
Asses determining a readiness to make a quit attempt, with two questions relation to “importance” and “self-efficacy”.
-
Those questions should be, "Would you like to be a non-tobacco user?" and "Do you think you have a chance of quitting successfully?".
-
"“What do you not like about being a smoker?”, can determine implementation, with “Well, I don’t like how much I spend on tobacco”.". Any answer that a the tobacco user isn't ready for the quit attempt is to use the 5R's intervention.
5A(s) defined
- Help the patient to develop the assistance of the action plan and implement a strategy for implementation,.
- Use the STAR method or facilitating and helping in developing a plan includes Set a quit date for within 2 weeks, and tell your family, friends, co workers, and ask for supportive.
- For all patients or help, you should see if identify any problems already encountered to make up for lost time, remind patients, assess medication problems, schedule, and congratulate patients.
- Reminds have view of the relapse, review, circumstances, or available intensive treatment available.,
The 5Rs Model to Increase the Motivation to Quit
-
5Rs (relevance, risks, rewards, roadblocks, and repetition) should be addressed during counseling for those not ready to quite because they they do not consider quitting important.
-
It is critical to provide the Five R(s) in motivational speech, after discussing the benefits of tobacco, and encourage individuals who make a quitting effort, should be assisted.
-
Risk in tobacco use should be discussed because if the patient doesn't think quitting is important, you must show them the danger of smoking.
-
Roadblocks should be assessed as the patient has a feel confident to make the ability to quit, you should use the Roadblocks strategy.
-
It is critical to end on a positive note when patients are not prepared to quit while still providing an invitation to return if they change their mind.
-
motivational and brief. Table 2 discusses effective ideas for implementing brief motivational assistance in primary care.
-
You shou8ld encourage a patient to show how quitting will be helpful for them. "How is quitting most relevant to you?" , or if you suppose smoking is bad, for your health".'
-
Motivating a person through providing the greatest and most effective assistance in improving their disease status situation .
-
Social situations include home, with the family or other close people, which is a important factor, ,
-
The the medical professional should make sure that they express that it is bad to have cancer.
-
An example is, "what do you know about the risks."
-
Shortness can be a great way of providing more context so that people will see the truth in smoking, or an implication of harm on pregnancy or in fertility,
-
examples can cause strokes or some cancers or other health issues.
-
Improved health will be effective
-
"How often do you stop the taste of tobacco" Rewards are to make patients get to feel better, can improve, such as getting a home that does not have strong odors and a a well body.
-
Roadblocks of asking, "How will it affect you?", and should provide problem solving counseling and medication that can address barriers.
-
An example is nicotine replacing other substances which allow cravings to not be a problem and gives the determination to carry on.
-
Repetition includes a repeat evaluation and in being ready and to repeat it with more dates.
Strengthening Oral Health Care Systems to improve integrated delivery of Brief Intervention By Professionals
- More than two-thirds of the health-care professionals dont think it is effective to have a whole healthcare program as they are concerned about patient tobacco usage. These are important to have health professionals who are responsible in handling.
- The building plans are to provide service, workers, information, medical things, financing , and governance.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.