Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue?
- Is avascular
- Contains abundant blood vessels (correct)
- Exhibits polarity
- Has a basement membrane
What separates epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue?
What separates epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue?
- Basal surface
- Apical membrane
- Intercellular junctions
- Basement membrane (correct)
Which type of epithelial tissue is specialized for secretion?
Which type of epithelial tissue is specialized for secretion?
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- Transitional epithelium
- Glandular epithelium (correct)
Which of the following best describes the arrangement of epithelial cells?
Which of the following best describes the arrangement of epithelial cells?
What is a distinguishing feature of epithelial cells regarding their surface?
What is a distinguishing feature of epithelial cells regarding their surface?
What is the primary characteristic of dense regular connective tissue?
What is the primary characteristic of dense regular connective tissue?
Which type of cartilage is known for having chondrocytes housed in lacunae?
Which type of cartilage is known for having chondrocytes housed in lacunae?
What type of loose connective tissue provides protective cushioning and insulation?
What type of loose connective tissue provides protective cushioning and insulation?
Elastic connective tissue primarily allows for what function?
Elastic connective tissue primarily allows for what function?
In which structure would you find dense irregular connective tissue?
In which structure would you find dense irregular connective tissue?
Which component in cartilage is responsible for producing chondroitin sulfates?
Which component in cartilage is responsible for producing chondroitin sulfates?
Where are reticular fibers primarily found?
Where are reticular fibers primarily found?
What is the primary function of lacunae within cartilage?
What is the primary function of lacunae within cartilage?
What type of cartilage provides flexible support and is predominantly found in the external ear?
What type of cartilage provides flexible support and is predominantly found in the external ear?
Where is fibrocartilage primarily located in the body?
Where is fibrocartilage primarily located in the body?
Which type of membrane is the thickest and covers the body surface?
Which type of membrane is the thickest and covers the body surface?
What is the primary function of the synovial membrane?
What is the primary function of the synovial membrane?
What type of connective tissue forms an imperceptible network providing support in various locations?
What type of connective tissue forms an imperceptible network providing support in various locations?
What is the primary role of mucous membranes?
What is the primary role of mucous membranes?
Which cartilage type is known for being the most abundant in the body?
Which cartilage type is known for being the most abundant in the body?
What is a primary characteristic of serous membranes in the body?
What is a primary characteristic of serous membranes in the body?
What is a key characteristic of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is a key characteristic of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which of the following types of epithelium lines the hollow organs of the urinary system?
Which of the following types of epithelium lines the hollow organs of the urinary system?
What feature distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from typical columnar epithelium?
What feature distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from typical columnar epithelium?
Which component forms the structural matrix that holds cells and fibers in connective tissue?
Which component forms the structural matrix that holds cells and fibers in connective tissue?
Which layer is NOT a part of the basement membrane?
Which layer is NOT a part of the basement membrane?
What is the primary function of cilia in pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of cilia in pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Which type of fiber in connective tissue is known for its strength?
Which type of fiber in connective tissue is known for its strength?
Which substance represents the majority composition of the extracellular matrix?
Which substance represents the majority composition of the extracellular matrix?
What is the primary function of the mucous membranes?
What is the primary function of the mucous membranes?
Which of the following structures is NOT lined with mucous membranes?
Which of the following structures is NOT lined with mucous membranes?
What type of cells produce mucus in the epithelial lining of mucous membranes?
What type of cells produce mucus in the epithelial lining of mucous membranes?
What is the composition of serous membranes?
What is the composition of serous membranes?
What is the function of serous fluid?
What is the function of serous fluid?
What is the role of the lamina propria in mucous membranes?
What is the role of the lamina propria in mucous membranes?
Which serous membrane surrounds the lungs?
Which serous membrane surrounds the lungs?
What is NOT a characteristic of serous membranes?
What is NOT a characteristic of serous membranes?
Which statement correctly describes the polarity of epithelial cells?
Which statement correctly describes the polarity of epithelial cells?
What is a general characteristic of epithelial tissue?
What is a general characteristic of epithelial tissue?
What separates epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue?
What separates epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue?
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily responsible for secretion?
Which type of epithelial tissue is primarily responsible for secretion?
Why is epithelial tissue considered avascular?
Why is epithelial tissue considered avascular?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and provides cushioning and support?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and provides cushioning and support?
Which of the following is considered a specialized type of connective tissue?
Which of the following is considered a specialized type of connective tissue?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from other connective tissues?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from other connective tissues?
Which type of connective tissue primarily functions in providing strength while allowing some flexibility?
Which type of connective tissue primarily functions in providing strength while allowing some flexibility?
Which glycosaminoglycan (GAG) is found in proteoglycans that are important for cartilage structure?
Which glycosaminoglycan (GAG) is found in proteoglycans that are important for cartilage structure?
What defines keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What defines keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which statement accurately describes nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which statement accurately describes nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is a key characteristic of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is a key characteristic of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of cilia in pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of cilia in pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Which layer is part of the basement membrane?
Which layer is part of the basement membrane?
What are the primary components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in connective tissue?
What are the primary components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in connective tissue?
What type of fibers in connective tissue is known for its elasticity?
What type of fibers in connective tissue is known for its elasticity?
Which polysaccharides are known as glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the ECM?
Which polysaccharides are known as glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in the ECM?
What is the main function of mucous membranes?
What is the main function of mucous membranes?
Which type of cell is responsible for producing mucus in mucous membranes?
Which type of cell is responsible for producing mucus in mucous membranes?
What layers comprise the structure of mucous membranes?
What layers comprise the structure of mucous membranes?
What is the primary characteristic of serous membranes?
What is the primary characteristic of serous membranes?
What is a primary characteristic of dense irregular connective tissue?
What is a primary characteristic of dense irregular connective tissue?
Which of the following locations would be lined by mucous membranes?
Which of the following locations would be lined by mucous membranes?
Which type of connective tissue serves as a protective cushion and performs insulation?
Which type of connective tissue serves as a protective cushion and performs insulation?
What terminology is used to describe the two layers of serous membranes?
What terminology is used to describe the two layers of serous membranes?
What type of cells are primarily found in cartilage?
What type of cells are primarily found in cartilage?
What type of body cavities are lined by serous membranes?
What type of body cavities are lined by serous membranes?
Which of the following structures primarily contains elastic connective tissue?
Which of the following structures primarily contains elastic connective tissue?
Which fluid produced by serous membranes resembles blood serum?
Which fluid produced by serous membranes resembles blood serum?
Which component primarily makes up the extracellular matrix in cartilage tissue?
Which component primarily makes up the extracellular matrix in cartilage tissue?
What type of loose connective tissue forms the lamina propria of mucous membranes?
What type of loose connective tissue forms the lamina propria of mucous membranes?
What is the primary function of lacunae in cartilage?
What is the primary function of lacunae in cartilage?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by having a 'bubble-like' appearance and a small amount of matrix?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by having a 'bubble-like' appearance and a small amount of matrix?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Major Tissue Types
- Four major tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
- Tissues consist of groups of similar cells working together for specific functions.
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
- Two main types: glandular (specialized for secretion) and covering & lining (covers body surfaces).
- Separated from connective tissues by a basement membrane.
- Avascular (no blood supply) but innervated (supplied with nerves).
- Cells exhibit polarity, with distinct apical and basal surfaces.
- Rapid reproduction leads to quick healing.
Classification of Epithelial Tissues
- Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium has dead cells packed with keratin.
- Nonkeratinized type (alive, no keratin) lines the mouth, esophagus, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium appears stratified but is a single layer; has varying cell heights and involves cilia and mucus secretion. Common in upper respiratory passages.
Basement Membrane Structure
- Thin, acellular, and part of the extracellular matrix (ECM).
- Located between epithelial tissue and underlying connective tissue.
- Composed of two layers: basal lamina (lamina lucida and lamina densa) and reticular lamina.
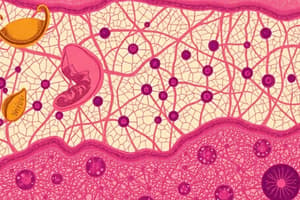
Connective Tissue Structure
- Extracellular matrix (ECM) consists of a gel-like material with fibers and fluid.
- Contains collagen and elastic fibers for structural support and elasticity.
- Types of connective tissue include dense regular, dense irregular, elastic, loose (areolar, adipose, reticular).
Types of Connective Tissue
- Dense Regular: Collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles, resists tension, found in tendons and ligaments.
- Dense Irregular: Fibers arranged in various planes, resists tension from multiple directions, found in the dermis and joint capsules.
- Elastic: Rich in elastic fibers, allows recoil after stretching; found in large arteries.
- Loose Areolar: Forms lamina propria, supports mucous membranes in various tracts.
- Adipose: Provides cushioning and insulation; stores energy.
- Reticular: Forms a supportive network for blood cells in lymphoid organs.
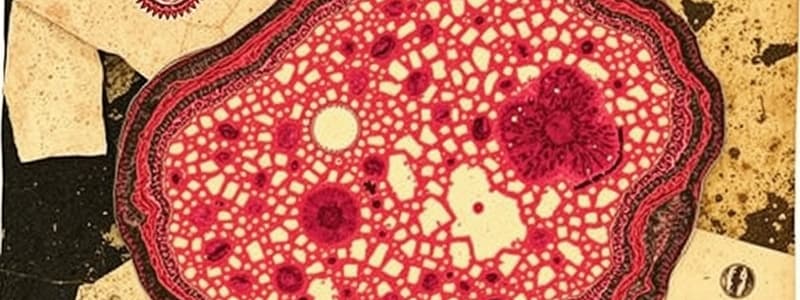
Skeletal Cartilage Composition
- A type of dense connective tissue consisting of chondrocytes within lacunae in the extracellular matrix.
- Contains collagenous fibers and chondroitin sulfates, produced by chondroblasts.
Types of Cartilage in Skeletal System
- Elastic: Predominant elastic fibers, provides flexible support (external ear).
- Fibrocartilage: Tough and shock-absorbing, found between vertebrae.
- Hyaline: Most abundant, forms costal cartilage of ribs, supports joints, and provides padding.
Body Membranes
- Thin sheets of tissue covering and lining body structures, consist of epithelial and connective tissue layers.
- Types of membranes include:
- Synovial: Lines joint cavities, secretes synovial fluid for lubrication.
- Cutaneous: Skin, the thickest membrane, covers body surface.
- Mucous: Lines open body cavities (respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive), produces mucus for protection and lubrication.
- Serous: Lines closed body cavities, consists of layers with mesothelium, secretes serous fluid to reduce organ friction, includes pericardium, pleura, and peritoneum.
Tissue Types
- Four major tissue types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous.
- Tissues consist of similar cells performing common functions.
Epithelial Tissue
-
Types of Epithelial Tissue:
- Glandular epithelium: Specialized for secretion, forms glands.
- Covering & Lining epithelium: Covers body surfaces internally and externally.
-
Characteristics:
- Avascular (lack blood supply) but innervated (supplied with nerves).
- Exhibits polarity with distinct apical and basal surfaces.
- Rapid cell division enables quick healing.
-
Classification:
- Keratinized: Surface cells are dead and filled with keratin.
- Nonkeratinized: Living cells that line moist areas (e.g., mouth, esophagus).
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: Appears stratified but is a single layer with varying cell heights; often contains cilia and mucus-secreting cells.
Basement Membrane
- Thin, acellular layer separating epithelium from underlying connective tissue.
- Composed of two layers:
- Basal Lamina: Contains lamina lucida and lamina densa.
- Reticular Lamina: Provides structural support.
Connective Tissue
-
Comprises the extracellular matrix (ECM) and cells.
-
Components: Gel-like matrix consisting of water (90%) and large organic molecules (10%).
-
Fibers:
- Collagen fibers: Strongest, forming networks for support.
- Elastic fibers: Allow tissues to recoil after stretching.
-
Types of Connective Tissue:
- Proper (loose and dense)
- Specialized (bone, blood, cartilage).
Loose vs. Dense Connective Tissue
-
Loose Connective Tissue:
- Areolar tissue: Forms lamina propria in mucous membranes.
- Adipose tissue: Provides insulation and energy storage.
- Reticular tissue: Supports blood cells in lymphoid organs.
-
Dense Connective Tissue:
- Dense Regular: Parallel collagen fibers resist unidirectional tension (e.g., tendons, ligaments).
- Dense Irregular: Collagen fibers arranged in multiple planes resist tension from various directions.
- Elastic: Contains high proportions of elastic fibers for recoil (e.g., arterial walls).
Cartilage
- A type of dense connective tissue consisting of chondrocytes in lacunae within a firm matrix.
- Lacks blood supply and nerve fibers, making it avascular.
Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline Cartilage: Provides support with flexibility, found in the nose, and articulating surfaces of bones.
- Elastic Cartilage: Contains more elastic fibers for flexibility, found in the ear.
- Fibrocartilage: Very strong, withstands heavy pressure and tension; found in intervertebral discs.
Membranes
-
Mucous Membranes (Mucosa):
- Line cavities open to exterior (e.g., respiratory, digestive, urinary tracts).
- Composed of epithelial tissue with goblet cells producing mucus.
-
Serous Membranes (Serosa):
- Line closed body cavities; consist of mesothelium resting on connective tissue.
- Secretes serous fluid to reduce friction between organs.
- Major types include pericardium, pleural, and peritoneum.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.