Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of tissue is described as sheet-like and covers surfaces or lines cavities?
Which type of tissue is described as sheet-like and covers surfaces or lines cavities?
- Epithelial tissue (correct)
- Muscle tissue
- Connective tissue
- Nervous tissue
Connective tissue is responsible for covering surfaces of organs in the body.
Connective tissue is responsible for covering surfaces of organs in the body.
False (B)
What is histology?
What is histology?
The study of tissues, especially their structure and arrangement.
Epithelial tissue is often found above a __________ tissue layer.
Epithelial tissue is often found above a __________ tissue layer.
Match the type of epithelial tissue to its characteristic:
Match the type of epithelial tissue to its characteristic:
What is the primary function of flagella in a cell?
What is the primary function of flagella in a cell?
Cilia are only motile and do not ever exist as nonmotile structures.
Cilia are only motile and do not ever exist as nonmotile structures.
What are pseudopodia and their primary function?
What are pseudopodia and their primary function?
Root hairs aid in the absorption of water from the soil through the process of _____ .
Root hairs aid in the absorption of water from the soil through the process of _____ .
Match the following cell structures with their primary functions:
Match the following cell structures with their primary functions:
Which type of epithelial tissue is found lining the trachea and bronchi?
Which type of epithelial tissue is found lining the trachea and bronchi?
Erythrocytes are part of the immune system.
Erythrocytes are part of the immune system.
What is the primary function of neurons?
What is the primary function of neurons?
The type of muscle tissue that is involuntary and found in the small intestine is called __________.
The type of muscle tissue that is involuntary and found in the small intestine is called __________.
Match the types of connective tissue with their corresponding descriptions:
Match the types of connective tissue with their corresponding descriptions:
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial cells?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium is typically found in the urinary tract.
Stratified squamous epithelium is typically found in the urinary tract.
Name the three basic types of neurons.
Name the three basic types of neurons.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Tissue Structure and Function
- Tissue is an aggregation of cells and cell products of similar structure that perform a common function.
- Histology is the study of tissues, emphasizing their structure and arrangement.
Basic Tissue Types
- Four main tissue types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous.
- An organ is a functional unit comprised of an aggregation of tissues.
- A system consists of organs working together to perform specific functions.
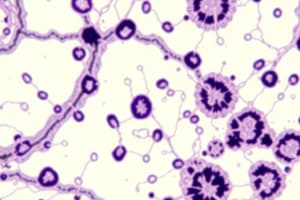
Epithelial Tissue
- Composed of sheet-like layers of cells that cover surfaces and line cavities.
- Contains glandular cells for fluid secretion, e.g., endothelium lining blood vessels.
- Key locations: epidermis of the skin, lining of hollow organs, and above connective tissue.
Epithelial Cell Shapes
- Squamous: scale-like, resembling pancakes.
- Cuboidal: cube-shaped.
- Columnar: elongated, resembling columns.
Types of Epithelial Tissues
- Simple Epithelium:
- Simple squamous: lining of blood vessels.
- Simple cuboidal: lining of ducts and kidney tubules.
- Simple columnar: lining of the small intestine.
- Pseudostratified columnar: found in the trachea and bronchi.
- Stratified Epithelium:
- Stratified squamous: skin surface.
- Transitional: lining of the urinary tract and bladder.
Functions of Epithelial Cells
- Protection from physical, chemical, and microbial injury.
- Contains nerve endings that respond to stimuli.
- Functions in filtration, secretion, reabsorption, and lubrication of joints.
Connective Tissue
- Connective tissue connects different body parts.
- Types include:
- Loose connective tissue: adipose (fat).
- Dense connective tissue: cartilage and bone.
- Vascular tissue: includes erythrocytes (red blood cells), leucocytes (white blood cells), and platelets.
Muscle Tissue Types
- Smooth Muscle: Involuntary, found in structures like the small intestine.
- Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary, associated with large body movements.
- Cardiac Muscle: Specialized muscle found in the heart.
Nervous Tissue
- Comprises the nerves, spinal cord, and brain; cells are called neurons.
- Functions include generating and transmitting nerve impulses, carrying messages utilizing neurotransmitters, and providing insulation to nerve cells.
Types of Neurons
- Sensory neurons: transmit information from the environment to the CNS.
- Motor neurons: send signals from the CNS to muscles or glands.
- Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons; can vary in axon length.
Cell Modifications
- Flagella: Whiplike structures enabling cell propulsion, connected to cytoplasm.
- Cilia: Hairlike protrusions producing vibratory movement; can be motile or nonmotile (primary cilia).
- Microvilli: Tiny fingerlike projections that increase surface area for absorption and secretion.
- Pseudopodia: Temporary extensions of cytoplasm used in movement and engulfing food (associated with amoebas).
- Root Hairs: Long, thin projections that maximally absorb water through osmosis from soil.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.