Podcast
Questions and Answers
If the President vetoes a bill passed by Congress, what action can Congress take to override the veto?
If the President vetoes a bill passed by Congress, what action can Congress take to override the veto?
- A simple majority vote in both the House and Senate.
- A two-thirds vote in both the House and Senate. (correct)
- A two-thirds vote in the House and a simple majority in the Senate.
- A three-fourths vote in both the House and Senate.
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the system of checks and balances between the legislative and executive branches?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the system of checks and balances between the legislative and executive branches?
- The President issues an executive order without Congressional approval.
- Congress impeaches a federal judge.
- Congress passes a bill, and the President signs it into law. (correct)
- The Supreme Court declares a law passed by Congress to be unconstitutional.
What is the primary role of the Supreme Court in the U.S. government?
What is the primary role of the Supreme Court in the U.S. government?
- Interpreting laws and ensuring their fair application. (correct)
- Enforcing laws passed by Congress.
- Nominating federal officials.
- Declaring war.
Which of the following powers is exclusively reserved for the Senate?
Which of the following powers is exclusively reserved for the Senate?
How does the representation in the House of Representatives differ from that in the Senate?
How does the representation in the House of Representatives differ from that in the Senate?
What check does the President have on the judicial branch?
What check does the President have on the judicial branch?
Which action falls under the responsibility of the executive branch?
Which action falls under the responsibility of the executive branch?
If a state law conflicts with a federal law, which principle dictates which law should be followed?
If a state law conflicts with a federal law, which principle dictates which law should be followed?
Which of the following scenarios demonstrates the legislative branch's power of the purse?
Which of the following scenarios demonstrates the legislative branch's power of the purse?
How does the judicial branch check the power of the executive branch?
How does the judicial branch check the power of the executive branch?
Which action demonstrates the principle of checks and balances?
Which action demonstrates the principle of checks and balances?
What is the role of a conference committee in the lawmaking process?
What is the role of a conference committee in the lawmaking process?
Which scenario exemplifies the division of powers in a federal system?
Which scenario exemplifies the division of powers in a federal system?
What is the most direct effect of the Supremacy Clause?
What is the most direct effect of the Supremacy Clause?
If the President vetoes a bill, what action can Congress take to override the veto and pass the bill into law?
If the President vetoes a bill, what action can Congress take to override the veto and pass the bill into law?
Which of the following powers is shared by both the federal and state governments?
Which of the following powers is shared by both the federal and state governments?
A bill is being debated in the Senate. Several senators propose amendments that fundamentally alter the original intent of the bill. What is the next step in the legislative process if the Senate approves the amended version?
A bill is being debated in the Senate. Several senators propose amendments that fundamentally alter the original intent of the bill. What is the next step in the legislative process if the Senate approves the amended version?
The President nominates a candidate for a federal judgeship. What is the next step in the process of appointing the judge?
The President nominates a candidate for a federal judgeship. What is the next step in the process of appointing the judge?
A state law mandates that all public school students must recite a specific prayer each morning. A group of parents sues the state, arguing that the law violates the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment. Which entity would ultimately decide whether the state law is constitutional?
A state law mandates that all public school students must recite a specific prayer each morning. A group of parents sues the state, arguing that the law violates the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment. Which entity would ultimately decide whether the state law is constitutional?
Congress passes a law regulating intrastate commerce. Several businesses challenge the law, arguing that Congress has exceeded its authority under the Commerce Clause. What is the most likely basis for their argument?
Congress passes a law regulating intrastate commerce. Several businesses challenge the law, arguing that Congress has exceeded its authority under the Commerce Clause. What is the most likely basis for their argument?
Flashcards
Legislative Branch
Legislative Branch
The branch of the U.S. government that creates laws.
Congress
Congress
A body of elected officials that is divided into the House of Representatives and the Senate.
House of Representatives
House of Representatives
435 members, representation based on each state's population. Serves two-year terms.
The Senate
The Senate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Executive Branch
Executive Branch
Signup and view all the flashcards
President
President
Signup and view all the flashcards
Judicial Branch
Judicial Branch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supreme Court
Supreme Court
Signup and view all the flashcards
Judicial Review
Judicial Review
Signup and view all the flashcards
District Courts
District Courts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Checks and Balances
Checks and Balances
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impeachment
Impeachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presidential Veto
Presidential Veto
Signup and view all the flashcards
Override a Veto
Override a Veto
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conference Committee Role
Conference Committee Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism
Federalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delegated Powers
Delegated Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reserved Powers
Reserved Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supremacy Clause
Supremacy Clause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
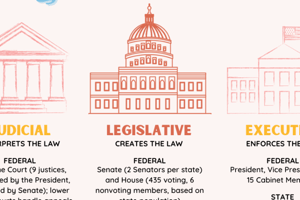
- The US government is structured into three distinct branches: the legislative, the executive, and the judicial.
Legislative Branch
- The legislative branch is Congress, consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate.
- Congress has the responsibility of creating laws.
- Congress holds the power to declare war.
- Congress manages the federal budget through its power of the purse.
- The House of Representatives has 435 members, with representation based on each state's population size.
- Representatives serve two-year terms.
- The Senate has 100 members, with each state having two senators.
- Senators serve six-year terms.
- The main powers of Congress include:
- Passing legislation
- Impeaching and removing federal officials
- Declaring war
- Regulating interstate and foreign commerce
- Controlling federal spending
Executive Branch
- The executive branch is headed by the President.
- The President is responsible for enforcing laws.
- The President is also the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces.
- The President is elected to a four-year term.
- The President can serve a maximum of two terms.
- Key roles of the executive branch include:
- Enforcing laws passed by Congress
- Conducting foreign policy
- Commanding the military
- Appointing federal officials
- Granting pardons and reprieves
- The Vice President assumes the presidency if the President is unable to serve.
- Cabinet members are nominated by the President.
- Cabinet appointments require Senate confirmation.
- Executive agencies and departments, such as the Department of State and the Department of Defense, carry out the day-to-day administration of the government.
Judicial Branch
- The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court.
- The judicial branch interprets laws.
- It ensures laws are applied fairly.
- The Supreme Court has the final say in legal disputes.
- The Supreme Court consists of nine justices.
- Justices are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
- Justices serve lifetime appointments.
- The judicial branch includes:
- District Courts: These are the trial courts of the federal system.
- Courts of Appeals: These courts hear appeals from the district courts.
- Supreme Court: This is the highest court in the nation and has the final say in legal disputes.
- Judicial review is a key power, allowing courts to declare laws or executive actions unconstitutional.
- The Supreme Court's decisions shape the interpretation of laws and set precedents for future cases.
Checks and Balances
- Checks and balances are designed to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
- Congress can impeach and remove the President or federal judges e.g. checks on Executive and Judicial branches.
- The President can veto legislation passed by Congress.
- The judiciary can declare laws unconstitutional.
- Congress can override a presidential veto with a two-thirds vote in both houses.
- The President appoints judges, but the Senate must confirm them.
- Treaties negotiated by the President require Senate ratification.
Lawmaking Process
- A bill can start in either the House or the Senate, except for tax bills, which must originate in the House.
- A bill is introduced, debated, and voted on in each chamber of Congress.
- If the House and Senate pass different versions of the same bill, a conference committee is formed to reconcile the differences.
- The revised bill is then sent back to both chambers for a final vote.
- Once passed by both the House and the Senate, the bill is sent to the President.
- The President can sign the bill into law or veto it.
Federalism
- Federalism is the division of powers between the federal and state governments.
- The Constitution delegates certain powers to the federal government.
- Powers not delegated to the federal government are reserved to the states.
- Both the federal and state governments have the power to tax.
- Both can make and enforce laws
- Both can establish courts.
- States have power over education, intrastate commerce, and local law enforcement.
- The Supremacy Clause establishes that the Constitution and federal laws are the supreme law of the land.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
An overview of the three branches of the U.S. government: the legislative, executive, and judicial. Focus on the structure, roles, and responsibilities of each branch, including Congress, the President, and the Supreme Court. Key powers such as lawmaking, enforcement, and judicial review are highlighted.