Podcast
Questions and Answers
What was the primary mode of transportation used on the Silk Road?
What was the primary mode of transportation used on the Silk Road?
- River transportation
- Maritime trade
- Air travel
- Land route (correct)
What was the primary good traded from China on the Silk Road?
What was the primary good traded from China on the Silk Road?
- Porcelain
- Tea
- Silk (correct)
- Precious stones
Which of the following was NOT a major export of India on the Silk Road?
Which of the following was NOT a major export of India on the Silk Road?
- Glassware (correct)
- Precious stones
- Textiles
- Spices
What was the primary reason for the decline of the Silk Road?
What was the primary reason for the decline of the Silk Road?
Which of the following was NOT a cultural exchange that occurred on the Silk Road?
Which of the following was NOT a cultural exchange that occurred on the Silk Road?
What was the approximate length of the Silk Road?
What was the approximate length of the Silk Road?
What was the primary impact of the Silk Road on the regions it connected?
What was the primary impact of the Silk Road on the regions it connected?
Which of the following was a major export of the Middle East on the Silk Road?
Which of the following was a major export of the Middle East on the Silk Road?
What was the time period during which the Silk Road existed?
What was the time period during which the Silk Road existed?
Which of the following was a result of the Silk Road's cultural exchange?
Which of the following was a result of the Silk Road's cultural exchange?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Silk Road Trade
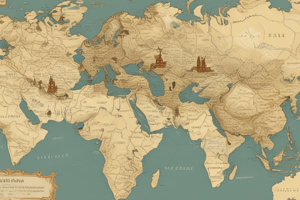
What was the Silk Road?
- A network of trade routes connecting China with the Mediterranean region (Europe, Africa, and the Middle East)
- Spanned over 4,000 miles (6,400 km) and existed from the 2nd century BCE to the 15th century CE
Key Features:
- Land Route: The Silk Road was primarily a land route, with merchants traveling along the Great Wall of China, through the Gobi Desert, and across the mountains of Central Asia
- Maritime Trade: A maritime route also existed, with ships sailing from China to India, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean
Goods Traded:
- Chinese Exports: Silk, tea, porcelain, spices, and precious stones
- Indian Exports: Spices, textiles, and precious stones
- Middle Eastern Exports: Horses, carpets, and glassware
- European Exports: Wine, olive oil, and luxury goods
Cultural Exchange:
- Buddhism: Spread from India to China and other parts of Asia through the Silk Road
- Islam: Spread from the Middle East to China and other parts of Asia through the Silk Road
- Technological Exchange: The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and innovations between civilizations
Impact of the Silk Road:
- Economic Growth: The Silk Road stimulated economic growth and development in the regions it connected
- Cultural Diversity: The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of cultures, ideas, and values between civilizations
- Political Relations: The Silk Road helped establish political relations and diplomatic ties between empires and kingdoms
Decline of the Silk Road:
- Mongol Conquests: The Mongol Empire's conquests in the 13th century CE disrupted the Silk Road and led to its decline
- Rise of Maritime Trade: The rise of maritime trade in the 15th century CE led to a decline in the importance of the Silk Road
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.