Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the grey matter in the brain?
What is the primary function of the grey matter in the brain?
- Regulating hormone production.
- Maintaining balance and coordination.
- Processing neural signals and information. (correct)
- Storing long-term memories.
Which of the following best describes the composition of grey matter?
Which of the following best describes the composition of grey matter?
- It is composed of white adipose tissue.
- It is primarily made up of neuron cell bodies. (correct)
- It contains mainly glial cells.
- It consists mostly of myelinated axons.
How does grey matter contribute to brain function?
How does grey matter contribute to brain function?
- By facilitating communication between different brain regions.
- By fostering emotional responses to stimuli.
- By insulating nerve fibers and increasing signal speed.
- By storing and organizing sensory information. (correct)
In which brain regions is grey matter primarily found?
In which brain regions is grey matter primarily found?
What role does grey matter play in cognitive functions?
What role does grey matter play in cognitive functions?
Flashcards
Grey matter function
Grey matter function
Processes information, controls movement, and enables thought.
Brain function
Brain function
Processing information and controlling actions within the body through nerves.
Brain Processing
Brain Processing
Information handling and decision making within the brain.
Brain Control
Brain Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thought Process
Thought Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
The Nervous System
- The nervous system is one of the most important systems in the body. It acts as the control center and communication network.
- The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Its role is to send electrical signals between the brain and the rest of the body, regulating bodily functions.
Homeostasis and the Nervous System
- Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions to ensure enzymes and cells function effectively.
- This includes blood glucose, body temperature, and water levels.
- Control systems can involve the nervous system (electrical) and the endocrine system (chemical).
Two Main Parts of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The CNS is the command center of the body.
- It processes information and controls all bodily activities (voluntary and involuntary).
- The CNS is made up of the brain and the spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The PNS is made up of all the nerves outside the CNS.
- These nerves branch out from the brain and spinal cord.
- This network connects every area to the CNS, and plays a crucial role in sending and receiving signals.
Central Nervous System (CNS) Details
Brain
- The brain is the control center for the entire body.
- It processes sensory information, thoughts, emotions, and controls body functions (like movement).
- The brain has different regions that handle specific tasks.
Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord acts as a highway for information traveling between the brain and the body.
- It sends instructions from the brain to the body, and carries sensory information back to the brain.
- It coordinates reflexes, which are fast, automatic responses to stimuli.
Brain Anatomy
- The frontal lobe controls problem-solving, emotional traits, reasoning, and voluntary motor activity.
- The parietal lobe controls knowing right from left, sensation, body orientation, and reading.
- The occipital lobe processes vision and color perception.
- The temporal lobe controls understanding language, memory, hearing, and object recognition.
- The brainstem controls breathing, heart rate, alertness, sleep patterns, and body temperature.
Brainstem
- The brainstem includes the medulla, pons, and midbrain.
- The medulla oblongata controls gland function, breathing, and heart rate.
- The pons links the brain to the spinal cord and handles unconscious processes like sleep-wake cycles and breathing.
- The cerebellum controls motor control, balance, posture, and movement.
- The midbrain consists of the center for visual and auditory reflexes, regulating eye movement and pupil dilation.
Cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It has two hemispheres, which control movement, speech, intelligence, emotion, and what we see and hear.
Left vs Right Brain
- The left side of the brain focuses on analysis, logic, ideas, facts, mathematics and training.
- The right side of the brain focuses on creativity, intuition, arts, creation, feeling, and imagination.
Thalamus and Hypothalamus
- The thalamus is involved with sensory and motor information.
- The hypothalamus has major control of the endocrine system.
Grey Matter
- Grey matter in the brain contains neurons which process information and release new information.
- They enable the body to control movement, memory and emotions.
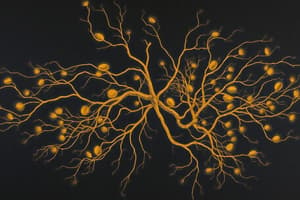
Neuron Parts
- Dendrites receive signals from other cells.
- The cell body organizes and keeps the cell functional.
- The cell membrane protects the cell.
- Axon hillock generates impulse in the neuron.
- Node of Ranvier allows diffusion of ions.
- The Schwann cell produces the myelin sheath.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- The SNS controls voluntary movements of muscles.
- It sends sensory information to the CNS.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- The ANS regulates involuntary functions (heart rate, digestion, and breathing).
Sympathetic Nervous System
- The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations ("fight or flight").
- It increases heart rate and widens airways.
- It slows digestion to provide energy and focus.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
- The parasympathetic nervous system helps the body relax and recover after stress ("rest and digest").
- It slows heart rate and promotes digestion and energy conservation.
How the Nervous System Works
- Neurons communicate using electrical and chemical signals.
- The signals travel along neurons until they reach a synapse (a small gap between neurons).
- Neurotransmitters carry signals across the gap.
Sensory Input
- The nervous system collects information from the external environment (through receptors in the skin, eyes, and ears).
- This process sends signals to the brain.
Integration
- The brain processes and interprets sensory information.
- It decides how to respond.
Motor Output
- The nervous system sends signals to muscles or glands to make the body respond.
- For instance, if the brain detects something is hot, it signals hand muscles to pull away.
Key Takeaways
- The nervous system coordinates bodily functions (thinking, feeling, and movement).
- It maintains homeostasis (balance in the body).
- The system has voluntary and involuntary functions.
- It is essential for overall bodily function.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.