Podcast
Questions and Answers
Short bones are roughly shaped like a cube.
Short bones are roughly shaped like a cube.
True (A)
Short bones are mainly found in your ribs.
Short bones are mainly found in your ribs.
False (B)
Curved bones help to attach muscles to our bones.
Curved bones help to attach muscles to our bones.
True (A)
The shoulder bone is an example of a short bone.
The shoulder bone is an example of a short bone.
The main job of curved bones is to protect internal organs.
The main job of curved bones is to protect internal organs.
The skull forms a cavity for the liver.
The skull forms a cavity for the liver.
The ribs protect internal organs such as the heart and lungs.
The ribs protect internal organs such as the heart and lungs.
The spine provides support for the pectoral and pelvic girdles.
The spine provides support for the pectoral and pelvic girdles.
The skull supports the structures of the face.
The skull supports the structures of the face.
The spine does not protect any organs.
The spine does not protect any organs.
Skeletal muscles are controlled involuntarily.
Skeletal muscles are controlled involuntarily.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart.
Flexion occurs when the angle of a joint decreases.
Flexion occurs when the angle of a joint decreases.
There are four types of muscle tissue in the human body.
There are four types of muscle tissue in the human body.
The shoulder flexes when we throw an underarm.
The shoulder flexes when we throw an underarm.
The femur is the longest and strongest bone in the human skeleton.
The femur is the longest and strongest bone in the human skeleton.
The bones that make up the fingers and toes are called metatarsals.
The bones that make up the fingers and toes are called metatarsals.
The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone.
The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone.
Each of your toes contains three bones.
Each of your toes contains three bones.
The tarsals and metatarsals form the arches of the foot.
The tarsals and metatarsals form the arches of the foot.
The metacarpals in your hands are visible when you make a fist.
The metacarpals in your hands are visible when you make a fist.
The largest bone in the body is the femur.
The largest bone in the body is the femur.
Bones are made entirely of hard material.
Bones are made entirely of hard material.
The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones.
The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones.
The skeleton provides a framework for muscles to attach to create movement.
The skeleton provides a framework for muscles to attach to create movement.
There are six bones in each human ear.
There are six bones in each human ear.
The skull protects the brain.
The skull protects the brain.
The human foot contains 26 bones.
The human foot contains 26 bones.
The image labels the femur as part of the arm.
The image labels the femur as part of the arm.
The foot has more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
The foot has more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
There are 33 joints in the human foot, with 20 of them being actively articulated.
There are 33 joints in the human foot, with 20 of them being actively articulated.
The scapula is located in the leg.
The scapula is located in the leg.
The traps help move your head and assist the upper back when lifting heavy objects.
The traps help move your head and assist the upper back when lifting heavy objects.
The shoulders, or delts, allow for overhead lifting and the rotation of your legs.
The shoulders, or delts, allow for overhead lifting and the rotation of your legs.
The chest muscles control the movement of the arms, help in pushing open doors, and play a role in inhalation.
The chest muscles control the movement of the arms, help in pushing open doors, and play a role in inhalation.
Biceps are primarily responsible for extending the elbow and counteracting actions performed by the triceps.
Biceps are primarily responsible for extending the elbow and counteracting actions performed by the triceps.
The triceps contract to straighten the arm and extend the elbow.
The triceps contract to straighten the arm and extend the elbow.
The forearm allows you to rotate your forearm outward and inward.
The forearm allows you to rotate your forearm outward and inward.
The quads help in the extension and flexion of the knee and hip.
The quads help in the extension and flexion of the knee and hip.
Lats are not involved in any breathing movements.
Lats are not involved in any breathing movements.
The glutes help in raising your knee to your chest.
The glutes help in raising your knee to your chest.
Calves enable the curling of your toes.
Calves enable the curling of your toes.
Hamstrings do not contribute to the extension of the ankle.
Hamstrings do not contribute to the extension of the ankle.
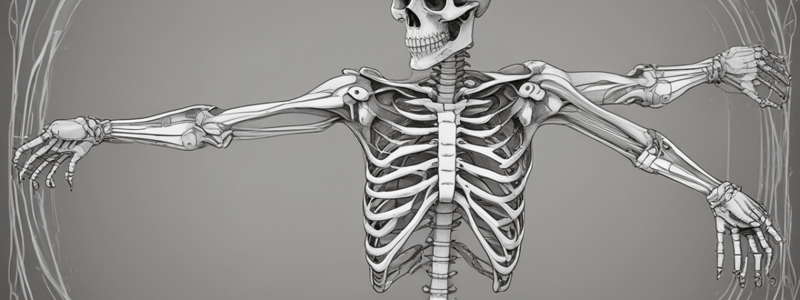
The skeleton is made up of bones, joints, and cartilage.
The skeleton is made up of bones, joints, and cartilage.
The femur is the smallest bone in the human body.
The femur is the smallest bone in the human body.
A shoulder joint extends when the humerus moves backwards from the rest of the body.
A shoulder joint extends when the humerus moves backwards from the rest of the body.
There are three bones in each ear that help with hearing.
There are three bones in each ear that help with hearing.
Extension of the hip joint occurs when the femur moves forward.
Extension of the hip joint occurs when the femur moves forward.
Bones are very heavy, which is why they are strong.
Bones are very heavy, which is why they are strong.
The elbow extends when performing a split leap.
The elbow extends when performing a split leap.
The long bones in the body include the femur, humerus, and bones of fingers and toes.
The long bones in the body include the femur, humerus, and bones of fingers and toes.
The human skeleton has 106 bones.
The human skeleton has 106 bones.
The take-off knee extends when a high-jumper takes off.
The take-off knee extends when a high-jumper takes off.
Both knees extend when a high-jumper takes off.
Both knees extend when a high-jumper takes off.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Skeleton System
- The skeleton is the central structure of the body, composed of bones, joints, and cartilage.
- It provides a framework for muscles to attach, giving us our human shape.
- The human skeleton contains 206 bones, with 6 tiny bones in the middle ear that function in hearing.
- The largest bone in the body is the femur (thigh bone).
- Bones are strong but light, with lots of air under the surface, and store minerals needed by the body.
4 Functions of the Skeleton
- Support: Provides a framework to support the organs and tissues of the body.
- Protection: Protects internal organs, such as the brain, heart, lungs, and other viscera.
- Movement: Provides a framework for muscles to attach, allowing for movement through muscle contraction.
- Supply & Storage: A source of red blood cells (transport oxygen) and white blood cells (fight infection) formed within the bone marrow.
Types of Bones
- Long Bones: Longer than they are wide, examples include femur, humerus, and bones of fingers and toes.
- Short Bones: Equal proportions, roughly shaped like a cube, examples include bones of wrists and ankles.
- Curved Bones: Thin and slightly curved, examples include skull, scapula, and ribs.
- Curved bones protect internal organs, attach muscles to bones, and provide stability to joints.
Functions of Important Bones
- Skull: Forms the head, supports face structures, forms a cavity for the brain, and protects the brain from injury.
- Ribs: Protects internal organs, provides support, and aids in respiration.
- Spine: Protects the spinal cord, provides stiffening for the body, and attaches to pectoral and pelvic girdles.
The Human Skeleton
- The legs support and bear the weight of the upper body, and allow for daily activities.
- The bones that make up the fingers and toes are called phalanges.
- The femur is the longest and strongest bone in the human skeleton, and articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone to form the hip joint.
Types of Muscle
- Smooth Muscle: Involuntary, found in internal organs, causes movements within the body.
- Cardiac Muscle: Involuntary, found only in the heart.
- Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary, attached to bones, controls movement.
Types of Movement
- Flexion: Bending a joint, decreasing the angle of the joint.
- Extension: Straightening a joint, increasing the angle of the joint.
Functions of Muscles
- Traps: Allows for head movement, helps with upper back lifting.
- Shoulders: Allows for overhead lifting, arm rotation.
- Chest: Controls arm movement, pushes open doors, aids in inhalation.
- Biceps: Helps with curling motion, flexing the elbow, controls shoulder and elbow.
- Triceps: Contracts to straighten the arm, extends the elbow, counteracts biceps action.
- Lats: Allows for support, sitting up, tilting the pelvis, bending the lower spine, aids in breathing and posture.
- Glutes: Allows for leg movement, prevents knee buckling, aids in squats, climbing stairs, standing, and walking.
- Hamstrings: Allows for knee and hip movement, prevents knee buckling, aids in running, jumping, and squatting.
- Calves: Helps with ankle movement, curling toes, bending the knee.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.