Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does a System Sequence Diagram (SSD) primarily emphasize?
What does a System Sequence Diagram (SSD) primarily emphasize?
- Events that cross the system boundary from actors to systems (correct)
- The graphical representation of object interactions
- The specific attributes of each object
- The internal workings of the system
Which elements should be specified in a System Sequence Diagram?
Which elements should be specified in a System Sequence Diagram?
- Internal tasks and algorithms of the system
- The physical layout of the components in the system
- Only the names of the external actors involved
- Order of external actors and their respective messages (correct)
In the context of a System Sequence Diagram, what is meant by treating systems as a black box?
In the context of a System Sequence Diagram, what is meant by treating systems as a black box?
- Presenting a detailed model of the system's architecture
- Concentrating on the inputs and outputs without detailing internal processes (correct)
- Focusing solely on the algorithms used within the system
- Ignoring all external factors influencing system performance
What should each use case have according to the guidelines for System Sequence Diagrams?
What should each use case have according to the guidelines for System Sequence Diagrams?
What type of diagram helps summarize the events generated by external actors in relation to use cases?
What type of diagram helps summarize the events generated by external actors in relation to use cases?
What do interaction diagrams primarily represent in UML dynamic modeling?
What do interaction diagrams primarily represent in UML dynamic modeling?
Which types of diagrams are classified as dynamic diagrams in UML?
Which types of diagrams are classified as dynamic diagrams in UML?
What is the main purpose of using use case diagrams in software engineering?
What is the main purpose of using use case diagrams in software engineering?
Which of the following statements about static diagrams is true?
Which of the following statements about static diagrams is true?
Dynamic modeling in UML is necessary to link which two aspects of system design?
Dynamic modeling in UML is necessary to link which two aspects of system design?
What do state diagrams specifically describe within UML?
What do state diagrams specifically describe within UML?
Which of the following best describes an interaction between objects in dynamic modeling?
Which of the following best describes an interaction between objects in dynamic modeling?
What is meant by 'fork & cascade' in the context of UML modeling?
What is meant by 'fork & cascade' in the context of UML modeling?
What does a communication diagram add to an object diagram?
What does a communication diagram add to an object diagram?
How is object creation represented in a communication diagram?
How is object creation represented in a communication diagram?
What is the primary difference between a sequence diagram and a collaboration diagram?
What is the primary difference between a sequence diagram and a collaboration diagram?
Which of the following best describes the concept of activation boxes in interaction diagrams?
Which of the following best describes the concept of activation boxes in interaction diagrams?
In a collaboration diagram, how can object destruction be indicated?
In a collaboration diagram, how can object destruction be indicated?
What does the notation '1.1' signify in a collaboration diagram?
What does the notation '1.1' signify in a collaboration diagram?
Which statement accurately describes messages to 'self' or 'this' in interaction diagrams?
Which statement accurately describes messages to 'self' or 'this' in interaction diagrams?
What is a key purpose of conditions and iterations in interaction diagrams?
What is a key purpose of conditions and iterations in interaction diagrams?
What are the system events in the 'Buy a Beverage' use case?
What are the system events in the 'Buy a Beverage' use case?
Which strategy minimizes the knowledge that the user interface must have of the business model?
Which strategy minimizes the knowledge that the user interface must have of the business model?
What is a major disadvantage of using a One Central Class strategy?
What is a major disadvantage of using a One Central Class strategy?
What is the purpose of sending a message to the corresponding actor class?
What is the purpose of sending a message to the corresponding actor class?
Which problem can a division into several packages help alleviate?
Which problem can a division into several packages help alleviate?
Which option best describes the interface's knowledge requirement when using One Central Class?
Which option best describes the interface's knowledge requirement when using One Central Class?
In the context of interaction diagrams, what are the messages that the interface sends used for?
In the context of interaction diagrams, what are the messages that the interface sends used for?
What is a central class often associated with in a One Central Class strategy?
What is a central class often associated with in a One Central Class strategy?
What primarily distinguishes a sequence diagram from a collaboration diagram?
What primarily distinguishes a sequence diagram from a collaboration diagram?
What is one of the weaknesses of sequence diagrams?
What is one of the weaknesses of sequence diagrams?
In building a sequence diagram, what should be the first step?
In building a sequence diagram, what should be the first step?
How are the strengths of communication diagrams characterized compared to sequence diagrams?
How are the strengths of communication diagrams characterized compared to sequence diagrams?
What aspect of a use case is crucial when considering the starting point for the first message in a sequence diagram?
What aspect of a use case is crucial when considering the starting point for the first message in a sequence diagram?
What role do post-conditions of use cases play in creating a sequence diagram?
What role do post-conditions of use cases play in creating a sequence diagram?
Which of the following statements is TRUE about sequence diagrams?
Which of the following statements is TRUE about sequence diagrams?
What is a primary characteristic of a collaboration (communication) diagram?
What is a primary characteristic of a collaboration (communication) diagram?
What is a key advantage of using use case objects in object-oriented modeling?
What is a key advantage of using use case objects in object-oriented modeling?
What is one disadvantage of defining classes for each use case?
What is one disadvantage of defining classes for each use case?
How can a message be sent to another object without direct association in an interaction diagram?
How can a message be sent to another object without direct association in an interaction diagram?
What limitation is associated with using an Actor-Class for a Guest in an application?
What limitation is associated with using an Actor-Class for a Guest in an application?
What is a potential complication when there are two actors initiating an interaction?
What is a potential complication when there are two actors initiating an interaction?
What is a disadvantage of having a large number of use case classes?
What is a disadvantage of having a large number of use case classes?
Why might using actors as classes complicate traceability?
Why might using actors as classes complicate traceability?
In the context of sending messages in an interaction diagram, what does a fork do?
In the context of sending messages in an interaction diagram, what does a fork do?
Flashcards
Interaction Diagrams
Interaction Diagrams
UML diagrams that visualize the interaction between objects in a system.
Sequence Diagrams
Sequence Diagrams
UML diagrams that show the sequential order of messages exchanged between objects over time.
Collaboration Diagrams
Collaboration Diagrams
UML diagrams that focus on the relationships and dependencies between objects, without a strict time order.
System Sequence Diagram
System Sequence Diagram
Signup and view all the flashcards
State Diagrams
State Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Activity Diagrams
Activity Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dynamic Modeling
Dynamic Modeling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Behavior (Operations) defined for each class
Behavior (Operations) defined for each class
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Sequence Diagram (SSD)
System Sequence Diagram (SSD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Event
System Event
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main Success Scenario
Main Success Scenario
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collaboration (Communication) Diagrams
Collaboration (Communication) Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Finding Message Originator
Finding Message Originator
Signup and view all the flashcards
Message Flow Analysis
Message Flow Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-condition Validation
Post-condition Validation
Signup and view all the flashcards
State Transition Diagrams
State Transition Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scenario Exploration for Interaction Diagrams
Scenario Exploration for Interaction Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Object Creation ({new})
Object Creation ({new})
Signup and view all the flashcards
Object Destruction ({destroyed})
Object Destruction ({destroyed})
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multi-Stage Numbers (1.1, 2.1 etc.)
Multi-Stage Numbers (1.1, 2.1 etc.)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Message to 'Self' or 'This'
Message to 'Self' or 'This'
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conversion from Sequence to Collaboration Diagram
Conversion from Sequence to Collaboration Diagram
Signup and view all the flashcards
Use Cases as Classes
Use Cases as Classes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Use Case Objects
Use Case Objects
Signup and view all the flashcards
One Central Class Strategy
One Central Class Strategy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Direct Association
Direct Association
Signup and view all the flashcards
Actor Class Strategy
Actor Class Strategy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Use-Case Class Strategy
Use-Case Class Strategy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fork or Cascade
Fork or Cascade
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fork (Interaction Diagrams)
Fork (Interaction Diagrams)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the advantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
What is the advantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cascade (Interaction Diagrams)
Cascade (Interaction Diagrams)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is another advantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
What is another advantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the disadvantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
What is the disadvantage of the 'One Central Class' strategy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can the problem with the 'One Central Class' strategy be partially resolved?
How can the problem with the 'One Central Class' strategy be partially resolved?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the advantage and disadvantage of the 'Use-Case Class' strategy?
What is the advantage and disadvantage of the 'Use-Case Class' strategy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Software Engineering 1 - Lecture 6 (CS251)
- Lecture covers OO Modeling, Interaction Diagrams (Sequence, Collaboration, & System Sequence Diagrams)
- The lecture objectives are to understand the notation of interaction diagrams, visualizing system-user interaction using various diagrams, and deciding on issues such as forks, cascades, and implementing use cases.
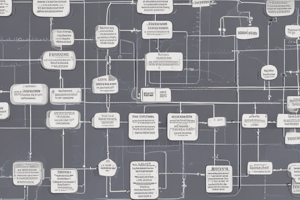
- UML diagrams are described, including Functional Diagrams (Use case diagrams), Static Diagrams (Class, Object, & Package diagrams), and Dynamic Diagrams (Interaction diagrams(Sequence, & Collaboration diagrams), State diagrams & Activity diagrams).
- UML static modeling involves use cases, activity diagrams, and class/object modeling. Use cases describe system behavior, while an initial class model identifies classes and relationships but lacks a complete list of attributes and operations.
- Dynamic Modeling shows object interactions through message sending to implement use case functionality.
- Interaction diagrams are UML notations for dynamic modeling, used for decisions relating to class behavior (operations).
- Two types of interaction diagrams exist: Sequence Diagrams and Communication (Collaboration) Diagrams.
- Sequence Diagrams show object interaction in time sequence (2-dimensional, horizontal for participating objects, and vertical for time).
- Collaboration Diagrams show cooperating objects interacting dynamically via messages. Strengths/Weaknesses for each diagram are described (e.g. time relationship extremely clear in Sequence Diagrams, but overall pattern of message flow is not easily seen).
- A sequence diagram shows participants in an interaction (use case or part of it) and message sequence. Each use case needs one or more sequence diagrams for behavior description.
- Building sequence diagrams starts from use case interactions and identifying the first message origin (often a user interface). Message flows and post-conditions for use cases are considered.
- Object lifelines represent the extent of an object's lifetime in a diagram.
- Newly created objects are placed at their creation point. Destruction, or <
> messages, use a large X on a lifeline to indicate explicit object destruction. - Messages in sequence diagrams include returns and activation boxes, as well as conditional messages.
- Diagrams show conditions and iterations, as well as messages to self/this.
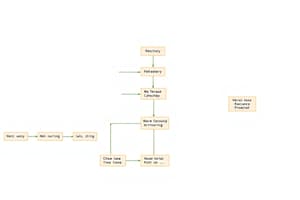
- Example sequence diagrams illustrating use case scenarios (e.g., reporting an emergency, a simple 2BWatch).
- Example conversion from sequence to class diagrams is also provided.
- Communication (collaboration) diagrams are object diagrams with message sends; each message has a multi-stage number (e.g., 1.1.).
- Conversion guidelines from sequence to communication diagrams.
- Object creation and destruction are represented by constraints (new} and {destroyed} in communication diagrams.
- Example use case (vending machine) and its summarization (e.g., buy a beverage) and other functions such as scheduled maintenance, repairs, and loading of items.
- Use cases are converted into system sequence diagrams, emphasizing system events and actor interactions. Strategies for implementing use cases, including one central class, actor class, and use case class approaches for receiving user interface messages are explained.
- Methods for handling forks and cascades in design issues.
- Fork and cascade strategies for interaction between objects without direct associations (ex. Company -> Job -> Person), and specific examples such as collecting employee ages. Alternative methods for designing such interactions are also described.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.