Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which expert system is primarily used for diagnosing diseases?
Which expert system is primarily used for diagnosing diseases?
- MYCIN (correct)
- Financial analysis systems
- Chatbots
- CAD systems
In the context of expert systems, what does CAD stand for?
In the context of expert systems, what does CAD stand for?
- Cognitive Assessment Device
- Custom Application Development
- Computer Aided Design (correct)
- Computerized Analytical Data
What role do chatbots play in expert systems?
What role do chatbots play in expert systems?
- Providing legal advice
- Diagnosing diseases
- Assisting with customer support (correct)
- Analyzing investment options
How does an expert system generate recommendations for treatment in medical diagnostics?
How does an expert system generate recommendations for treatment in medical diagnostics?
Which of the following tasks is NOT typically performed by expert systems?
Which of the following tasks is NOT typically performed by expert systems?
What is a primary function of a Management Information System (MIS)?
What is a primary function of a Management Information System (MIS)?
Which of the following is NOT a function of a Management Information System?
Which of the following is NOT a function of a Management Information System?
In which scenario would a Decision Support System (DSS) be most appropriately used?
In which scenario would a Decision Support System (DSS) be most appropriately used?
Which system is responsible for monitoring stock levels and inventory needs?
Which system is responsible for monitoring stock levels and inventory needs?
Which of the following describes a Decision Support System's data analysis function?
Which of the following describes a Decision Support System's data analysis function?
What role does report generation play in a Management Information System (MIS)?
What role does report generation play in a Management Information System (MIS)?
Which example is considered a type of Management Information System?
Which example is considered a type of Management Information System?
What is a feature of both Management Information Systems and Decision Support Systems?
What is a feature of both Management Information Systems and Decision Support Systems?
What is the primary function of a Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
What is the primary function of a Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
How does a Management Information System (MIS) utilize data from a TPS?
How does a Management Information System (MIS) utilize data from a TPS?
Which of the following is NOT a typical use case for a Transaction Processing System?
Which of the following is NOT a typical use case for a Transaction Processing System?
What might be a consequence of a TPS failing to operate correctly?
What might be a consequence of a TPS failing to operate correctly?
What does a Management Information System primarily provide to its users?
What does a Management Information System primarily provide to its users?
What is the primary purpose of a Decision Support System (DSS)?
What is the primary purpose of a Decision Support System (DSS)?
Which statement best describes the relationship between TPS and MIS?
Which statement best describes the relationship between TPS and MIS?
Which of the following is NOT a function of an Expert System?
Which of the following is NOT a function of an Expert System?
In which organizational context would you expect to find a Transaction Processing System at work?
In which organizational context would you expect to find a Transaction Processing System at work?
Which of the following best defines the primary role of a TPS in an organization?
Which of the following best defines the primary role of a TPS in an organization?
Which type of DSS would be most suitable for analyzing logistics and inventory?
Which type of DSS would be most suitable for analyzing logistics and inventory?
What characteristic distinguishes an Expert System from a traditional information system?
What characteristic distinguishes an Expert System from a traditional information system?
How do advanced versions of Expert Systems improve their performance?
How do advanced versions of Expert Systems improve their performance?
Which application would a Healthcare DSS most likely be used for?
Which application would a Healthcare DSS most likely be used for?
What role does visualization play in a Decision Support System?
What role does visualization play in a Decision Support System?
Which of the following best describes the knowledge representation in Expert Systems?
Which of the following best describes the knowledge representation in Expert Systems?
What is the primary goal of System Analysis and Design?
What is the primary goal of System Analysis and Design?
Which of the following is NOT a responsibility of a System Analyst?
Which of the following is NOT a responsibility of a System Analyst?
Which skill is critical for a System Analyst to understand organizations?
Which skill is critical for a System Analyst to understand organizations?
What essential aspect does a system include beyond hardware and software?
What essential aspect does a system include beyond hardware and software?
Which role is NOT typically associated with System Analysts?
Which role is NOT typically associated with System Analysts?
Which type of approach is essential for successful System Analysis and Design?
Which type of approach is essential for successful System Analysis and Design?
What do information systems primarily do?
What do information systems primarily do?
Which of the following reflects the interpersonal skills required for a System Analyst?
Which of the following reflects the interpersonal skills required for a System Analyst?
What type of knowledge is NOT necessary for System Analysts?
What type of knowledge is NOT necessary for System Analysts?
Which tool is essential for System Analysts to determine system requirements?
Which tool is essential for System Analysts to determine system requirements?
Flashcards
Management Information System (MIS)
Management Information System (MIS)
A system that helps organizations make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. It bridges the gap between data collection and decision-making.
Data Collection (MIS function)
Data Collection (MIS function)
Collecting raw data from various sources within an organization.
Data Processing (MIS function)
Data Processing (MIS function)
Converting raw data into meaningful information through sorting, aggregating, and analyzing.
Data Storage (MIS function)
Data Storage (MIS function)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Report Generation (MIS function)
Report Generation (MIS function)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Problem Identification (MIS function)
Problem Identification (MIS function)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support System (DSS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Data Collection (DSS function)
Data Collection (DSS function)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scenario Evaluation
Scenario Evaluation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decision Support
Decision Support
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visualization
Visualization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expert System
Expert System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knowledge Base
Knowledge Base
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reasoning Algorithms
Reasoning Algorithms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knowledge Representation
Knowledge Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostics
Diagnostics
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Expert Systems?
What are Expert Systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Information Systems in Business
Information Systems in Business
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some applications of Expert Systems?
What are some applications of Expert Systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transaction Processing System (TPS)
Transaction Processing System (TPS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
How TPS Automates Business Operations
How TPS Automates Business Operations
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does a medical diagnostic Expert System work?
How does a medical diagnostic Expert System work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
TPS as the Foundation for Other Systems
TPS as the Foundation for Other Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can an agricultural Expert System help farmers?
How can an agricultural Expert System help farmers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Examples of TPS Applications
Examples of TPS Applications
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role do Expert Systems play in System Analysis and Design (SAD)?
What role do Expert Systems play in System Analysis and Design (SAD)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
MIS: Transforming Data into Insights
MIS: Transforming Data into Insights
Signup and view all the flashcards
MIS: Combining People, Technology, and Processes
MIS: Combining People, Technology, and Processes
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analysis and Design
System Analysis and Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goal of System Analysis and Design
Goal of System Analysis and Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analyst
System Analyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Understanding Organizational Needs
Understanding Organizational Needs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Understanding Technology Capabilities
Understanding Technology Capabilities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Information System
Information System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Application Software
Application Software
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Analysis
System Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Design
System Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
System Thinking
System Thinking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter 1: Introduction to System Analysis Design
- System Analysis and Design Fundamentals (CSC 1403) is the course.
- This chapter introduces System Analysis and Design.
Learning Objectives
- After completing this topic, students should be able to:
- Identify the significance of System Analysis and Design.
- Identify the roles and responsibilities of a System Analyst.
- Compare the four types of Information Systems.
- Identify the tools and techniques for System Analysis and Design.
1.1 Overview of System Analysis and Design
- A method for creating and maintaining systems that perform fundamental business functions.
- The main goal is increasing staff efficiency by applying software to improve business processes.
- Structured methods are important to ensure success.
- Key elements for a Systems Analyst include:
- Understanding organizational objectives, structures, and procedures.
- Exploiting information technology to gain an advantage.
1.1 Overview of System Analysis and Design (continued)
- The primary objective is to improve organizational systems leveraging software development and employee training.
- Application software supports organizational functions and procedures.
1.1 Overview of System Analysis and Design (continued)
- Systems encompass hardware, software, documentation, roles, controls, and the users.
1.1 Overview of System Analysis and Design (continued)
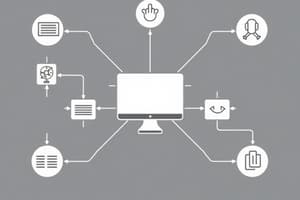
- This section presents a visual diagram illustrating the various components of a Computer-Based Information System Application.
1.1 Overview of System Analysis and Design (continued)
- Benefits of successful System Analysis and Design include:
- Improved Data Accuracy: reduces errors, ensuring data integrity.
- Cost Savings: minimizes the costs of development and upkeep.
- Enhanced Flexibility: easily adapting to system modifications.
- Increased Productivity: streamlined processes and user-friendly interfaces
1.2 Roles as System Analyst
- Investigating the problems and necessities within an organization.
- Establishing the most effective approach for improvement. - Considering People, Methods, and Information Technology.
- Helping users and managers define the requirements for new or enhanced systems.
1.2 Roles as System Analyst (continued)
- Analytical skills for comprehending organizations.
- Problem-solving proficiency.
- Systemic thinking and recognizing organizational and information systems as systems.
- Understanding the potential and limitations of technology.
1.2 Roles as System Analyst (continued)
- Managerial abilities for effectively managing projects, resources, risks, and changes.
- Excellent oral and written communication skills.
1.3 Type of Information System
- Information systems collect, process, store, and disseminate information, utilized by numerous individuals for various tasks, like communication and online shopping.
- Companies use these to communicate with suppliers and customers, operate essential business functions, and administer marketing initiatives.
1.3 Type of Information System (continued)
- Presents a pyramid illustrating different management levels and the corresponding types of information systems.
1.3 Type of Information System (continued)
- Lists different business functions within Operational, Management, and Strategic levels.
a. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
- Designed for handling, recording, and managing routine, repetitive, and structured business transactions efficiently and accurately.
- Automates the process of recording business data (transactions) vital to business operations.
- Offers a foundation for management and decision-support systems.
- Example use cases: Retail point-of-sale systems, Banking ATMs, Airline Reservations, and Manufacturing tracking.
a. Transaction Processing System (TPS) (continued)
- Provides an example of a Transaction Processing System (TPS) through a Payroll example.
b. Management Information System (MIS)
- A system that gathers, processes, stores, and analyzes data to present meaningful insights for managerial decision-making and organizational operations.
- Conveys raw data into usable formats via TPS data.
- Integrates people, technology, and processes to achieve operational efficiency, and a competitive edge.
- Bridging the gap between data gathering and decision-making.
b. Management Information System (MIS) (continued)
- Provides a breakdown of the specific functions of an MIS. This encompasses Data Collection, Processing, Storage, Report Generation, and Problem Identification.
b. Management Information System (MIS) (continued)
- Examples include the Sales Reporting, Inventory Management, Financial Management, and Human Resource Systems.
b. Management Information System (MIS) (continued)
- Displays a diagram illustrating a MIS system encompassing various interconnected functions to generate reports, data processing, and data presentation.
c. Decision Support System (DSS)
- Supports complex decision-making processes,analyzing, providing insights, suggesting potential actions and solutions.
- Provides an interactive environment for decision-making.
- Used by managers and professionals, integrating human judgment and computer-aided analytics for semi/unstructured problems.
c. Decision Support System (DSS) (continued)
- Presents a list of DSS functions: Data Collection, Analysis, Scenario Evaluation, Decision Support, and Visualization
c. Decision Support System (DSS) (continued)
- Presents examples of DSS, including Financial Planning, Supply Chain, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and Healthcare DSS.
c. Decision Support System (DSS) (continued)
- Displays a diagram of an example DSS, depicting interconnection to analytical models, databases, and data collection methods.
d. Expert System
- Emulates human expertise for specific domains.
- Uses a knowledge base and reasoning algorithms for advice, complex problem-solving, and decision-making.
- A powerful tool for solving specialized problems, mirroring expert decision-making in a specific field, but it cannot fully replicate human versatility and creativity.
d. Expert System (continued)
- Lists the functions of an Expert System: Problem-solving, Decision-Making, Diagnostics, Learning and Adaptation.
d. Expert System (continued)
- Presents examples of Expert Systems: Medical Diagnosis, Engineering Design, Customer Support, Financial Planning, and Legal Advisory
d. Expert System (continued)
- Provides an illustration of an Expert System in action, specifically illustrating a medical diagnosis system.
d. Expert System (continued)
- Offers another illustration, emphasizing the application of expert systems in agriculture.
Summary of TPS, MIS, DSS, and ES
- Presents a visual representation of the four types of information systems, showcasing their interrelationships and the flow of information between them.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.