Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary focus of the subject 'Strength of Materials'?
What is the primary focus of the subject 'Strength of Materials'?
- Examining the behavior of solid bodies under various types of loading. (correct)
- Analyzing chemical reactions within solid bodies.
- Investigating the thermal conductivity of composite materials.
- Studying the optical properties of different materials.
What is stress defined as in the context of mechanical properties?
What is stress defined as in the context of mechanical properties?
- The temperature gradient within a solid object.
- The total force applied to a body.
- The deformation of a material under load.
- The intensity of internal forces acting on a specific plane, expressed as force per unit area. (correct)
Which type of stress occurs when a force acts parallel to the area of a material?
Which type of stress occurs when a force acts parallel to the area of a material?
- Normal stress
- Tensile stress
- Compressive stress
- Shear stress (correct)
What does strain measure?
What does strain measure?
According to Hooke's Law, what is the relationship between stress and strain for linearly elastic materials?
According to Hooke's Law, what is the relationship between stress and strain for linearly elastic materials?
What material property does Poisson's ratio describe?
What material property does Poisson's ratio describe?
What information can be obtained from a stress-strain diagram?
What information can be obtained from a stress-strain diagram?
What is yield strength?
What is yield strength?
What does ductility measure?
What does ductility measure?
How is toughness represented on a stress-strain curve?
How is toughness represented on a stress-strain curve?
What is the modulus of resilience?
What is the modulus of resilience?
Which of the following best describes the phenomenon of fatigue in materials?
Which of the following best describes the phenomenon of fatigue in materials?
What is the purpose of the factor of safety (FS) in engineering design?
What is the purpose of the factor of safety (FS) in engineering design?
Under what conditions is creep most pronounced in materials?
Under what conditions is creep most pronounced in materials?
How is hardness related to the strength of a material?
How is hardness related to the strength of a material?
A material with a high yield strength and low ductility is likely to exhibit what kind of failure?
A material with a high yield strength and low ductility is likely to exhibit what kind of failure?
If a material has a Poisson's ratio close to 0.5, what does this indicate about its behavior under tensile stress?
If a material has a Poisson's ratio close to 0.5, what does this indicate about its behavior under tensile stress?
How does an increase in temperature generally affect the tensile strength and ductility of a metal?
How does an increase in temperature generally affect the tensile strength and ductility of a metal?
A cylindrical steel rod is subjected to a tensile force that causes it to elongate. If the axial strain is 0.001 and Poisson's ratio is 0.3, what is the magnitude of the lateral strain?
A cylindrical steel rod is subjected to a tensile force that causes it to elongate. If the axial strain is 0.001 and Poisson's ratio is 0.3, what is the magnitude of the lateral strain?
A hypothetical material exhibits a stress-strain relationship defined by $\sigma = K \epsilon^n$, where $K$ is a material constant and $n$ is the strain-hardening exponent. If $n = 1$, what does this imply about the material's behavior?
A hypothetical material exhibits a stress-strain relationship defined by $\sigma = K \epsilon^n$, where $K$ is a material constant and $n$ is the strain-hardening exponent. If $n = 1$, what does this imply about the material's behavior?
Flashcards
Tensile Stress
Tensile Stress
Normal stress caused by pulling or stretching.
Stress
Stress
Intensity of internal forces on a plane, expressed as force per unit area.
Compressive Stress
Compressive Stress
Normal stress caused by pushing or compressing.
Shear Stress
Shear Stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Strain
Strain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Strain
Normal Strain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shear Strain
Shear Strain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poisson's Ratio
Poisson's Ratio
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yield Strength
Yield Strength
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Behavior
Elastic Behavior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resilience
Resilience
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductility
Ductility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Toughness
Toughness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tensile Strength
Tensile Strength
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hardness
Hardness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatigue
Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Creep
Creep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factor of Safety
Factor of Safety
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Strength of materials deals with the behavior of solid bodies under various types of loading.
- Understanding the relationship between external loads, internal forces, and deformations is crucial.
Mechanical Properties
- Mechanical properties dictate a material's behavior when subjected to loads.
Stress
- Stress represents the intensity of internal forces acting on a specific plane through a point.
- It's quantified as force per unit area.
- Stress is categorized as normal or shear, based on force direction relative to the area.
- Normal stress (σ) signifies force acting perpendicularly to the area.
- Tensile stress is a normal stress caused by pulling or stretching.
- Compressive stress is a normal stress caused by pushing or compressing.
- Shear stress (τ) signifies force acting parallel to the area.
Strain
- Strain measures a material's deformation.
- It's a dimensionless quantity.
- Normal strain (ε) is the change in length per unit length.
- Tensile strain is positive, compressive strain is negative.
- Shear strain (γ) represents the change in angle between originally perpendicular lines.
Hooke's Law
- Hooke's Law states that stress is proportional to strain for linearly elastic materials.
- σ = Eε, where E is the modulus of elasticity (Young's modulus).
- τ = Gγ, where G is the shear modulus of elasticity.
Poisson's Ratio
- Poisson's ratio (ν) is the ratio of lateral strain to axial strain.
- ν = - (lateral strain) / (axial strain).
- It's a material property relating deformation in one direction to perpendicular deformation.
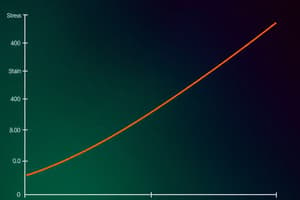
Stress-Strain Diagram
- A stress-strain diagram graphically represents the stress-strain relationship for a material.
- It is obtained by tensile testing a specimen and recording force and elongation.
- The diagram shows elastic behavior, yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility.
Elastic Behavior
- Elastic behavior is a material's ability to return to its original shape after load removal.
- The elastic region of the stress-strain diagram shows a linear stress-strain relationship.
- The slope of this curve in the elastic region represents the modulus of elasticity (Young's modulus).
Yield Strength
- Yield strength is the stress at which permanent deformation begins.
- It's the point where the stress-strain curve deviates from linearity.
- The offset method determines yield strength for materials lacking a clear yield point.
Tensile Strength
- Tensile strength (ultimate tensile strength) is the maximum stress a material can withstand before necking.
- Necking is the localized reduction in cross-sectional area under tension.
Ductility
- Ductility is a material's capacity for large plastic deformations before fracturing.
- It is measured by percent elongation and percent reduction in area.
- Percent elongation is the percentage increase in length at fracture compared to the original length
- Percent reduction in area is the percentage decrease in cross-sectional area at fracture compared to the original area
Resilience
- Resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when deformed elastically and release that energy upon unloading
- Modulus of resilience is the strain energy per unit volume required to stress a material from zero stress to the yield strength
Toughness
- Toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy up to fracture
- It is represented by the area under the stress-strain curve
- A material with high toughness can withstand both high stress and high strain before fracturing
Hardness
- Hardness is the resistance of a material to localized plastic deformation, such as indentation or scratching
- Common hardness tests include Brinell, Rockwell, and Vickers hardness tests
- Hardness is related to the strength of the material
Fatigue
- Fatigue is the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads
- Fatigue strength (endurance limit) is the stress level below which a material can withstand an infinite number of load cycles without failure
- Fatigue life is the number of load cycles that a material can withstand at a specific stress level before failure
Creep
- Creep is the time-dependent deformation of a material under sustained load
- It is more pronounced at elevated temperatures
- Creep strength is the stress that a material can withstand for a specified time period at a specific temperature without exceeding a specified amount of creep
Factor of Safety
- Factor of safety (FS) is the ratio of the allowable stress to the actual stress
- FS = (Allowable Stress) / (Actual Stress)
- It accounts for uncertainties in material properties, loading, and design.
- A higher factor of safety indicates a more conservative design
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.