Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the anterior spinal nerve root?
What is the primary function of the anterior spinal nerve root?
- Motor function (correct)
- Regulation of autonomic functions
- Sensory perception
- Integration of reflexes
From where does the anterior root originate?
From where does the anterior root originate?
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
- Spinal cord (correct)
- Cerebral cortex
Where does the conus medullaris typically terminate in adults?
Where does the conus medullaris typically terminate in adults?
- Between C1 and C2 vertebrae
- Between T12 and L1 vertebrae (correct)
- At the sacrum
- Between L4 and L5 vertebrae
Which anatomical structure is innervated by the cauda equina?
Which anatomical structure is innervated by the cauda equina?
If a patient experiences paralysis of the left leg following an experimental procedure that severs a spinal nerve root, which root was most likely cut?
If a patient experiences paralysis of the left leg following an experimental procedure that severs a spinal nerve root, which root was most likely cut?
After selectively cutting the right anterior root at L1, if the distal end is stimulated, what is the expected outcome?
After selectively cutting the right anterior root at L1, if the distal end is stimulated, what is the expected outcome?
What is the expected result of stimulating the central portion of the transected posterior root at L1 on the right side?
What is the expected result of stimulating the central portion of the transected posterior root at L1 on the right side?
What deficits would a patient exhibit with damage to the cauda equina?
What deficits would a patient exhibit with damage to the cauda equina?
Why is lumbar puncture performed at the L3-L4 or L4-L5 vertebral levels?
Why is lumbar puncture performed at the L3-L4 or L4-L5 vertebral levels?
What neurological deficit arises from severing the anterior root, while allowing the central segment to degenerate?
What neurological deficit arises from severing the anterior root, while allowing the central segment to degenerate?
A person has a spinal cord injury that results in paralysis of both legs. Lesions are suspected at which of the following?
A person has a spinal cord injury that results in paralysis of both legs. Lesions are suspected at which of the following?
What is the appropriate term to describe paralysis affecting both legs?
What is the appropriate term to describe paralysis affecting both legs?
A patient has traumatic quadriplegia; an injury high in the cervical spinal column is verified via radiological exam. What spinal levels are likely involved in this injury?
A patient has traumatic quadriplegia; an injury high in the cervical spinal column is verified via radiological exam. What spinal levels are likely involved in this injury?
Which of the following responses is expected in a Babinski reflex test on a healthy adult?
Which of the following responses is expected in a Babinski reflex test on a healthy adult?
The spinothalamic tract carries which type of sensory information?
The spinothalamic tract carries which type of sensory information?
The pyramidal tracts are most directly involved in controlling what function?
The pyramidal tracts are most directly involved in controlling what function?
What symptoms are expected in patients who sustain damage to the pyramidal tracts?
What symptoms are expected in patients who sustain damage to the pyramidal tracts?
The extrapyramidal tracts have influence on which of the following?
The extrapyramidal tracts have influence on which of the following?
In a patient presenting with a disturbance in voluntary movement, but not paralysis, and also displaying tremors, which of the following brain structure locations should be assessed as the most likely origin of these symptoms?
In a patient presenting with a disturbance in voluntary movement, but not paralysis, and also displaying tremors, which of the following brain structure locations should be assessed as the most likely origin of these symptoms?
What term describes uncoordinated movements due to neurological dysfunction?
What term describes uncoordinated movements due to neurological dysfunction?
Flashcards
Racine rachidienne
Racine rachidienne
Arises from the spinal cord.
Racine antérieure
Racine antérieure
Arises from the spinal cord.
Corne terminale de la moelle
Corne terminale de la moelle
Concludes at L1-L2.
Queue de cheval
Queue de cheval
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racine rachidienne
Racine rachidienne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racine rachidienne
Racine rachidienne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racine antérieure
Racine antérieure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racine antérieure
Racine antérieure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racine postérieure
Racine postérieure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutting anterior root at L3 (left)
Cutting anterior root at L3 (left)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutting posterior root at L3 (right)
Cutting posterior root at L3 (right)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutting anterior root L3 (left) and posterior root at L3 (right)
Cutting anterior root L3 (left) and posterior root at L3 (right)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbar puncture level
Lumbar puncture level
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutting anterieur droite at L1
Cutting anterieur droite at L1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excitation du bout distal de la racine antérieure L1 droite
Excitation du bout distal de la racine antérieure L1 droite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excitation du bout central racine postérieure du L1 droite
Excitation du bout central racine postérieure du L1 droite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excitation bout distal racine postérieure du L1 droite
Excitation bout distal racine postérieure du L1 droite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paralysie lower limbs after accident
Paralysie lower limbs after accident
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paralaysie
Paralaysie
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiologic examen montre la fracture en C4-C5
Radiologic examen montre la fracture en C4-C5
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
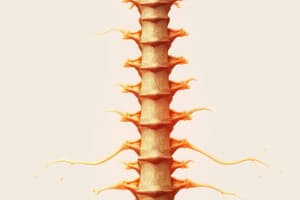
- Spinal nerve roots originate from the spinal cord and are part of the peripheral nervous system.
- The anterior nerve root originates from the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
- The conus medullaris, or terminal cone of the spinal cord, ends at the L1-L2 level.
- The cauda equina, or "horse's tail," innervates the pelvic organs.
Spinal Nerve Roots Count
- There are 33 pairs of spinal nerve roots.
- Spinal nerve roots result from the union of anterior and posterior roots.
- The anterior root originates from the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
Anterior Nerve Root Function
- The anterior nerve root is primarily motor in function.
- Cutting the anterior root at L3 on the left side results in paralysis of the left leg.
- Cutting the posterior root at L3 on the right side results in anesthesia of the right leg.
- Cutting the anterior root at L3 on the left and the posterior root at L3 on the right results in paralysis of the left leg and anesthesia of the right leg.
Lumbar Puncture
- Lumbar punctures are usually performed at the L3-L4 level.
- Severing the right anterior root at L1 causes a loss of motor function in the associated area.
Nerve Stimulation
- Stimulating the distal end of the severed anterior L1 root results in motor activity of the right leg.
- Stimulating the central end of the severed posterior L1 root results in sensation in the right leg.
- Distal stimulation of the posterior L1 nerve root elicits no sensation or motor function.
Spinal Cord Injury
- Bilateral leg paralysis following an accident suggests a fracture of the lumbar spine.
- Paralysis is characterized by bilateral leg paralysis.
- A patient with a C4-C5 fracture on an X-ray exam presents with quadriplegia.
- Cauda equina syndrome includes urinary and fecal retention.
- Anterior nerve roots conduct efferent/centrifugal nerve impulses.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Lumbar punctures are performed to diagnose meningitis.
- Hypersensitivity to stimulation is caused by excitation of the posterior root.
- The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system.
- A dermatome is an area of skin innervated by a posterior nerve root.
- A myotome is a muscle innervated by an anterior nerve root.
Root Degeneration
- Cutting the anterior nerve root leads to distal degeneration.
- After cutting the posterior nerve root, degeneration occurs distally between the spinal cord and the spinal ganglion.
- Ascending tracts in the spinal cord transmit tactile, pain, and general sensory information. These are called "Les faisceaux asce".
- Descending tracts in the spinal cord transmit motor information.
Spinal Cord Structures
- Goll and Burdach's tracts are located in the posterior columns.
- The spinothalamic tract is located in the anterior lateral columns.
- Goll and Burdach's tracts transmit contralateral sensation.
- Spinocerebellar tracts are located in the lateral columns that transmit tactile, painful, and epicritic sensibilities.
Pyramidal Tracts
- Pyramidal tracts are descending tracts.
- Pyramidal tracts conduct voluntary motor information.
- Pyramidal tracts originate in the cerebrum.
- Extrapyramidal tracts originate from the cerebral cortex and pass through the gray nuclei.
Tract Functions
- Extrapyramidal tracts transmit deep sensation and voluntary motor information.
- Severing pyramidal tracts leads to locomotor ataxia.
- Paraplegia is caused by a spinal cord lesion.
- Hemiplegia is caused by a cerebral cortex lesion.
- Ataxia is characterized by uncoordinated movement.
Sensitivity
- Sensitivity of the direction of movement and position is a deep sensibility.
- Central pain is best treated with strong analgesics.
- Reflexes are tested to check the integrity of the nervous system.
- The patellar reflex is elicited by tapping the patellar tendon.
- The Achilles reflex is elicited by tapping the heel.
Reflexes Examination
- The triceps reflex is tested at the elbow.
- The abdominal reflex is elicited by lightly stroking the skin of the abdomen.
- Cremasteric reflexes are elicited by stroking the inner thigh.
- Plantar reflexes are elicited by stroking the sole of the foot.
- A normal plantar reflex involves the big toe flexing downwards while the other toes flex.
- The Babinski sign involves the big toe flexing upwards and the other toes fanning out. It is caused by pyramidal tract lesions.
Brain Structure
- Gray central nuclei are located in the white matter of the cerebrum.
- Excitation of the gray central nuclei causes choreoathetotic movements.
- Destruction of the gray central nuclei causes contralateral paralysis.
- Parkinson's disease results from senescence of the gray central nuclei.
- Choreoathetosis is characterized by abrupt, involuntary movements.
- Concentrating can stop tremors caused by excited gray nuclei.
- Destruction of the gray central nuclei causes rigidity.
Sleep Requirements and Patterns
- Sleep is a basic human need.
- A person deprived of sleep for 10 days may die.
- Newborns sleep about 20 hours a day as a normal sleep requirement.
- Adults require at least 6 hours of sleep per day.
- A 60-year-old has slept approximately 20 years of their life.
- A person who sleeps 10 years can expect to dream approximately 3 years of the time.
- The depth of sleep is measured by sound levels.
Types of sleep & Sleep Phenomena
- Three states of sleep exist: slow-wave sleep, REM sleep, and behavioral sleep.
- Sleep is a misinterpretation of cerebral cortex neurons.
- Sleep deprivation is researched using the neurological vegetative method. Conditioned reflexes are learned rather than innate.
Reflexes and Cortex
- Conditioned reflexes disappear if not reinforced regularly.
- The fourth layer of the cerebral cortex is the internal granular layer.
- The external face of the cerebral cortex contains six convolutions.
- The inferior face of the cerebral cortex has the ascending frontal convolution.
- The convolution of the corpus callosum is located in the lower face of the cerebral cortex.
Brain Function
- The external perpendicular fissure divides the ascending frontal and parietal lobes.
- The ascending frontal lobe controls voluntary movement.
- Rupture of the left meningeal artery causes left hemiplegia.
- Loss of function in the frontal ascending cortex results in general contractions.
- Epileptic convulsions have four stages.
- The cortex of the ascending frontal lobe has the largest surface area near the hands.
Medical Conditions
- Parietal ascending functions include voluntary motor activity and sensitivity.
- Visual areas are located in the occipital lobe.
- The auditory area is located in the temporal lobe.
- The center for sexual sensation is the ascending parietal lobe.
- The center for smell (olfaction) is located in the hippocampus.
- The gustatory area is located on the hippocampus in the Rolandic operculum.
- Loss of vision is called cecity.
- Loss of taste is called ageusia.
- Loss of smell is called anosmia.
- Loss of hearing is called surdity.
- One-sided loss of vision is called hemianopia.
Hemianopia
- Homonymous lateral hemianopia results from total unilateral lesions of the calcarine region.
- The speech center is located in the left cerebral cortex for right-handed people.
- Verbal deafness is the inability to name objects.
- Verbal blindness is the inability to understand written words.
- Aphasia mortice de Broca is the inability to speak due to paralysis of the vocal cords.
- Aphasia sensorielle de Wernicke involves hearing but not understanding.
- Dream analysis involves analyzing the patient's most vivid dreams.
- After birth, newborns sleep 20 hours a day due to physiological sleep patterns.
- A person who eats and drinks enough but doesn't sleep eventually dies.
- Quinal is a medication containing paracetamol and caffeine.
- Blindness caused by a problem in the brain is called central blindness.
Muscle Actions
- Inability to sleep is referred to as hyperesthesia.
- People pretending to be unconscious are checked for pupillary reflexes.
- Swallowing is a normal reflex.
- Examining pupils checks a pupilary reflex.
- The source of oxygen for babies is from umbilical cords
- Inability to urinate is called Syndrome de la queue de chival.
- Retention due to increased sensitivity in reflex areas is called cystitis.
- Constipation is the lack of urine.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.