Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average number of sperms ejaculated by a human male during coitus?
What is the average number of sperms ejaculated by a human male during coitus?
- 500 to 600 million
- 100 to 200 million
- 200 to 300 million (correct)
- 400 to 500 million
What percentage of sperms must have normal shape and size for normal fertility?
What percentage of sperms must have normal shape and size for normal fertility?
- 50%
- 70%
- 40%
- 60% (correct)
What percentage of sperms must show vigorous motility for normal fertility?
What percentage of sperms must show vigorous motility for normal fertility?
- 30%
- 40% (correct)
- 50%
- 60%
What is the composition of semen?
What is the composition of semen?
What is the process of formation of ovum from oogonia called?
What is the process of formation of ovum from oogonia called?
How many oogonia are formed during the embryonic stage?
How many oogonia are formed during the embryonic stage?
What is the stage at which all oogonia undergo first meiotic division and get temporarily arrested?
What is the stage at which all oogonia undergo first meiotic division and get temporarily arrested?
What is the term for the first menstruation that begins at puberty?
What is the term for the first menstruation that begins at puberty?
How many sperms are produced from each spermatocyte?
How many sperms are produced from each spermatocyte?
What is the role of the zona pellucida layer during fertilization?
What is the role of the zona pellucida layer during fertilization?
How many polar bodies are produced from each oocyte during maturation?
How many polar bodies are produced from each oocyte during maturation?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovary later in pregnancy that helps in relaxing the pelvic ligaments?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovary later in pregnancy that helps in relaxing the pelvic ligaments?
What contribution do acrosomal secretions make during fertilization?
What contribution do acrosomal secretions make during fertilization?
What are the additional hormones increased in maternal blood during pregnancy besides hCG and hPL?
What are the additional hormones increased in maternal blood during pregnancy besides hCG and hPL?
What is the primary outcome of fertilization?
What is the primary outcome of fertilization?
Which of the following statements about oocyte development is true?
Which of the following statements about oocyte development is true?
What is the process called that transforms spermatids into spermatozoa?
What is the process called that transforms spermatids into spermatozoa?
Which structure within the sperm is responsible for energy production?
Which structure within the sperm is responsible for energy production?
What is the term for the release of sperm from the seminiferous tubules?
What is the term for the release of sperm from the seminiferous tubules?
Which part of the sperm contains lytic enzymes to assist in penetrating the ovum?
Which part of the sperm contains lytic enzymes to assist in penetrating the ovum?
During which process do the mammary glands start producing milk?
During which process do the mammary glands start producing milk?
Which part of the female anatomy stores the milk before it is ejected?
Which part of the female anatomy stores the milk before it is ejected?
What is the shape of the sperm head?
What is the shape of the sperm head?
Which type of tissue is found in mammary glands?
Which type of tissue is found in mammary glands?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
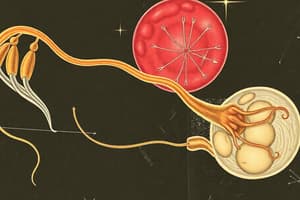
Spermatogenesis and Sperm Structure
- Spermatids transform into spermatozoa through spermiogenesis.
- Sperm heads embed in Sertoli cells before being released from seminiferous tubules via spermiation.
- Structure of sperm includes:
- Head: Oval shaped with a nucleus and an acrosome containing lytic enzymes for penetrating the ovum.
- Middle Piece: Contains mitochondria providing energy for sperm motility.
- Tail: Facilitates movement in a fluid medium.
- Approximately 200 to 300 million sperm are ejaculated during coitus; fertility requires:
- 60% of sperm with normal shape and size.
- 40% demonstrating vigorous motility.
- Sperm combined with seminal plasma forms semen.
Mammary Glands
- Female mammary glands are paired structures composed of glandular and fatty tissue.
- Differentiation occurs during pregnancy; milk production begins towards the end of pregnancy through lactation, aiding in newborn nutrition.
- Mammary gland structure includes:
- 15-20 lobes divided into clusters of alveoli, which secrete milk into cavities (lumens).
- Milk ejection pathway: alveoli → mammary tubules → mammary duct → mammary ampulla → lactiferous duct → nipple.
Fertilization Process
- Fertilization involves the fusion of sperm and ovum, creating a zygote, dependent on simultaneous transport to the ampullary region.
- A sperm contacts the zona pellucida of the ovum, leading to membrane changes to block additional sperm entry.
- Each primary spermatocyte produces four sperm, while each oocyte results in one ovum and three polar bodies.
Hormonal Control During Pregnancy
- Hormones like hCG, hPL, relaxin, estrogens, progestogens, cortisol, prolactin, and thyroxine increase significantly during pregnancy.
- Relaxin assists in preparing the body for childbirth.
Menstrual Cycle and Oogenesis
- Oogenesis is the formation of ovum from oogonia, occurring in fetal ovaries.
- Menstrual cycles reflect cyclical ovarian activity and hormonal changes, averaging 28-29 days.
- Menstruation starts at puberty (menarche) and ceases around age 50 (menopause).
- Oogonia (46 chromosomes, 2n) form approximately 2 million primary oocytes that are arrested at prophase I of the first meiotic division.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.