Podcast
Questions and Answers
What initiates the process of sound transmission through the ear?
What initiates the process of sound transmission through the ear?
- Action potentials in sensory neurons
- Vibrations of the cochlear nerve
- Sound waves striking the tympanic membrane (correct)
- Fluid waves in the cochlear duct
Which structure is responsible for amplifying sound in the middle ear?
Which structure is responsible for amplifying sound in the middle ear?
- Oval window
- Tympanic membrane
- Cochlear duct
- Three ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes (correct)
How do hair cells in the cochlear duct convert mechanical energy into electrical signals?
How do hair cells in the cochlear duct convert mechanical energy into electrical signals?
- Via neurotransmitter release from the oval window
- Through vibrations of the tympanic membrane
- By dissipating energy back into the middle ear
- By opening ion channels upon bending (correct)
What role does the stapes play in the sound transmission process?
What role does the stapes play in the sound transmission process?
Which of the following accurately describes the function of the round window?
Which of the following accurately describes the function of the round window?
What occurs after neurotransmitter release onto sensory neurons in the auditory system?
What occurs after neurotransmitter release onto sensory neurons in the auditory system?
What happens to sound waves when they strike the tympanic membrane?
What happens to sound waves when they strike the tympanic membrane?
The cochlear nerve is responsible for sending action potentials to the brain.
The cochlear nerve is responsible for sending action potentials to the brain.
What is the main function of the stapes in the ear?
What is the main function of the stapes in the ear?
Energy from the waves transfers across the cochlear duct into the tympanic duct and is dissipated back into the middle ear at the ______.
Energy from the waves transfers across the cochlear duct into the tympanic duct and is dissipated back into the middle ear at the ______.
Match the structures of the ear to their functions:
Match the structures of the ear to their functions:
Which process occurs after fluid waves push on the flexible membranes of the cochlear duct?
Which process occurs after fluid waves push on the flexible membranes of the cochlear duct?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
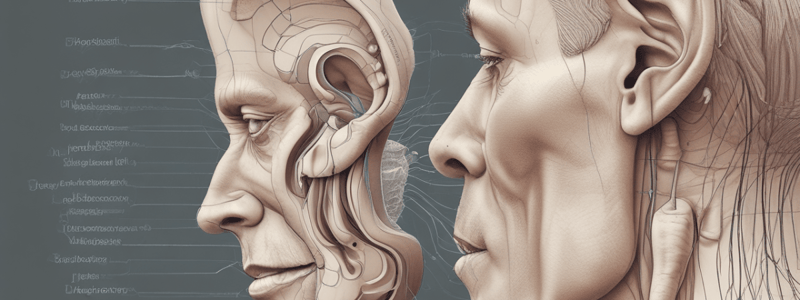
Anatomy of the Human Ear
- The human ear comprises essential components: ear canal, tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, stapes, oval window, round window, cochlear duct, vestibular duct, tympanic duct, and cochlear nerve.
Sound Transmission Process
- Sound waves enter through the ear canal and impact the tympanic membrane, generating vibrations.
- Vibrations from the tympanic membrane are amplified by the three ossicles in the middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes).
- The stapes connects to the oval window, where its vibrations induce fluid waves in the cochlea, a key structure for hearing.
Cochlear Activity
- Fluid waves in the cochlea exert pressure on the membranes of the cochlear duct, leading to bending of hair cells.
- Bending of hair cells opens ion channels, resulting in the generation of electrical signals and neurotransmitter release.
Neural Transmission
- Released neurotransmitters stimulate sensory neurons, triggering action potentials that transmit auditory information through the cochlear nerve to the brain.
Energy Dissipation
- Energy from fluid waves is transferred across the cochlear duct into the tympanic duct, ultimately being dissipated at the round window, allowing for efficient sound processing.
Sound Transmission Process
-
Components of the Ear: Major structures include ear canal, tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, stapes, oval window, round window, cochlear duct, vestibular duct, tympanic duct, and cochlear nerve.
-
Sound Reception: Sound waves hit the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate and initiate the conversion of sound energy into mechanical vibrations.
-
Vibration Transmission: The energy from sound waves is transmitted to the three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) in the middle ear, which amplify the vibrations.
-
Oval Window Interaction: The stapes is connected to the oval window; its vibrations generate fluid waves within the cochlea, crucial for sound perception.
-
Fluid Mechanics: Fluid waves within the cochlear duct exert pressure on flexible membranes, causing hair cells to bend and open ion channels.
-
Signal Transduction: Bending of hair cells leads to neurotransmitter release, which generates action potentials in sensory neurons.
-
Neural Pathway to Brain: Action potentials travel through the cochlear nerve to the brain, enabling sound interpretation.
-
Wave Dissipation: Energy from fluid waves transfers into the tympanic duct and is ultimately dissipated at the round window to prevent damage from excess pressure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.