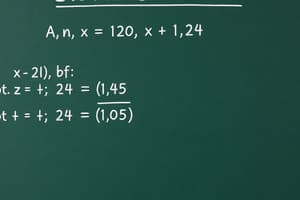Podcast
Questions and Answers
Using Slovin's formula, if you have a population of 2,500 and desire a 95% confidence level, what is the required sample size?
Using Slovin's formula, if you have a population of 2,500 and desire a 95% confidence level, what is the required sample size?
- 286
- 357
- 333
- 345 (correct)
A researcher wants to survey a population of 10,000 individuals. They aim for a 98% confidence level. According to Slovin's formula, what should their sample size be, rounded to the nearest whole number?
A researcher wants to survey a population of 10,000 individuals. They aim for a 98% confidence level. According to Slovin's formula, what should their sample size be, rounded to the nearest whole number?
- 2041 (correct)
- 2439
- 6944
- 1667
A market research team needs to determine the sample size for a survey with a population of 1,500, using Slovin's Formula. If they are willing to accept a 5% margin of error, what will be the sample size?
A market research team needs to determine the sample size for a survey with a population of 1,500, using Slovin's Formula. If they are willing to accept a 5% margin of error, what will be the sample size?
- 300
- 316 (correct)
- 214
- 1429
What is the alpha level (α) associated with a 98% confidence level when using Slovin's formula?
What is the alpha level (α) associated with a 98% confidence level when using Slovin's formula?
A university with 8,000 students wants to survey them about their satisfaction with campus services. If the university uses Slovin's formula with a 95% confidence level, approximately how many students need to be surveyed?
A university with 8,000 students wants to survey them about their satisfaction with campus services. If the university uses Slovin's formula with a 95% confidence level, approximately how many students need to be surveyed?
In Slovin's formula, what does 'N' represent?
In Slovin's formula, what does 'N' represent?
A small town has a population of 800 residents. The local council wants to conduct a survey to gather opinions on a proposed new park, and they want a 98% confidence level. Using Slovin's formula, what is the minimum sample size they should aim for?
A small town has a population of 800 residents. The local council wants to conduct a survey to gather opinions on a proposed new park, and they want a 98% confidence level. Using Slovin's formula, what is the minimum sample size they should aim for?
What adjustment should you make to a sample size calculated using Slovin's formula before conducting a survey?
What adjustment should you make to a sample size calculated using Slovin's formula before conducting a survey?
A researcher aims to understand public perception of a new urban development project prior to its implementation. Which data collection method is most suitable for gathering broad opinions efficiently?
A researcher aims to understand public perception of a new urban development project prior to its implementation. Which data collection method is most suitable for gathering broad opinions efficiently?
A clinical psychologist seeks to deeply understand the experiences of a single patient undergoing a novel therapy for PTSD. Which data collection method would provide the most detailed and nuanced insights?
A clinical psychologist seeks to deeply understand the experiences of a single patient undergoing a novel therapy for PTSD. Which data collection method would provide the most detailed and nuanced insights?
An anthropologist wants to study the daily social interactions within a remote tribe without interfering with their natural behavior. Which data collection method is best suited for this type of unobtrusive research?
An anthropologist wants to study the daily social interactions within a remote tribe without interfering with their natural behavior. Which data collection method is best suited for this type of unobtrusive research?
To determine if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between sunlight exposure and mood, what research method should be used?
To determine if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between sunlight exposure and mood, what research method should be used?
A researcher aims to collect detailed accounts of individual experiences during a natural disaster. This requires direct interaction with the affected individuals to gather comprehensive narratives. Which data collection method is most appropriate?
A researcher aims to collect detailed accounts of individual experiences during a natural disaster. This requires direct interaction with the affected individuals to gather comprehensive narratives. Which data collection method is most appropriate?
A market research firm wants to quickly gauge customer satisfaction with a new product line across a large and diverse customer base. Which data collection method offers the most efficient way to gather this information?
A market research firm wants to quickly gauge customer satisfaction with a new product line across a large and diverse customer base. Which data collection method offers the most efficient way to gather this information?
A university is performing a study on student success after graduation. They intend to track a group of students over a 10 year period, and analyze what factors contributed to their success. Which research method is most appropriate?
A university is performing a study on student success after graduation. They intend to track a group of students over a 10 year period, and analyze what factors contributed to their success. Which research method is most appropriate?
A researcher is hired by the local government to understand why the population in the area is moving away at an alarming rate. The local government wants to take action to solve the problem, and reverse the trend. Which research method should the researcher use?
A researcher is hired by the local government to understand why the population in the area is moving away at an alarming rate. The local government wants to take action to solve the problem, and reverse the trend. Which research method should the researcher use?
In a study examining the effects of a new teaching method on student test scores, which of the following would be considered the population?
In a study examining the effects of a new teaching method on student test scores, which of the following would be considered the population?
A researcher wants to study the political opinions of college students in the United States. Due to resource constraints, they only survey students at 50 randomly selected universities. What does the group of students at those 50 universities represent?
A researcher wants to study the political opinions of college students in the United States. Due to resource constraints, they only survey students at 50 randomly selected universities. What does the group of students at those 50 universities represent?
Which of the following is the best example of a qualitative variable?
Which of the following is the best example of a qualitative variable?
A researcher is studying consumer preferences for different brands of coffee. Which type of data is being collected if the researcher asks participants to rank the coffee brands from most to least preferred?
A researcher is studying consumer preferences for different brands of coffee. Which type of data is being collected if the researcher asks participants to rank the coffee brands from most to least preferred?
Which scenario involves collecting quantitative data?
Which scenario involves collecting quantitative data?
A professor records the final grades (A, B, C, D, or F) of students in a class. Is this data qualitative or quantitative?
A professor records the final grades (A, B, C, D, or F) of students in a class. Is this data qualitative or quantitative?
A study aims to determine if there is a correlation between the number of hours students study per week and their GPA. What type of variables are 'hours of study' and 'GPA' in this study?
A study aims to determine if there is a correlation between the number of hours students study per week and their GPA. What type of variables are 'hours of study' and 'GPA' in this study?
Which of the following best illustrates the use of both qualitative and quantitative variables in a single study?
Which of the following best illustrates the use of both qualitative and quantitative variables in a single study?
A researcher is planning a study in a city with a population of 1,500 people. Using Slovin's formula, what is the minimum sample size required if the researcher wants a 4% margin of error?
A researcher is planning a study in a city with a population of 1,500 people. Using Slovin's formula, what is the minimum sample size required if the researcher wants a 4% margin of error?
In a town with a population of 2,000 people, a survey is conducted with a sample size of 400. What is the margin of error used for this survey based on Slovin's Formula?
In a town with a population of 2,000 people, a survey is conducted with a sample size of 400. What is the margin of error used for this survey based on Slovin's Formula?
A data set is collected to analyze customer satisfaction. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the data points and the data set?
A data set is collected to analyze customer satisfaction. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the data points and the data set?
In the context of data collection, how are samples and populations related to the concept of sets?
In the context of data collection, how are samples and populations related to the concept of sets?
A company is trying to determine the effectiveness of a new marketing strategy. What is the role of statistics in this scenario?
A company is trying to determine the effectiveness of a new marketing strategy. What is the role of statistics in this scenario?
A researcher is studying the heights of all students at a university. In this context, what does the 'population' refer to?
A researcher is studying the heights of all students at a university. In this context, what does the 'population' refer to?
A market research company decides to survey a sample of households in a city to estimate the average household income. If the city has a total of 10,000 households, and the company uses Slovin's formula with a 5% margin of error to determine the sample size, approximately how many households should they survey?
A market research company decides to survey a sample of households in a city to estimate the average household income. If the city has a total of 10,000 households, and the company uses Slovin's formula with a 5% margin of error to determine the sample size, approximately how many households should they survey?
A quality control engineer wants to estimate the proportion of defective items produced in a factory. They plan to sample from the production line. Which statement accurately describes the relationship between the sample and the population in this context?
A quality control engineer wants to estimate the proportion of defective items produced in a factory. They plan to sample from the production line. Which statement accurately describes the relationship between the sample and the population in this context?
When is Slovin's formula most appropriate for determining sample size?
When is Slovin's formula most appropriate for determining sample size?
A researcher aims for a 95% confidence level in their study. According to the information provided, what would be the corresponding error tolerance (e) to use in Slovin’s formula?
A researcher aims for a 95% confidence level in their study. According to the information provided, what would be the corresponding error tolerance (e) to use in Slovin’s formula?
Given a population of 500, which calculation correctly applies Slovin's formula to determine the sample size needed with an error tolerance of 0.05?
Given a population of 500, which calculation correctly applies Slovin's formula to determine the sample size needed with an error tolerance of 0.05?
A town has a total population of 2,000 residents. If a researcher uses Slovin's formula with an error tolerance of 0.03 to determine the sample size for a survey, approximately how many residents should be surveyed?
A town has a total population of 2,000 residents. If a researcher uses Slovin's formula with an error tolerance of 0.03 to determine the sample size for a survey, approximately how many residents should be surveyed?
What happens to the required sample size calculated by Slovin's formula as the error tolerance (e) increases, assuming the population size stays constant?
What happens to the required sample size calculated by Slovin's formula as the error tolerance (e) increases, assuming the population size stays constant?
A market research firm is planning to survey a city with a population of 50,000. They decide to use Slovin's formula because they lack detailed information about residents' preferences. Which error tolerance would result in the smallest sample size?
A market research firm is planning to survey a city with a population of 50,000. They decide to use Slovin's formula because they lack detailed information about residents' preferences. Which error tolerance would result in the smallest sample size?
When using Slovin's formula, if a researcher decreases the error tolerance from 0.05 to 0.01, how is the necessary sample size affected?
When using Slovin's formula, if a researcher decreases the error tolerance from 0.05 to 0.01, how is the necessary sample size affected?
Flashcards
Slovin's Formula
Slovin's Formula
A formula used to calculate the minimum sample size needed for a study.
Data Collection
Data Collection
The process of gathering information for analysis.
Data Set
Data Set
A collection of related data points.
Sample
Sample
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population
Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subset
Subset
Signup and view all the flashcards
Statistics
Statistics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population (in statistics)
Population (in statistics)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Variables
Variables
Signup and view all the flashcards
Qualitative Variable
Qualitative Variable
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quantitative Variable
Quantitative Variable
Signup and view all the flashcards
Qualitative (Example)
Qualitative (Example)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quantitative (Example)
Quantitative (Example)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Qualitative Data (Example.)
Qualitative Data (Example.)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sampling in Statistics
Sampling in Statistics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Error Tolerance (e)
Error Tolerance (e)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calculating Error Tolerance
Calculating Error Tolerance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slovin's Formula Equation
Slovin's Formula Equation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Size (N)
Population Size (N)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sample Size (n)
Sample Size (n)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the margin of error?
What is the margin of error?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is confidence level?
What is confidence level?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is alpha level (e)?
What is alpha level (e)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Slovin's Formula?
What is Slovin's Formula?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is population size (N)?
What is population size (N)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Sample size (n)?
What is Sample size (n)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rounding the sample size
Rounding the sample size
Signup and view all the flashcards
If N=1000 and e=0.05, what is n?
If N=1000 and e=0.05, what is n?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surveys
Surveys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interviews
Interviews
Signup and view all the flashcards
Observations
Observations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Experiments
Experiments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Case Studies
Case Studies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Questionnaires
Questionnaires
Signup and view all the flashcards
In-depth Investigations
In-depth Investigations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Public Opinion Polls
Public Opinion Polls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Statistics looks at a population's behavior by taking a sample.
- It can be impossible to survey an entire population due to money or time constraints.
- Surveying samples are preferrable among researchers to surveying an entire population.
- Slovin's formula is used when there is no pre-existing information about a population.
- Slovin formulated the Slovin's formula in 1960.
- Use the formula to figure out what sample size to take.
Slovin's Formula
- Formula: n = N / (1 + Ne^2),
- n = Number of samples
- N = Total population
- e = Error tolerance level
Example question
-
Use question to find out what sample of population of 1,000 people, taking a survey on soda preferences:
-
Step 1: Figure out your confidence level:
-
e = 1.00 - 0.95 = 0.05
-
e = 1.00 - 0.98 = 0.02.
-
You might want a confidence level of 95% (alpha level of 0.05), good accuracy at the 98% confidence level (alpha level of 0.02).
-
Step 2: Use your data in the formula
-
Use a 95% confidence level
-
Population size of 1,000
-
N = 1000
-
e = 0.05
-
n = 285.7142857
-
Step 3: Round your result:
-
285.7142857 = 286
Data set
- Each piece of gathered information is a data point that makes up a data set.
- A sample represents a set of finite observations.
- Population can be considered an infinite set.
- Collected data in sampling represents a subset of a population.
Definitions
- Statistics: Branch collecting, organizing, and interpreting data to address real world topics.
- Population: Set of all possible cases from which data is collected.
- Ex: A study regarding the average height of students requires the population of all the students in the school.
- Sample:A subset.
- Variables: Vary over time from subject to subject.
- Qualitative variable: Focuses on quality/characteristics of an experimental unit.
- Ex: civil status/gender/color
- Quantitative variable: Measures numerical quantity of experimental unit.
- Ex: age, height, weight, daily allowance
Data Collection Methods
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Predetermined questions gathering opinions/behaviors.
- This is used in social sciences, market research, and public opinion polls, is cost effective, standardised format.
- Disadvantage is the response bias and a limited depth of information
- Interviews: Direct interaction, questions asked and recorded.
- Useful in qualitative research, case studies, and in-depth investigations that allows in-depth exploration, flexibility in questions.
- Disadvantage is its time consuming, potential for interviewer bias
- Observations: Observe and record behavior, events, or phenomena without interaction.
- Used in realism research, which gives firsthand information, minimizes response bias.
- Disadvantage is the observer bias and limited insight into underlying motivations
- Experiments: Manipulate variables to observe the effect on the outcome.
- Helpful in natural science due to controlled conditions help provide case and effect relationships.
- Disadvantage is artificial settings and ethical concerns may limit generalizability.
- Case Studies: Examination of a single person or small people for insight.
- Useful in psychology, medicine, and social science since it is suitable for complex/unique cases.
- Disadvantage is limited data with potential research bias.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.