Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a critical diagnostic factor for identifying cold sores?
What is a critical diagnostic factor for identifying cold sores?
- Location on the body (correct)
- Color of the crust
- Size of the lesions
- Time of year
Which of the following can be a precipitating factor for cold sores?
Which of the following can be a precipitating factor for cold sores?
- Increased hydration
- Regular exercise
- Cold weather
- Sunlight exposure (correct)
How many attacks do most sufferers experience each year?
How many attacks do most sufferers experience each year?
- 3 to 5
- 5 to 10
- 10 to 20
- 1 to 3 (correct)
What should be done if cold sore lesions affect the eye?
What should be done if cold sore lesions affect the eye?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as a trigger for cold sores?
Which factor is NOT mentioned as a trigger for cold sores?
What is primarily associated with the development of acne in individuals exposed to certain occupational environments?
What is primarily associated with the development of acne in individuals exposed to certain occupational environments?
What can result from the inflammation of deep lesions in acne?
What can result from the inflammation of deep lesions in acne?
What type of lesion is characterized by the presence of a plug of keratin that is initially white?
What type of lesion is characterized by the presence of a plug of keratin that is initially white?
Which bacterium is primarily associated with the inflammatory reactions in acne?
Which bacterium is primarily associated with the inflammatory reactions in acne?
In which stage does moderate acne consist of a combination of non-inflammatory and inflammatory lesions?
In which stage does moderate acne consist of a combination of non-inflammatory and inflammatory lesions?
What leads to the blockage of follicles and formation of microcomedones in acne?
What leads to the blockage of follicles and formation of microcomedones in acne?
What is the primary factor thought to contribute to the overgrowth of bacteria and subsequent inflammatory lesions in acne?
What is the primary factor thought to contribute to the overgrowth of bacteria and subsequent inflammatory lesions in acne?
Which type of acne lesion may develop from a microcomedone?
Which type of acne lesion may develop from a microcomedone?
What is the primary use of hydrocolloid in wound care?
What is the primary use of hydrocolloid in wound care?
What is recommended to minimize the risk of transmitting a cold sore?
What is recommended to minimize the risk of transmitting a cold sore?
Which of the following best describes scabies?
Which of the following best describes scabies?
Who is most commonly affected by eczema herpeticum?
Who is most commonly affected by eczema herpeticum?
At what age range is scabies infestation most common?
At what age range is scabies infestation most common?
What effect does scratching due to itching have on the skin?
What effect does scratching due to itching have on the skin?
What is a common characteristic of scabies-related itching?
What is a common characteristic of scabies-related itching?
Which statement is incorrect regarding scabies infestation?
Which statement is incorrect regarding scabies infestation?
What symptoms indicate the need for referral in the treatment of scabies?
What symptoms indicate the need for referral in the treatment of scabies?
What is the primary ingredient in first-line treatment for scabies?
What is the primary ingredient in first-line treatment for scabies?
How long should permethrin cream be left on the body according to treatment guidelines?
How long should permethrin cream be left on the body according to treatment guidelines?
In which scenario is malathion recommended as an alternative treatment?
In which scenario is malathion recommended as an alternative treatment?
What is a common misconception regarding treatment failure in scabies?
What is a common misconception regarding treatment failure in scabies?
What should be done if the hands are washed after applying permethrin cream?
What should be done if the hands are washed after applying permethrin cream?
What demographic is specifically mentioned as needing careful management for scabies?
What demographic is specifically mentioned as needing careful management for scabies?
Which statement about treatment options for scabies is accurate?
Which statement about treatment options for scabies is accurate?
What is the primary action of topical nicotinamide gel?
What is the primary action of topical nicotinamide gel?
What is a key characteristic of scabies that differentiates it from other skin conditions?
What is a key characteristic of scabies that differentiates it from other skin conditions?
What should be avoided to prevent side effects from benzoyl peroxide?
What should be avoided to prevent side effects from benzoyl peroxide?
Which body sites are commonly affected by scabies infestations?
Which body sites are commonly affected by scabies infestations?
What percentage of people are likely to have athlete’s foot at any one time?
What percentage of people are likely to have athlete’s foot at any one time?
What is a common symptom of athlete’s foot?
What is a common symptom of athlete’s foot?
How long can it take for symptoms of scabies to develop after initial exposure?
How long can it take for symptoms of scabies to develop after initial exposure?
What is a potential side effect of using topical nicotinamide gel?
What is a potential side effect of using topical nicotinamide gel?
What can happen as a result of scratching due to the itch of scabies?
What can happen as a result of scratching due to the itch of scabies?
Which statement regarding athlete’s foot is correct?
Which statement regarding athlete’s foot is correct?
What factors influence the prevalence of scabies in the population?
What factors influence the prevalence of scabies in the population?
What is generally recommended if scabies is suspected in infants and young children?
What is generally recommended if scabies is suspected in infants and young children?
What can potentially indicate the need for referral in long-standing conditions?
What can potentially indicate the need for referral in long-standing conditions?
What type of discharge is indicative of a potential secondary infection in scabies?
What type of discharge is indicative of a potential secondary infection in scabies?
What can help minimize damage to clothes when treating acne with certain topical medications?
What can help minimize damage to clothes when treating acne with certain topical medications?
How often does the prevalence of scabies peak?
How often does the prevalence of scabies peak?
Flashcards
Cold Sore Location
Cold Sore Location
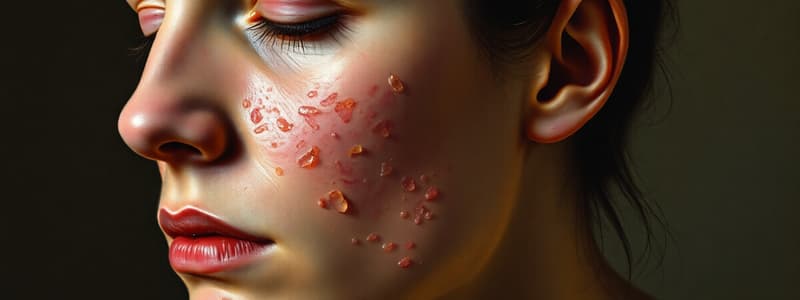
Cold sores typically appear on the lips or face. However, lesions inside the mouth, close to or affecting the eye require medical attention.
Cold Sore Triggers
Cold Sore Triggers
Cold sores can be triggered by various factors such as sunlight, wind, fever, menstruation, rundown state, local trauma, and emotional stress.
Cold Sore Appearance
Cold Sore Appearance
Cold sores usually start as a small, red, itchy bump that develops into a blister. The blister then forms a yellow-colored crust.
Cold Sore Spread
Cold Sore Spread
Signup and view all the flashcards
Recurring Cold Sores
Recurring Cold Sores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Athlete's foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete's foot (Tinea Pedis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrocolloid for Wounds
Hydrocolloid for Wounds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sharing Items with Cold Sores
Sharing Items with Cold Sores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topical Nicotinamide Gel
Topical Nicotinamide Gel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl Peroxide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cold Sore Treatment
Cold Sore Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eczema Herpeticum
Eczema Herpeticum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ceramides and Retinols
Ceramides and Retinols
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of Athlete's Foot Symptoms
Significance of Athlete's Foot Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies
Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Sheets and Pillowcases
White Sheets and Pillowcases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Itch
Scabies Itch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Age and Prevalence
Scabies Age and Prevalence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Old Clothes for Acne Treatments
Old Clothes for Acne Treatments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne Treatment Effectiveness
Acne Treatment Effectiveness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Transmission
Scabies Transmission
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a microcomedone?
What is a microcomedone?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a comedone?
What is a comedone?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes acne?
What causes acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are inflammatory lesions in acne?
What are inflammatory lesions in acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What bacteria is involved in acne?
What bacteria is involved in acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does sebum contribute to acne?
How does sebum contribute to acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between a blackhead and a whitehead?
What is the difference between a blackhead and a whitehead?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of androgen hormones in acne?
What is the role of androgen hormones in acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is scabies?
What is scabies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the symptoms of scabies?
What are the symptoms of scabies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is scabies spread?
How is scabies spread?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the treatment for scabies?
What is the treatment for scabies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How long does it take for scabies symptoms to appear?
How long does it take for scabies symptoms to appear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is itching worse at night?
Why is itching worse at night?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What can happen if scabies isn't treated?
What can happen if scabies isn't treated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When should I see a doctor about scabies?
When should I see a doctor about scabies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Treatment Failure
Scabies Treatment Failure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Symptoms
Scabies Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies: When to Refer?
Scabies: When to Refer?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permethrin for Scabies
Permethrin for Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Malathion for Scabies
Malathion for Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Treatment Duration
Scabies Treatment Duration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Itch After Treatment
Scabies Itch After Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Treatment Assessment
Scabies Treatment Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Skin Condition Problems
- Acne (acne vulgaris) is a condition involving blockage or inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous glands.
- 95% of adolescents experience acne.
- Mild to moderate acne typically responds to over-the-counter treatments.
- Acne often develops during puberty due to increased androgen production.
- Keratin and sebum production also contribute to acne formation.
- Excessive sebum may lead to an overgrowth of bacteria (Cutibacterium acnes), causing inflammation.
- Acne can be non-inflammatory (comedones) or inflammatory (papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts).
- Acne severity ranges from mild (mostly non-inflammatory comedones) to moderate (mixture of non-inflammatory comedones and inflammatory papules/pustules) to severe (widespread nodules and cysts).
- Acne predominantly affects the face, upper back/shoulders, and chest (these areas have many sebaceous glands).
- Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition sometimes mistaken for acne; it only affects the face.
Different Types of Acne
- Comedones:
- Open comedones (blackheads): A plug of keratin at the follicle entrance.
- Closed comedones (whiteheads): Similar to blackheads, but they appear white.
- Papules: Small red bumps.
- Pustules: Bumps with a white/yellow head (pus).
- Nodules: Large, inflamed bumps that feel firm.
- Cysts: Large, pus-filled bumps, softer than nodules.
Significance of Questions and Answers (Acne)
- Acne typically begins during puberty and can last until the late teens or early 20s.
- Acne is rare in young children/babies; if present, it may indicate a hormonal tumor.
- In patients who develop acne after their teenage years, other factors (e.g., hyperandrogenism in women, drug therapy, or occupational factors like oily substances) should be considered.
When to Refer (Acne)
- Severe acne.
- Acne that doesn't respond to treatment after 8 weeks.
- Possible drug-induced acne.
- Patient experiences significant distress.
Treatment Timescale (Acne)
- Patients with mild-to-moderate acne that doesn't improve within 8 weeks should be referred to a doctor/physician.
Different Types of Fungal Infections
- Athlete's foot (tinea pedis): A common fungal infection affecting feet and toes. Characterized by itchy, flaky skin, often between toes, and may spread to the sole or sides of the feet.
- Ringworm (Tinea): A fungal infection that causes circular lesions, typically spreading from a small red papule. This includes Tinea corporis (body), Tinea cruris (groin), and Tinea capitis (scalp).
- Fungal nail infection (onychomycosis): A common fungal infection affecting the toenails or fingernails. Manifests as deformed nails.
When to Refer (Fungal Infections)
- Severe infections that spread beyond the initial location.
- Signs of bacterial infection (e.g., weeping, pus, yellow crusts).
- Failure to respond to treatment within the expected timescale.
- Patients with known conditions (e.g., diabetes) or discomfort/distress.
- Involvement of toenails.
Management (Fungal Infections)
- Most cases are effectively managed with over-the-counter (OTC) products.
- Advice on reducing transmission risk (e.g., good foot hygiene, keeping feet dry).
- Topical preparations (e.g., allylamines, imidazoles, undecenoic acid, tolnaftate) are more effective than placebo.
Cold Sores
- Cold sores (herpes labialis) are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), usually HSV type 1.
- Cold sores occur most commonly on the lips or face, but lesions in the mouth or near the eye warrant medical referral.
When to refer (cold sores)
- Babies and young children.
- Cold sores that fail to resolve.
- Severe or worsening cold sores.
- Frequent recurring cold sores.
- Painless cold sores.
- Cold sores lasting longer than 2 weeks
- Cold sores affecting the eye.
- Uncertain diagnosis
- Immunocompromised patient
- Pregnancy
Management (cold sores)
- Antiviral creams that reduce healing time and discomfort (e.g., acyclovir, penciclovir) are often recommended. Treatment should begin at the early stage of the infection (prodromal phase).
- Analgesics (e.g., paracetamol, ibuprofen) to manage pain.
- Moisturizers (e.g., lip balm) to prevent dryness and cracking.
Scabies
- Scabies is an intensely itchy skin infestation caused by the human parasite Sarcoptes scabiei.
- Itching is typically worse at night, and scratching can lead to secondary infections (e.g., impetigo).
- Areas commonly infested include fingers, toes, wrists, armpits, nipples, buttocks, and genital area.
When to refer (scabies)
- Babies and young children.
- Crusted scabies.
- Scabies outbreaks in institutions.
- Scabies that isn’t resolving.
Management (scabies)
- Permethrin cream is a first-line treatment for scabies.
- Malathion lotion is another treatment option, used in specialized cases (elderly or young children).
- Treatment should be applied to the entire body, and the affected areas/body should be monitored for signs of negative reactions to the treatment.
- Itchiness after treatment can last for several weeks following treatment and may require secondary treatments (e.g. crotamiton).
- Family members/household members require treatment simultaneously, regardless of showing symptoms, as it can develop unknowingly.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.