Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of breathing in relation to ATP?
What is the primary purpose of breathing in relation to ATP?
- To eliminate toxins from the body
- To provide oxygen needed for ATP synthesis (correct)
- To maintain blood pressure levels
- To cool the body during metabolic processes
Which function is NOT performed by the respiratory system?
Which function is NOT performed by the respiratory system?
- Olfaction
- Blood pressure regulation
- Nutrient absorption (correct)
- Gas exchange
Where does gas exchange primarily occur in the lungs?
Where does gas exchange primarily occur in the lungs?
- Bronchioles
- Nasal cavity
- Trachea
- Alveoli (correct)
What separates the right and left halves of the nasal cavity?
What separates the right and left halves of the nasal cavity?
What characterizes the conducting division of the respiratory system?
What characterizes the conducting division of the respiratory system?
What structures are considered part of the upper respiratory tract?
What structures are considered part of the upper respiratory tract?
Which part of the nose is supported by nasal bones?
Which part of the nose is supported by nasal bones?
What is the primary role of the nose in the respiratory system?
What is the primary role of the nose in the respiratory system?
During inspiration, where does the air flow stop for gas exchange?
During inspiration, where does the air flow stop for gas exchange?
What happens during expiration?
What happens during expiration?
What is the primary function of the larynx?
What is the primary function of the larynx?
Which structure is found during swallowing to close the airway?
Which structure is found during swallowing to close the airway?
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
Which part of the respiratory system is known for having three regions?
Which part of the respiratory system is known for having three regions?
What does the term 'glottis' refer to?
What does the term 'glottis' refer to?
What anatomical feature separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung?
What anatomical feature separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung?
What structure comprises the root of the lung?
What structure comprises the root of the lung?
What is the primary function of the trachea?
What is the primary function of the trachea?
Which type of pleura directly adheres to the lung tissue?
Which type of pleura directly adheres to the lung tissue?
In which part of the respiratory system does phonation occur?
In which part of the respiratory system does phonation occur?
Flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
The process of taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, essential for cellular energy production, it is also involved in various bodily functions like communication, smell, and blood regulation.
Conducting Division
Conducting Division
The air passages that transport air from the nose to the lungs. This includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
Respiratory Division
Respiratory Division
The tiny air sacs within the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
Inspiration (Inhaling)
Inspiration (Inhaling)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expiration (Exhaling)
Expiration (Exhaling)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of the Nose
Function of the Nose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal Fossae
Nasal Fossae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibule
Vestibule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal Septum
Nasal Septum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Nasal Apertures (Choanae)
Posterior Nasal Apertures (Choanae)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal Conchae (Turbinates)
Nasal Conchae (Turbinates)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meatus
Meatus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharynx (Throat)
Pharynx (Throat)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Larynx (Voice Box)
Larynx (Voice Box)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis
Epiglottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glottis
Glottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea (Windpipe)
Trachea (Windpipe)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchi
Bronchi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lungs
Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleura
Pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Respiratory System
- Breath represents life, the first and last breaths are dramatic moments
- Breathing is essential for metabolism because most metabolic processes require ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
- ATP production requires oxygen and generates carbon dioxide. The respiratory system delivers oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
- The respiratory system is primarily composed of tubes that deliver air to the lungs for gas exchange.
Main Function
- The respiratory system provides oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide.
- It has diverse functions like gas exchange, communication, olfaction (smelling), sound production, blood pressure regulation, and expulsion of abdominal contents.
Respiratory Tract
- Divided into upper (nose to larynx) and lower (trachea to lungs) respiratory tracts
- Upper respiratory tract (nose, pharynx, larynx): Air filtration, warming , and humidification
- Lower respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, lungs): Air transport and gas exchange
Nose (Nasus)
- Warms, cleanses, and humidifies inhaled air
- Detects odors
- Resonating chamber amplifying voice
- Extends from nostrils (nares) to posterior nasal apertures (choanae)
Pharynx (Throat)
- Muscular funnel, about 13 cm long
- Common passageway for air, food, and liquid.
- Divided into three parts: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx
Larynx (Voice Box)
- Cartilaginous chamber, about 4 cm long
- Protects airway during swallowing
- Essential for sound production (phonation)
- Contains epiglottis (flap-like tissue) which closes during swallowing, preventing food/drinks from entering the airway
Trachea (Windpipe)
- Tube about 12 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter
- Supported by 16–20 C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
- Lies anterior to esophagus
- Divides into right and left primary bronchi
Bronchi
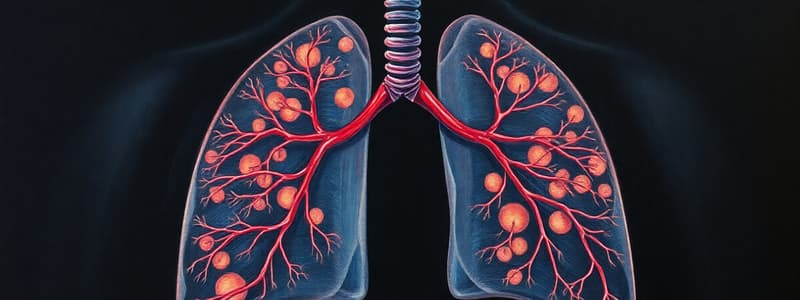
- Branching of bronchi: primary, secondary, tertiary, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli
- Bronchi carry air to the lungs for gas exchange within the alveoli
Lungs
- Located in the thoracic cavity, covered by pleura
- Three faces (diaphragmatic, costal, mediastinal)
- The radix (root) pulmonis is where vessels, nerves, enter and exit the lung
- Right lung: three lobes (superior, middle, inferior)
- Left lung: two lobes (superior, inferior)
- Divided by fissures
Pleura
- Two-layered serous membrane surrounding lungs
- Visceral pleura: on the surface of the lung
- Parietal pleura: lines the thoracic cavity
- Pleural cavity: space between the membranes containing fluid to reduce friction during breathing
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.