Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the larynx?
What is the primary function of the larynx?
- To move the rib cage during breathing
- To separate the chest from the abdomen
- To produce sound for speech (correct)
- To filter and warm air before it enters the lungs
What is the primary function of the nasal cavity?
What is the primary function of the nasal cavity?
- To move the rib cage during breathing
- To trap dust and particles using hairs and mucus
- To carry air to and from the lungs
- To act as a resonating chamber for speech sounds (correct)
What is the function of the epiglottis?
What is the function of the epiglottis?
- To produce sound for speech
- To filter, warm and moisten air before it enters the lungs
- To move the rib cage during breathing
- To close off the trachea during swallowing (correct)
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the primary function of the intercostal muscles?
What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
What is the primary function of the bronchioles?
What is the primary function of the bronchioles?
What is the primary function of the pleural membrane?
What is the primary function of the pleural membrane?
What is the primary function of the bronchi?
What is the primary function of the bronchi?
What is the primary function of the trachea/windpipe?
What is the primary function of the trachea/windpipe?
What are bronchioles and what do they do?
What are bronchioles and what do they do?
What are alveoli + its functions
What are alveoli + its functions
Which one of the following has walls once cell in thickness and is well supplied with blood?
Which one of the following has walls once cell in thickness and is well supplied with blood?
the main function of the nasal cavity is to
the main function of the nasal cavity is to
which of the following allows the lungs to move freely and with reduced friction
which of the following allows the lungs to move freely and with reduced friction
air enters the lungs during inspiration because
air enters the lungs during inspiration because
during expiration, the
during expiration, the
which of the following is true of gaseous exchange through the wall of the alveolus
which of the following is true of gaseous exchange through the wall of the alveolus
oxygen passes from the alveoli to the blood supply in capillaries by
oxygen passes from the alveoli to the blood supply in capillaries by
the substance to which oxygen becomes chemically bonded within the RBC is
the substance to which oxygen becomes chemically bonded within the RBC is
the trachea is prevented from collapsing by rings of ___
the trachea is prevented from collapsing by rings of ___
the dome shaped muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity
the dome shaped muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity
the muscles between ribs which assist in inhalation and exhalation
the muscles between ribs which assist in inhalation and exhalation
carbon dioxide attaches to this compound which is found in the RBC (term) which when binded is then called (term)
carbon dioxide attaches to this compound which is found in the RBC (term) which when binded is then called (term)
most of the carbon dioxide which travels in the blood plasma does so in the form of
most of the carbon dioxide which travels in the blood plasma does so in the form of
the cells which line the trachea and bronchi are ciliated, explain why this lining is necessary
the cells which line the trachea and bronchi are ciliated, explain why this lining is necessary
list the organs and tissues through which oxygen travels from its entry to the body at the nose until it moves into the blood plasma in the capillaries of the lungs
list the organs and tissues through which oxygen travels from its entry to the body at the nose until it moves into the blood plasma in the capillaries of the lungs
what are the three functions of the nasal cavity?
what are the three functions of the nasal cavity?
describe how air is drawn into the lungs during inhalation
describe how air is drawn into the lungs during inhalation
describe how air is forced out of the lungs during exhalation
describe how air is forced out of the lungs during exhalation
at rest a person breathes between 16 and 18 times per minute using only the diaphragm. which muscles increase the volume of each breath when exercising
at rest a person breathes between 16 and 18 times per minute using only the diaphragm. which muscles increase the volume of each breath when exercising
what percentage of inhaled air is oxygen and carbon dioxide respectively
what percentage of inhaled air is oxygen and carbon dioxide respectively
what percentage is exhaled air made of oxygen and carbon dioxide respectively?
what percentage is exhaled air made of oxygen and carbon dioxide respectively?
how is concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide maintained?
how is concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide maintained?
what percentage of carbon dioxide is transported by dissolving in plasma, as carbaminohaemoglobin and as bicarbonate ions in the plasma?
what percentage of carbon dioxide is transported by dissolving in plasma, as carbaminohaemoglobin and as bicarbonate ions in the plasma?
what are the most important organic wastes transported in solution in the blood plasma?
what are the most important organic wastes transported in solution in the blood plasma?
discuss the advantages of erythrocytes lacking a nucleus
discuss the advantages of erythrocytes lacking a nucleus
discuss disadvantages of erythrocytes lacking nucleus
discuss disadvantages of erythrocytes lacking nucleus
How is carbon dioxide diffused out of the alveolus starting as bicarbonate ions in plasma
How is carbon dioxide diffused out of the alveolus starting as bicarbonate ions in plasma
how does breathing affect the level of water vapour in plasma?
how does breathing affect the level of water vapour in plasma?
Emphysema is a disease which affects the alveoli and may be caused by long-term exposure to tobacco smoke. the lung tissue loses its elasticity and many of the capillaries which service the alveoli are destroyed. How do you think these changes to the lungs would affect its efficiency and why?
Emphysema is a disease which affects the alveoli and may be caused by long-term exposure to tobacco smoke. the lung tissue loses its elasticity and many of the capillaries which service the alveoli are destroyed. How do you think these changes to the lungs would affect its efficiency and why?
what wld be symptoms of emphysema
what wld be symptoms of emphysema
how can emphysema be slowed
how can emphysema be slowed
why wld sm1 with asthma find breathing difficult
why wld sm1 with asthma find breathing difficult
What is the primary purpose of a control test in an experiment?
What is the primary purpose of a control test in an experiment?
What is the term for a variable that is intentionally changed by the scientist in an experiment?
What is the term for a variable that is intentionally changed by the scientist in an experiment?
Why is it important to keep all other variables constant in an experiment, except for the one being tested?
Why is it important to keep all other variables constant in an experiment, except for the one being tested?
What would be the result if a scientist were testing the hypothesis that bacteria are killed by household bleach, and the bacteria in the experimental cultures were dead, but the bacteria in the control cultures were also dead?
What would be the result if a scientist were testing the hypothesis that bacteria are killed by household bleach, and the bacteria in the experimental cultures were dead, but the bacteria in the control cultures were also dead?
What is the purpose of an experiment, according to the scientific method?
What is the purpose of an experiment, according to the scientific method?
Why is it important to design an experiment so that only one variable is changed at a time?
Why is it important to design an experiment so that only one variable is changed at a time?
What is the primary purpose of a control group in a scientific experiment?
What is the primary purpose of a control group in a scientific experiment?
What is the main advantage of using measurement in scientific experiments?
What is the main advantage of using measurement in scientific experiments?
What is the purpose of a line graph in scientific experiments?
What is the purpose of a line graph in scientific experiments?
What is the primary reason for repeating an experiment in science?
What is the primary reason for repeating an experiment in science?
What is the purpose of a hypothesis in a scientific experiment?
What is the purpose of a hypothesis in a scientific experiment?
What is the main advantage of using a fair test in a scientific experiment?
What is the main advantage of using a fair test in a scientific experiment?
What is the primary reason for identifying variables in an experiment?
What is the primary reason for identifying variables in an experiment?
What is the characteristic of a good hypothesis?
What is the characteristic of a good hypothesis?
What is the primary purpose of reviewing existing literature during scientific investigation?
What is the primary purpose of reviewing existing literature during scientific investigation?
What is the primary role of curiosity in scientific investigation?
What is the primary role of curiosity in scientific investigation?
What is the primary difference between an independent variable and a dependent variable?
What is the primary difference between an independent variable and a dependent variable?
What is the primary characteristic of a scientific investigation?
What is the primary characteristic of a scientific investigation?
What is the primary purpose of a histogram in data representation?
What is the primary purpose of a histogram in data representation?
What is the outcome of an experiment that supports a hypothesis?
What is the outcome of an experiment that supports a hypothesis?
Why is it important to evaluate the experiment and its method?
Why is it important to evaluate the experiment and its method?
What is the difference between a bar graph and a column graph?
What is the difference between a bar graph and a column graph?
What is the purpose of controlling variables in an experiment?
What is the purpose of controlling variables in an experiment?
What is the outcome of collecting enough evidence to support a hypothesis?
What is the outcome of collecting enough evidence to support a hypothesis?
What is the main difference between human error and random error in an experiment?
What is the main difference between human error and random error in an experiment?
What is the purpose of an ethics committee in a research institution?
What is the purpose of an ethics committee in a research institution?
What is the principle of voluntary participation in research involving human participants?
What is the principle of voluntary participation in research involving human participants?
What is the main difference between confidentiality and anonymity in research involving human participants?
What is the main difference between confidentiality and anonymity in research involving human participants?
Why might an ethics committee decide to abandon a trial and make the procedure available to the control group?
Why might an ethics committee decide to abandon a trial and make the procedure available to the control group?
What is the main purpose of informed consent in research involving human participants?
What is the main purpose of informed consent in research involving human participants?
Why is it essential to halt a trial early if the results are drastically in favor of one group?
Why is it essential to halt a trial early if the results are drastically in favor of one group?
What is the primary purpose of using a placebo in medical research?
What is the primary purpose of using a placebo in medical research?
What is the term for the phenomenon where patients show improvement in their condition despite receiving an inactive treatment?
What is the term for the phenomenon where patients show improvement in their condition despite receiving an inactive treatment?
What is the purpose of a double-blind experiment in medical research?
What is the purpose of a double-blind experiment in medical research?
When should a trial be abandoned, even if continued testing is desirable?
When should a trial be abandoned, even if continued testing is desirable?
What is the purpose of a control group in a medical research study?
What is the purpose of a control group in a medical research study?
What is the primary reason for using a placebo that looks exactly the same as the real medication?
What is the primary reason for using a placebo that looks exactly the same as the real medication?
What is the advantage of using a placebo in a blind experiment?
What is the advantage of using a placebo in a blind experiment?
What is the purpose of designing an investigation with the five principles in mind?
What is the purpose of designing an investigation with the five principles in mind?
What is the benefit of using a placebo in a medical research study?
What is the benefit of using a placebo in a medical research study?
Flashcards
Larynx function
Larynx function
The larynx produces sound by vibrating vocal cords.
Pharynx function
Pharynx function
The passageway for air from the nasal cavity.
Trachea function
Trachea function
Carries air to and from lungs; lined with mucus and cilia.
Cilia function
Cilia function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasal cavity function
Nasal cavity function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis function
Epiglottis function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ribs function
Ribs function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchi function
Bronchi function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercostal muscles
Intercostal muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchioles function
Bronchioles function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli function
Alveoli function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lungs function
Lungs function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural membrane
Pleural membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleural fluid
Pleural fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm function
Diaphragm function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bar graph
Bar graph
Signup and view all the flashcards
Histogram
Histogram
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scientific method
Scientific method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothesis
Hypothesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Experimental error
Experimental error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human error
Human error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Random error
Random error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systematic error
Systematic error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethical consideration
Ethical consideration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
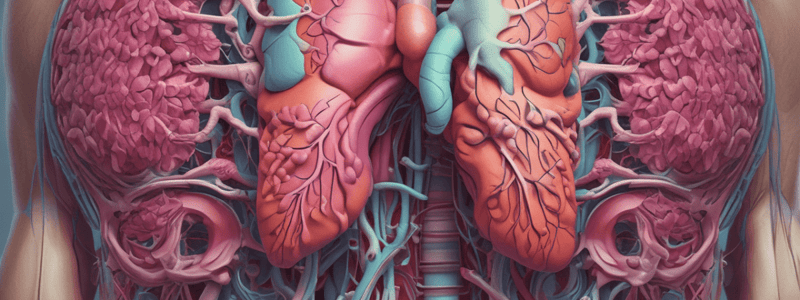
Respiratory System
- The larynx is the organ of voice, and it contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound.
- Air passes through the larynx, going to and from the lungs.
- The pharynx, or throat, is where air from the nasal cavity passes through.
- The trachea, or windpipe, carries air to and from the lungs and is lined with a mucous membrane and cells with cilia.
- The cilia beat to move mucus and trapped particles upwards.
Nasal Cavity and Epiglottis
- The nasal cavity contains projections that increase the internal surface area.
- It filters, warms, and moistens air before it enters the lungs.
- The nasal cavity contains smell receptors and acts as a resonating chamber for speech sounds.
- Hairs and mucus trap dust in the nasal cavity.
- The epiglottis is a flap of tissue that closes off the trachea during swallowing, preventing food and liquid from entering the lungs.
Ribs and Bronchi
- The ribs form the framework for the chest.
- Two primary bronchi branch from the trachea and divide into secondary and tertiary bronchi.
- The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs and move the rib cage upwards and outwards to increase the volume of the chest cavity and lungs when breathing in.
Bronchioles and Lungs
- Bronchioles are very fine tubes with walls of smooth muscle.
- The finest bronchioles end in groups of air sacs, called alveoli.
- The lungs occupy all the chest cavity, except for the space taken up by the heart.
- The lungs are covered by a pleural membrane that also lines the inside of the chest.
- Pleural fluid between the two layers holds the lungs against the inside of the chest.
Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen.
Graphs
- Bar or column graphs are used to display discrete data.
- The data is represented by rectangles of equal width, with spaces between them.
- The length of each rectangle indicates the quantity.
- Rectangles are drawn horizontally for a bar graph and vertically for a column graph.
- Histograms are used to show frequencies and have columns of equal width, but no spaces between them.
Scientific Method
- The scientific method involves identifying a problem, collecting information, identifying variables, developing a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and interpreting the results.
- A hypothesis is a definite statement that links the independent and dependent variables.
- A good hypothesis is short, has a single idea, and can be tested.
Experimental Error
- Experimental error is a limitation of the experiment itself.
- There are three types of error: human error, random error, and systematic error.
- Human error is a mistake, such as incorrectly reading the scale on an instrument.
- Random errors are unpredictable and occur because no measurement can be made with absolute precision.
- Systematic errors occur because of the way the experiment is designed or due to problems with equipment.
Ethics
-
Ethics are a set of moral principles or values.
-
Ethical behaviour is behaviour that conforms to those principles or values.
-
Ethical problems arise in scientific research, particularly research involving human participants.
-
Ethical considerations include voluntary participation, informed consent, risk of harm, confidentiality, and anonymity.
-
An ethical dilemma may arise when the effects of a trial on the experimental group are so advantageous that it seems unfair to withhold them from the control group.### Ethical Considerations in Research
-
The results of a trial may be so dramatic that it needs to be halted early to ensure the well-being of participants
-
Ethical problems arise when subjects are adversely affected by the research, and it is crucial to determine when to abandon the trial
Role of Placebos in Research
- Placebos are used to test the effectiveness of medical treatments, such as new medicinal drugs
- A placebo is an inactive substance that looks like the real medication, and is given to the control group in a trial
- The placebo should be indistinguishable from the real medication in terms of appearance and administration
- Subjects in the trial do not know whether they are receiving the real drug or the placebo
The Placebo Effect
- The placebo effect occurs when patients who receive a placebo show an improvement in their condition, despite the placebo being inactive
- The placebo effect is thought to be due to the patient's belief that the placebo is a real therapy that will bring about improvement
Reducing Bias in Experiments
- Blind experiments, where subjects do not know whether they are receiving the treatment or the placebo, reduce the risk of bias due to the placebo effect
- Double-blind experiments, where neither the researcher nor the subjects know who is receiving the treatment or the placebo, further reduce the risk of bias
- If the test group shows a better response than the control group despite the placebo effect, the therapy can be assumed to be effective
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.