Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the reproductive system?
What is the main function of the reproductive system?
- To provide energy for cellular functions
- To produce offspring (correct)
- To facilitate digestion
- To regulate hormone levels in the body
During meiosis, how many haploid cells are produced from one diploid cell?
During meiosis, how many haploid cells are produced from one diploid cell?
- Three haploid cells
- Eight haploid cells
- Two haploid cells
- Four haploid cells (correct)
What hormone is responsible for initiating sperm production?
What hormone is responsible for initiating sperm production?
- LH
- FSH (correct)
- Testosterone
- Estrogen
What is produced from each primary oocyte during oogenesis?
What is produced from each primary oocyte during oogenesis?
What is the function of the seminal vesicles?
What is the function of the seminal vesicles?
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
What is the longest portion of the male reproductive system?
What is the longest portion of the male reproductive system?
What role does the prostate gland play in the male reproductive system?
What role does the prostate gland play in the male reproductive system?
What triggers the release of the egg during ovulation?
What triggers the release of the egg during ovulation?
Which structure is responsible for secreting mucus for lubrication in females?
Which structure is responsible for secreting mucus for lubrication in females?
What happens if a fertilized egg does not implant in the uterus?
What happens if a fertilized egg does not implant in the uterus?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the corpus luteum secrete progesterone?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the corpus luteum secrete progesterone?
What is the average volume of semen produced?
What is the average volume of semen produced?
What is the role of prolactin in the context of breastfeeding?
What is the role of prolactin in the context of breastfeeding?
What is benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)?
What is benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)?
What is the function of the fimbriae in the female reproductive system?
What is the function of the fimbriae in the female reproductive system?
Which layer of the uterus is shed during menstruation?
Which layer of the uterus is shed during menstruation?
What characterizes amenorrhea?
What characterizes amenorrhea?
What is the main energy source for sperm provided by the seminal vesicles?
What is the main energy source for sperm provided by the seminal vesicles?
What is the temperature maintained by the scrotum for optimal sperm production?
What is the temperature maintained by the scrotum for optimal sperm production?
What hormone is produced by the follicle cells that matures the egg during oogenesis?
What hormone is produced by the follicle cells that matures the egg during oogenesis?
Which structure is responsible for storing and maturing sperm after spermatogenesis?
Which structure is responsible for storing and maturing sperm after spermatogenesis?
How many functional sperm cells are produced from each primary spermatocyte?
How many functional sperm cells are produced from each primary spermatocyte?
At what stage of life does oogenesis begin in females?
At what stage of life does oogenesis begin in females?
What component does the bulbourethral glands contribute to the male reproductive system?
What component does the bulbourethral glands contribute to the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What structure in the female reproductive system catches the released egg and transports it through the fallopian tube?
What structure in the female reproductive system catches the released egg and transports it through the fallopian tube?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the uterine lining during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the uterine lining during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
What is the main role of the endometrium in the female reproductive system?
What is the main role of the endometrium in the female reproductive system?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does a sharp increase in luteinizing hormone (LH) occur?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does a sharp increase in luteinizing hormone (LH) occur?
What condition describes the implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterus?
What condition describes the implantation of a fertilized egg outside the uterus?
What is the primary function of Bartholin's glands in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary function of Bartholin's glands in the female reproductive system?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for contractions during labor?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for contractions during labor?
What substance is primarily responsible for milk ejection during breastfeeding?
What substance is primarily responsible for milk ejection during breastfeeding?
What characterizes benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)?
What characterizes benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)?
What is a common effect of low progesterone levels on the menstrual cycle?
What is a common effect of low progesterone levels on the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary purpose of the scrotum in male reproductive anatomy?
What is the primary purpose of the scrotum in male reproductive anatomy?
During oogenesis, what is the outcome of the division of primary oocytes?
During oogenesis, what is the outcome of the division of primary oocytes?
Which gland contributes alkaline fluid to the urethra to neutralize acidity prior to ejaculation?
Which gland contributes alkaline fluid to the urethra to neutralize acidity prior to ejaculation?
What are the main components of semen?
What are the main components of semen?
What starts the process of spermatogenesis?
What starts the process of spermatogenesis?
What is the significance of testosterone in male reproductive health?
What is the significance of testosterone in male reproductive health?
What is the common pH level of semen?
What is the common pH level of semen?
What occurs in the epididymis?
What occurs in the epididymis?
Which reproductive structure is responsible for the expulsion of semen?
Which reproductive structure is responsible for the expulsion of semen?
At what stage does oogenesis cease in females?
At what stage does oogenesis cease in females?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of the corpus luteum after ovulation?
Which of the following correctly describes the role of the corpus luteum after ovulation?
What is the primary function of the myometrium during labor?
What is the primary function of the myometrium during labor?
Which feature distinguishes the basilar layer of the endometrium?
Which feature distinguishes the basilar layer of the endometrium?
Which hormone's rise during the follicular phase stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles?
Which hormone's rise during the follicular phase stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles?
What condition results from the implantation of a fertilized egg outside of the uterus?
What condition results from the implantation of a fertilized egg outside of the uterus?
What is the average length of the menstrual cycle?
What is the average length of the menstrual cycle?
Which structure is responsible for secreting mucus to aid in lubrication during sexual arousal?
Which structure is responsible for secreting mucus to aid in lubrication during sexual arousal?
What happens to the levels of progesterone and LH if the egg is not fertilized?
What happens to the levels of progesterone and LH if the egg is not fertilized?
Which term describes the thin membrane partially covering the vaginal opening?
Which term describes the thin membrane partially covering the vaginal opening?
What is the effect of low body fat on menstruation?
What is the effect of low body fat on menstruation?
Flashcards
Reproductive System Function
Reproductive System Function
To produce offspring through the creation and union of gametes (sperm and egg) forming a zygote.
Meiosis
Meiosis
A type of cell division that produces gametes (sperm and egg), reducing the chromosome number from diploid (46) to haploid (23) in four resulting cells.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm cell production in the testes.
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes Function
Testes Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen Composition
Semen Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovary Function
Ovary Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis Function
Epididymis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female Reproductive Structures
Female Reproductive Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstruation
Menstruation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Hypertrophy
Prostate Hypertrophy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia(BPH)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia(BPH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicular Phase
Follicular Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Luteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Meiosis?
What is Meiosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of Testosterone in Spermatogenesis?
What is the function of Testosterone in Spermatogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Oogenesis?
What is Oogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of FSH in Oogenesis?
What is the role of FSH in Oogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the Scrotum?
What is the function of the Scrotum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Epididymis?
What is the Epididymis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Semen?
What is Semen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the Prostate Gland?
What is the function of the Prostate Gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tubes
Fallopian Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus
Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix
Cervix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium
Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes menstruation?
What causes menstruation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the corpus luteum?
What is the corpus luteum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tube Function
Fallopian Tube Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus Function
Uterus Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix Function
Cervix Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the reproductive system?
What is the function of the reproductive system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does sperm production occur?
Where does sperm production occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of testosterone in sperm production?
What is the role of testosterone in sperm production?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) work in oogenesis?
How does FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) work in oogenesis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the scrotum's role?
What is the scrotum's role?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the epididymis?
What is the function of the epididymis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the urethra?
What is the function of the urethra?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Reproductive System Functions
- The main function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring.
- Reproductive systems produce gametes (sperm and eggs) and facilitate their union to create a zygote.
Meiosis
- Meiosis produces gametes.
- A diploid cell divides twice, resulting in four haploid cells.
- Diploid cells have 46 chromosomes, while haploid cells have 23 chromosomes.
Spermatogenesis
- Occurs in the testes within seminiferous tubules.
- Spermatogonia are sperm-generating cells.
- FSH initiates sperm production.
- Testosterone, stimulated by LH, promotes maturation and is crucial for forming sperm cells.
- For each primary spermatocyte, four functional sperm cells are produced.
- Production begins at puberty and continues throughout life, decreasing with age.
Oogenesis
- Occurs in the ovaries.
- Regulated by hormones.
- FSH initiates growth of ovarian follicles containing eggs.
- Follicle cells secrete estrogen, maturing the egg.
- For each primary oocyte, only one functional egg is produced, with the remaining cells being polar bodies.
- A mature ovarian follicle contains a secondary oocyte, which can be fertilized.
- Production begins at puberty and ends at menopause.
- A mature ovum (egg) is produced every 28 days.
Male Reproductive Structures
- Testes: Located in the scrotum, which maintains a temperature of 96 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Scrotum: Sac of skin that regulates temperature for sperm production.
- Seminiferous tubules: Located within the testes, produce sperm during spermatogenesis.
- Epididymis: 20-foot-long tube on the posterior of each testes, where sperm complete maturation and flagella activation.
- Ductus deferens (vas deferens): Extends from the epididymis through the inguinal canal to join the ejaculatory duct.
- Seminal vesicles: Posterior to the bladder, secrete fructose (energy for sperm) and an alkaline fluid for motility.
- Prostate gland: Below the bladder, secretes an alkaline fluid to enhance sperm motility and contributes to semen expulsion.
- Bulbourethral glands (Cowper's glands): Below the prostate, contribute alkaline fluid to the urethra to neutralize acidity prior to ejaculation.
- Urethra: The final duct for semen travel, longest portion is within the penis.
- Penis: External genital organ composed of erectile tissue that fills with blood during sexual stimulation, leading to erection.
Semen
- Consists of sperm and fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands.
- pH: 7.4
- Average volume: 2-4 milliliters.
- Contains about 100 million sperm per milliliter.
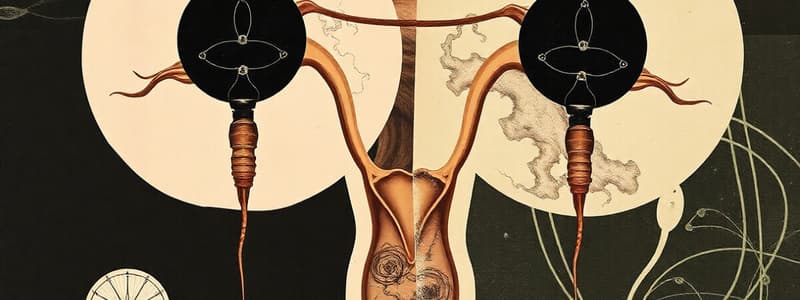
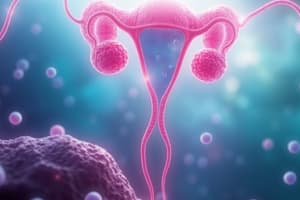
Female Reproductive Structures
- Ovaries: Paired organs about 1.5 inches long, held in place by the broad ligament.
- Follicles: Contain oocytes (potential eggs).
- Ovulation: Release of the egg from the ovary, stimulated by LH, the egg travels through the fallopian tube.
- Fallopian tubes: Four-inch-long tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus.
- Fimbriae: Finger-like projections at the ends of the fallopian tubes that catch the released egg and pull it into the tube.
- Uterus: Three-inch-long organ located superior to the urinary bladder and between the ovaries.
- Cervix: Lower portion of the uterus, opening into the vagina.
- Myometrium: Muscle layer of the uterus, responsible for contractions during labor and delivery.
- Endometrium: Inner lining of the uterus consisting of the basilar layer (permanent) and the functional layer (regenerates and is shed during menstruation).
- Vagina: Four-inch-long canal extending from the cervix to the vaginal orifice.
- Hymen: Thin membrane partially covering the vaginal opening.
- Vulva: External genitalia of females, including the clitoris, urethral opening, vaginal opening, Mons pubis, labia majora, and labia minora.
- Bartholin's glands: Located in the floor of the vestibule, secrete mucus for lubrication.
- Mammary glands: Produce milk for breastfeeding, located within breast tissue.
Additional Notes
- Ectopic pregnancy: Implantation of a fertilized egg outside of the uterus, commonly in the fallopian tube.
- Menstruation: Shedding of the functional layer of the endometrium if fertilization does not occur.
- Hernias: Occur when organs protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, particularly in the inguinal canal.
- Circumcision: Surgical removal of the foreskin.
- Sexual stimulation: Activates the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to erectile tissue in the penis filling with blood and causing an erection.
Pregnancy
- The areola, the darkened area around the nipple, becomes more prominent during pregnancy
- Estrogen and progesterone prepare the glands for milk production
- Sore breasts during early pregnancy are due to milk production preparation
- Prolactin is responsible for milk production after pregnancy
- Oxytocin is responsible for the release of milk from the breast in response to breastfeeding
Menstrual Cycle
- The first phase of the menstrual cycle is the menstrual phase
- Menstruation (menses) lasts 2-8 days with an average of 3-6 days
- Menstruation occurs when the functional layer of the uterus is shed due to a lack of pregnancy
- During menstruation, FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) rises, stimulating the growth of ovarian follicles
- The follicular phase follows the menstrual phase
- FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and the secretion of estrogen
- LH (luteinizing hormone) begins to rise slowly
- Estrogen prepares the uterus for pregnancy by increasing blood flow
- The follicular phase ends with ovulation, marked by a sharp increase in LH
- Ovulation is the rupture of a mature ovarian follicle, releasing an egg
- The luteal phase follows ovulation
- The ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone and estrogen
- Progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy by further increasing blood flow and storing nutrients like glycogen
- As progesterone increases, LH decreases
- If the egg is not fertilized, progesterone levels decrease
- Without progesterone, the uterine lining is shed, resulting in menstruation
- The cycle repeats
Menstrual Cycle Summary
- The cycle is approximately 28 days long
- Amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstruation
- Amenorrhea can occur due to low body fat, delayed puberty, or other medical conditions
Prostate Conditions
- Prostatic hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of the prostate
- Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate
- BPH is common in men over 60
- An enlarged prostate can press on the urethra, making urination difficult and causing urinary retention
- Treatment for BPH may involve surgical removal of the prostate, which can affect ejaculation
- Newer procedures are available to help preserve function following prostate removal
- Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men, typically affecting those over 50
- Prostate cancer treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and other options
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.