Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which lobe of the brain is primarily responsible for voluntary movements?
Which lobe of the brain is primarily responsible for voluntary movements?
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Frontal lobe (correct)
What is the function of the cerebellum in the brain?
What is the function of the cerebellum in the brain?
- Controlling balance and movement (correct)
- Facilitating analytical thought
- Processing sensory data
- Regulating survival functions
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle?
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle?
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamus
- Hippocampus
- Pineal gland (correct)
What connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain?
What connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain?
Which hemisphere of the brain is typically associated with verbal and analytical tasks?
Which hemisphere of the brain is typically associated with verbal and analytical tasks?
What is the main role of the thalamus in the brain?
What is the main role of the thalamus in the brain?
Which structure is primarily involved in the formation of new memories?
Which structure is primarily involved in the formation of new memories?
The primary function of the amygdala is to manage what type of responses?
The primary function of the amygdala is to manage what type of responses?
What is required for a study to be generalisable?
What is required for a study to be generalisable?
Which type of sampling involves selecting a small group that accurately represents a larger population?
Which type of sampling involves selecting a small group that accurately represents a larger population?
What defines extraneous variables in an experiment?
What defines extraneous variables in an experiment?
What is a key characteristic of probability sampling methods?
What is a key characteristic of probability sampling methods?
Which of the following statements about participant variables is true?
Which of the following statements about participant variables is true?
What is the purpose of psychological tests in research?
What is the purpose of psychological tests in research?
Which method involves a structured face-to-face conversation to gather information?
Which method involves a structured face-to-face conversation to gather information?
What is meant by categorical variables in psychological research?
What is meant by categorical variables in psychological research?
What role does a theory play in psychological research?
What role does a theory play in psychological research?
Which of the following is an example of physiological recording?
Which of the following is an example of physiological recording?
What symptom may indicate damage to the occipital lobe?
What symptom may indicate damage to the occipital lobe?
What is the primary goal of standardized procedures in psychological research?
What is the primary goal of standardized procedures in psychological research?
Which factor is most likely to affect the likelihood of remembering dreams?
Which factor is most likely to affect the likelihood of remembering dreams?
What is the purpose of examining archival records in psychological research?
What is the purpose of examining archival records in psychological research?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of continuous variables?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of continuous variables?
During REM sleep, which of the following occurs?
During REM sleep, which of the following occurs?
What is a common characteristic of NREM dreams?
What is a common characteristic of NREM dreams?
What defines a research method in the context of scientific study?
What defines a research method in the context of scientific study?
In the context of dreams, what role does cultural background play?
In the context of dreams, what role does cultural background play?
What does reliability in research refer to?
What does reliability in research refer to?
What typical cycle characterizes the transition between REM and NREM sleep?
What typical cycle characterizes the transition between REM and NREM sleep?
Which of the following best describes a hypothesis in scientific research?
Which of the following best describes a hypothesis in scientific research?
What distinguishes low dream recallers from high dream recallers?
What distinguishes low dream recallers from high dream recallers?
Study Notes
Biological Bases of Behaviour
- The cerebral cortex consists of four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal, each with distinct functions.
- The primary motor cortex, located in the frontal lobe, controls voluntary movements and correlates nerve density with motor control over body areas.
- Symptoms from brain-damaged patients provide insights into affected brain areas.
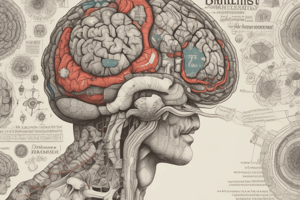
- Key brain components include:
- Cerebrum: Most visible part responsible for higher functions.
- Cerebral cortex: Outer layer for conscious thought.
- Corpus callosum: Connects left and right hemispheres.
- Cerebellum: Coordinates balance and movement.
- Brain stem: Regulates vital functions (heartbeat, breathing).
- Thalamus: Routes sensory information to cortex.
- Hypothalamus: Regulates temperature, appetite, thirst.
- Pineal gland: Controls sleep-wake cycles via melatonin.
- Hippocampus: Involved in memory formation and navigation.
- Amygdala: Processes emotions such as fear and anger.
- The left hemisphere is linked to verbal and analytical tasks; the right hemisphere is connected to creativity, artistic abilities, and emotional recognition.
- Brain damage symptoms can indicate specific area impairment (e.g., loss of sight = occipital lobe damage).
Sleep
- Average individuals dream five times a night but often forget 95% of dreams.
- Dream recall varies; low dream recallers wake slower and exhibit more electrical shifts upon waking.
- Dreams occur throughout the night, predominantly in REM (90% of dreaming).
- Sleep cycles alternate between REM and NREM every 90 minutes, with increased REM duration as the night progresses.
- REM sleep features high brain activity, fluctuating heart rates, relaxed muscles, and vivid dreams, often more memorable.
- NREM sleep has regular brainwaves and less intense, brief dreams resembling waking thoughts, with increased likelihood in anxious individuals.
- Dream content is influenced by cultural background and recent experiences.
Research Methods of Psychology
- Scientific methods involve systematic observations, experiments, and analyses to study phenomena.
- Research methods aim to obtain accurate and reliable data.
- The scientific method encompasses structured research planning, conducting, and reporting.
- Hypotheses serve as testable predictions regarding variable relationships.
- Various data collection methods include:
- Direct Observation: Monitoring participant behavior with tools like stopwatches.
- Surveys: Distributing written questionnaires to gauge attitudes and behaviors.
- Interviews: Conducting face-to-face discussions for deeper insights.
- Psychological Tests: Administering standardized assessments, like IQ tests.
- Physiological Recordings: Using instruments to measure biological responses.
- Examination of Archival Records: Analyzing pre-existing data from institutions.
- Psychological research follows theories that inform hypotheses about variable relationships.
- Variables can be continuous (measure of degrees) or categorical (distinct categories).
- Standardized procedures ensure consistency for participants.
- Validity in studies must cover internal (design) and external (real-world applicability) aspects.
Key Research Concepts
- Independent variables are manipulated to observe effects on dependent variables.
- Extraneous variables may interfere with results and must be controlled.
- Participant variables relate to individual traits that may bias findings.
- Sampling methods include:
- Probability Sampling: Uses random selection, enhancing representativeness.
- Non-Probability Sampling: Includes convenience and purposive sampling, often less generalized.
- Sampling errors occur when smaller groups fail to represent the broader population accurately.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the biological bases of behavior with a focus on the brain's lobes and their functions, as well as sleep and relevant case studies. Students will also review research methods in psychology. Prepare to test your knowledge on these fundamental concepts.